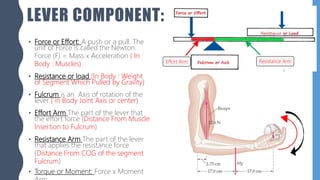
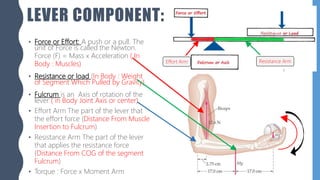
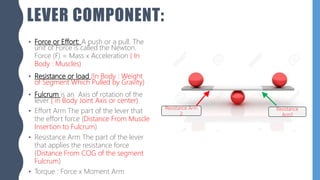
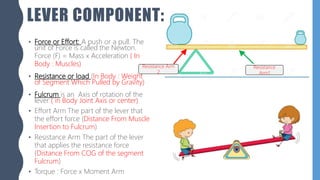
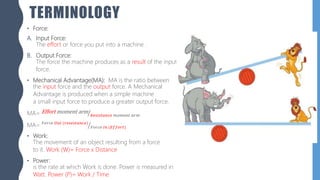
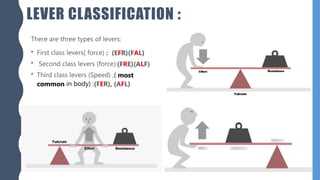
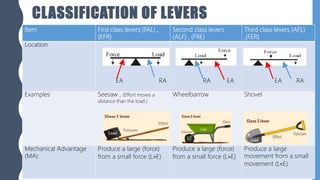
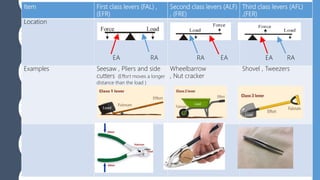
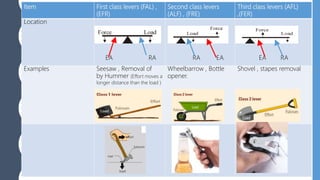
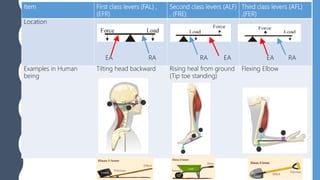
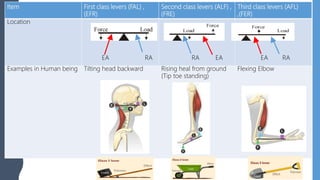
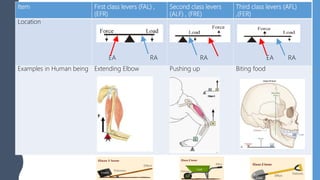
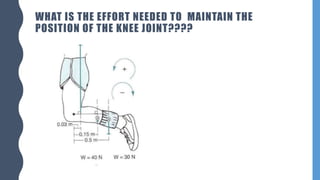
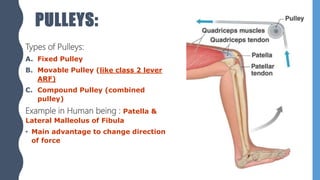
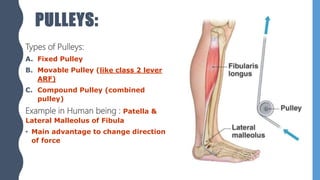
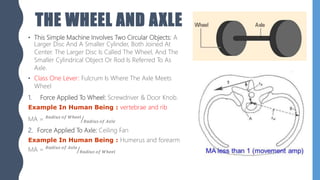
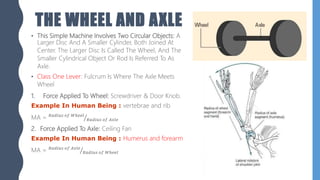
The document discusses different types of simple machines, including levers, pulleys, and the wheel and axle. It defines machines as devices that make work easier. There are two types of simple machines: force magnifiers and movement magnifiers. Levers are described as rigid objects that rotate around a fulcrum. There are three classes of levers based on the relative positions of the effort force, load, and fulcrum. Pulleys and the wheel and axle are also described as simple machines. Examples of these machines and their applications in the human body are provided.