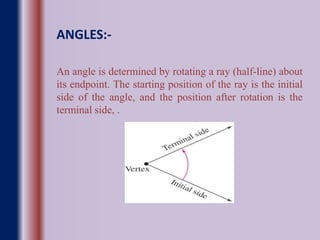
This document provides an overview of trigonometry including:
- Definitions of measuring angles in radians and degrees, and conversions between the two units.
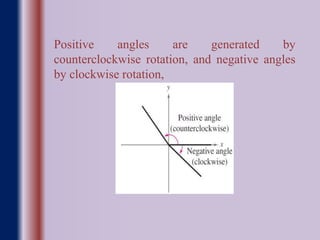
- Definitions of the six circular functions (sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, cotangent) and how they relate to positions on a unit circle.
- Examples of deriving the values of the six circular functions for a given angle.
- Important trigonometric identities like the Pythagorean identity of sine and cosine.
- A table of the values of the six trigonometric functions for common angles from 0 to 90 degrees.










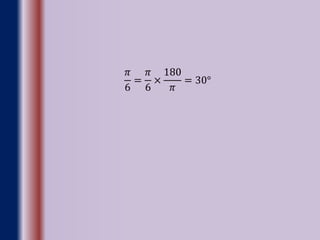





![Pythagorean Identities
When the Pythagoras theorem is expressed in the form of trigonometry
functions, it is said to be Pythagorean identity. There are majorly three
identities:
•sin2 x + cos2 x = 1 [Very Important]
•1+tan2 x = sec2 x
•cosec2 x = 1 + cot2 x
Trigonometric
Ratios/
angle= θ in
degrees
0 ° 30 ° 45 ° 60 ° 90 °
Sin θ 0 1/2 1/√2 √3/2 1
Cos θ 1 √3/2 1/√2 1/2 0
Tan θ 0 1/√3 1 √3 ∞
Cosec θ ∞ 2 √2 2/√3 1
Sec θ 1 2/√3 √2 2 ∞
Cot θ ∞ √3 1 1/√3 0
Table
The trigonometric ratio table for six functions like Sin, Cos, Tan, Cosec,
Sec, Cot, are:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7trignometry-220725151747-d9288523/85/Lecture-7-Trignometry-pptx-20-320.jpg)

