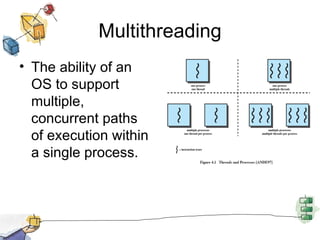
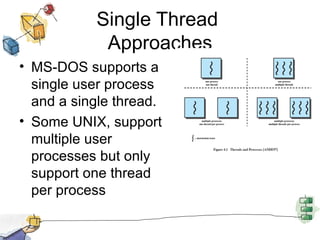
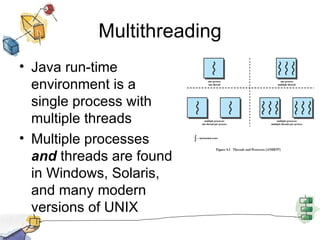
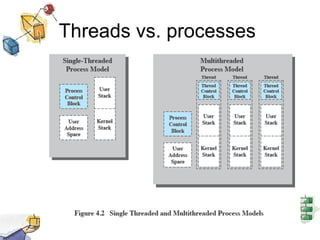
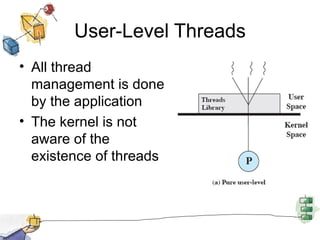
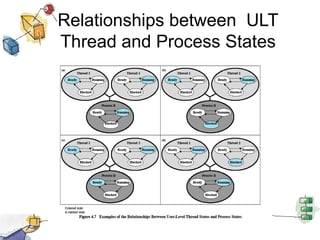
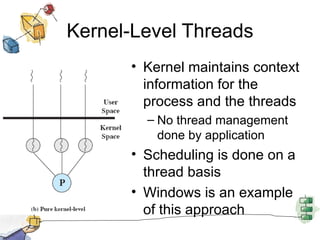
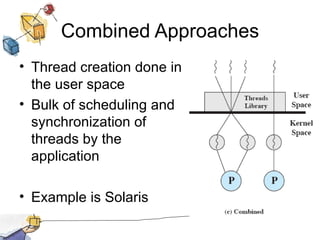
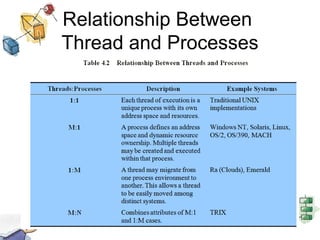
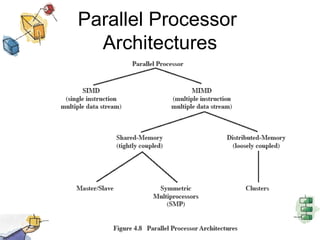
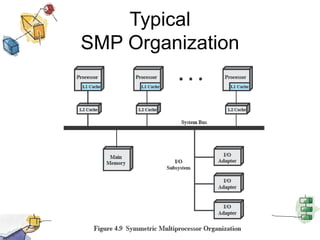
The document discusses processes, threads, and multithreading in operating systems. It defines processes as having virtual address spaces and execution paths, while threads are the unit of dispatching. Multithreading allows multiple concurrent execution paths within a single process. Early systems only supported single threading, while modern systems support multiple processes and threads. Threads share resources within a process and have execution states. User-level threads are managed by applications while kernel-level threads are scheduled by the kernel. Symmetric multiprocessing allows threads to execute in parallel on multiple processors.