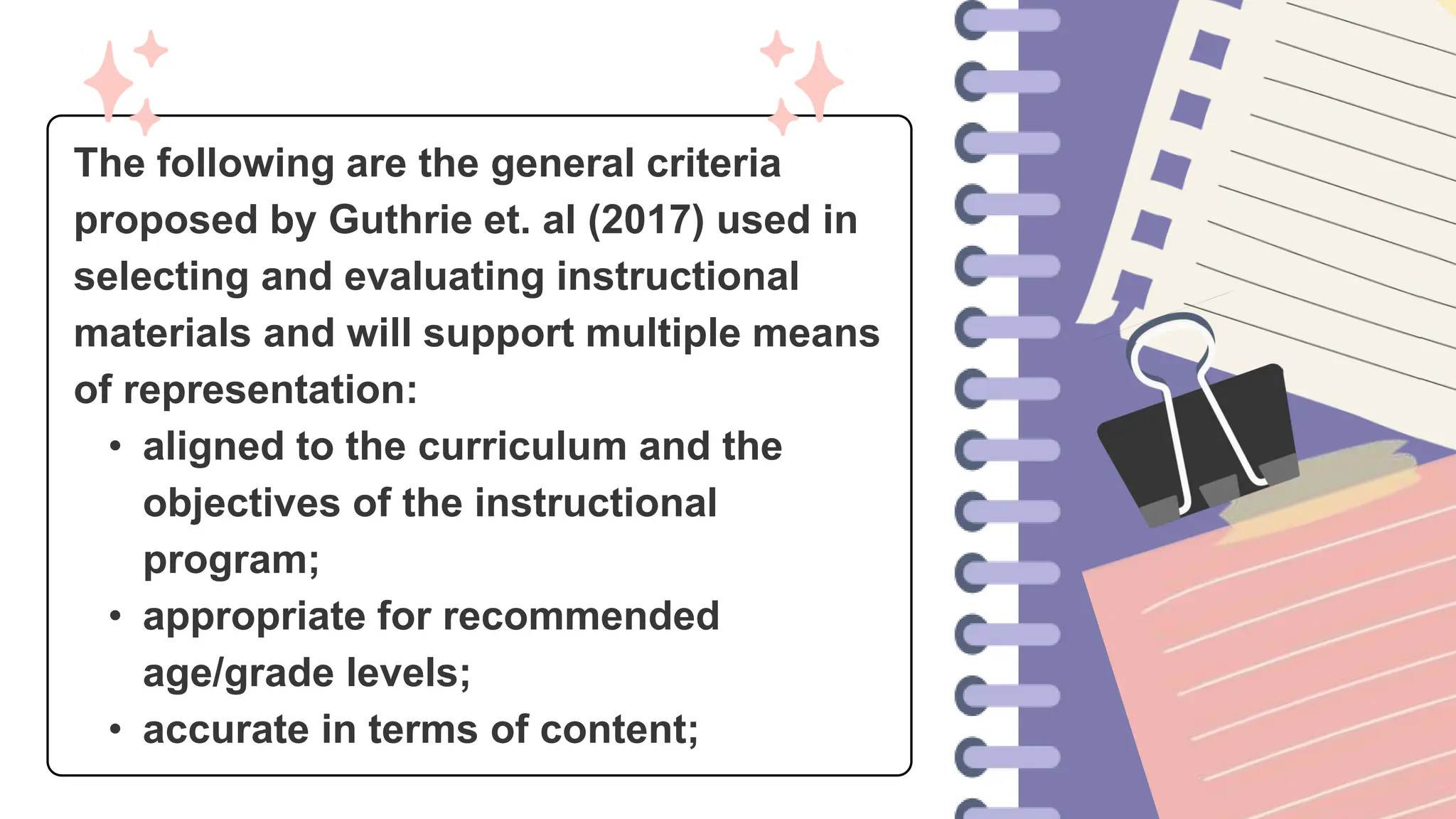
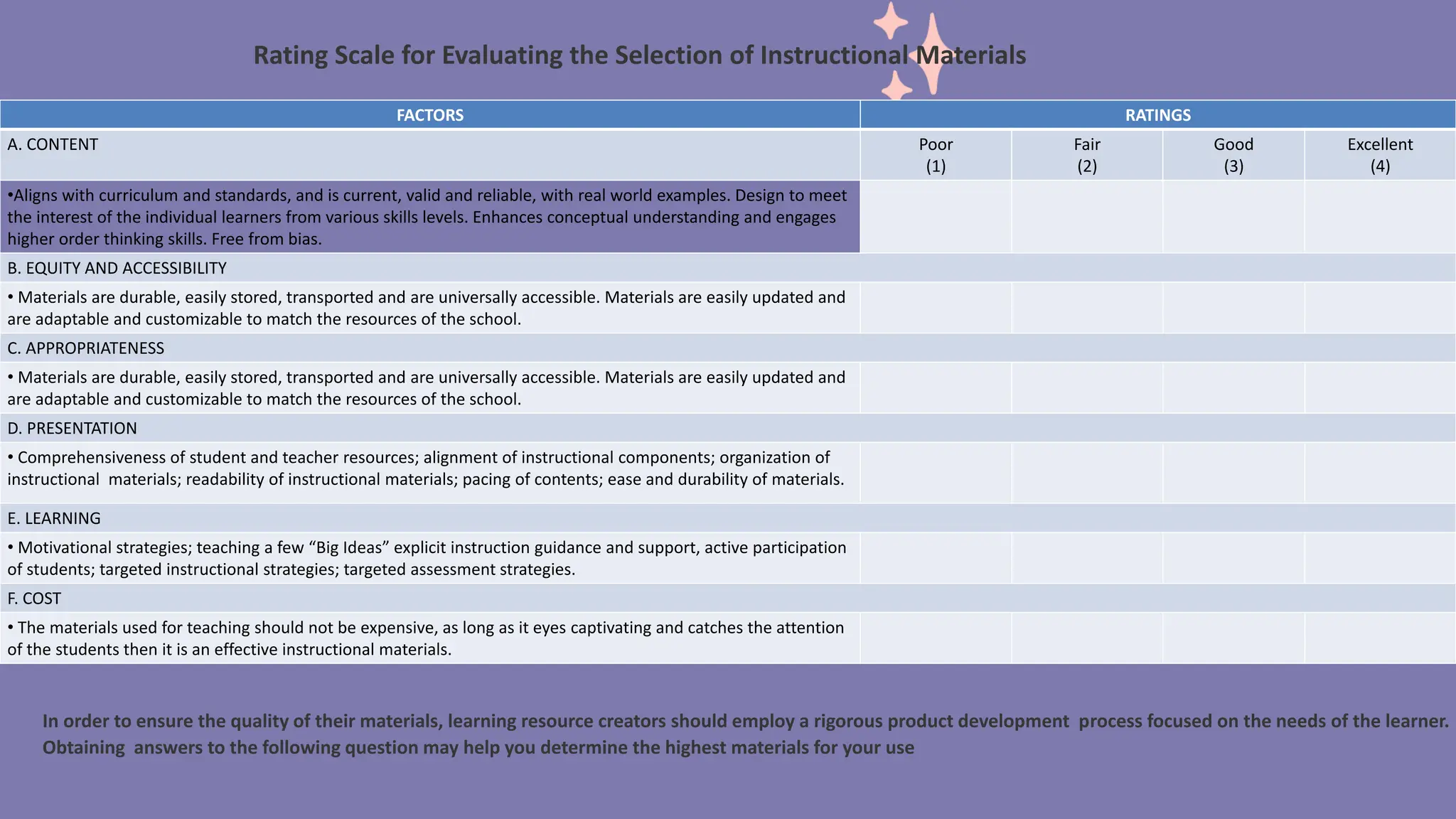
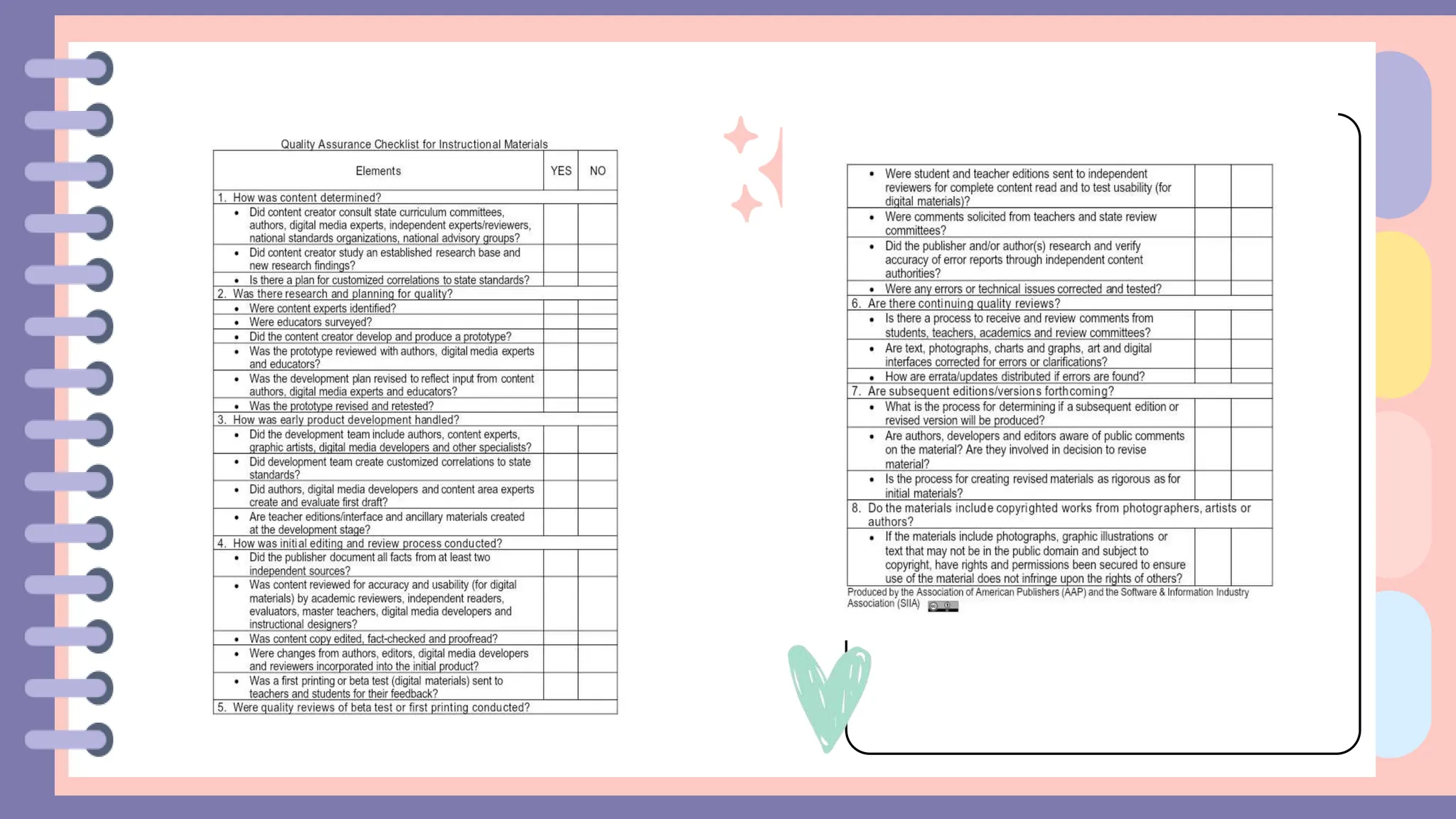
The document discusses the importance of evaluation in teaching and learning resources to assess their effectiveness in meeting educational goals and objectives. It outlines criteria for selecting and evaluating instructional materials, including alignment with curriculum, accuracy, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for a rigorous development process to ensure high-quality resources that engage diverse learners.