This document discusses several topics related to social and personality development in adolescence including identity formation, self-concept, relationships with peers and family, sexuality, dating, and risk-taking behaviors. Key aspects addressed are Erikson's psychosocial stages of identity vs role confusion, influences on self-esteem, types of peer groups, causes of juvenile delinquency, trends in adolescent sexual behavior, factors affecting teen pregnancy rates, and sexual orientation identity development.



![Erikson
Identity formation: Crisis or change?
Identity vs role (identity) confusion
Psychological difficulties in search for identity =
“the adolescent identity crisis” [Next]
Westernized teens seek:
•Individualism
•Independence
•Autonomy
12-4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lifespan-chapter-10online-stud-1208138646011075-9/85/Lifespan-Chapter-10-Online-Stud-4-320.jpg)





![Cliques and Crowds
Stereotypes ?
Cliques > [text] ~2 to 12 people;
frequent interaction; usu same sex
• Crowds > larger groups share some
characteristics; less personal; based
on reputation.
• Strong expectations that people in a
particular crowd behave in specific
ways. (A self-fulfilling prophecy?)
• Less impt by end of adolescence
12-11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lifespan-chapter-10online-stud-1208138646011075-9/85/Lifespan-Chapter-10-Online-Stud-11-320.jpg)







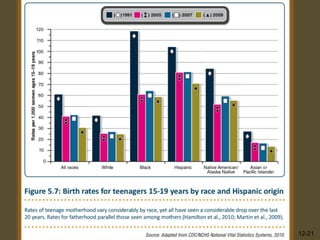
![Teen Pregnancy
• Teen pregnancy rate is declining
across all ethnic groups in U.S.
[next].
• Still higher in U.S. than in other
industrialized countries.
• Teenage mothers do not fare well:
– Poor health
• Increased neurological problems,
childhood illness; low birth wt.
– Poor school performance
– Cycle of poverty
12-20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lifespan-chapter-10online-stud-1208138646011075-9/85/Lifespan-Chapter-10-Online-Stud-20-320.jpg)