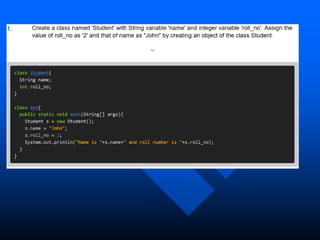
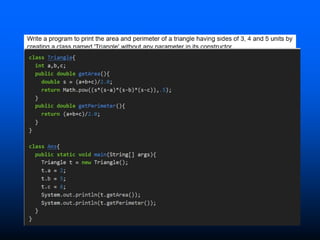
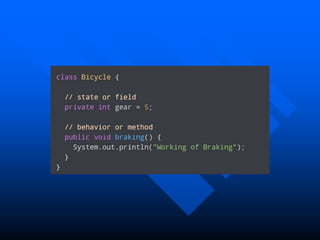
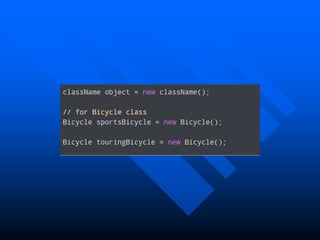
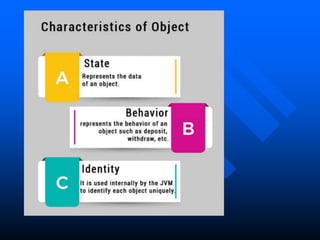
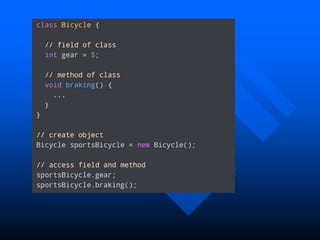
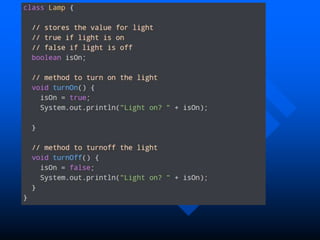
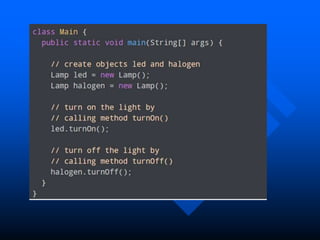
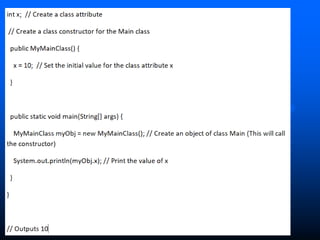
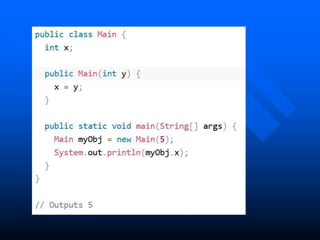
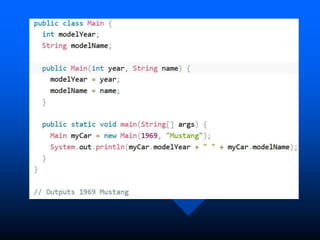
The lecture introduces object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts, particularly focusing on access control modifiers such as private, package, protected, and public. It explains the relationship between classes and objects, including how objects are instances of classes and can access class members. Additionally, it covers the purpose of constructors in Java for initializing objects and demonstrates how constructors can take parameters.


![public class Pencil {
public String color = “red”;
public int length;
public float diameter;
private float price;
public static long nextID = 0;
public void setPrice (float newPrice) {
price = newPrice;
}
}
public class CreatePencil {
public static void main (String args[]){
Pencil p1 = new Pencil();
p1.price = 0.5f;
}
}
Pencil.java
CreatePencil.java
%> javac Pencil.java
%> javac CreatePencil.java
CreatePencil.java:4: price has private
access in Pencil](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecturejavacontinued-220221185918/85/Lecture-java-continued-3-320.jpg)