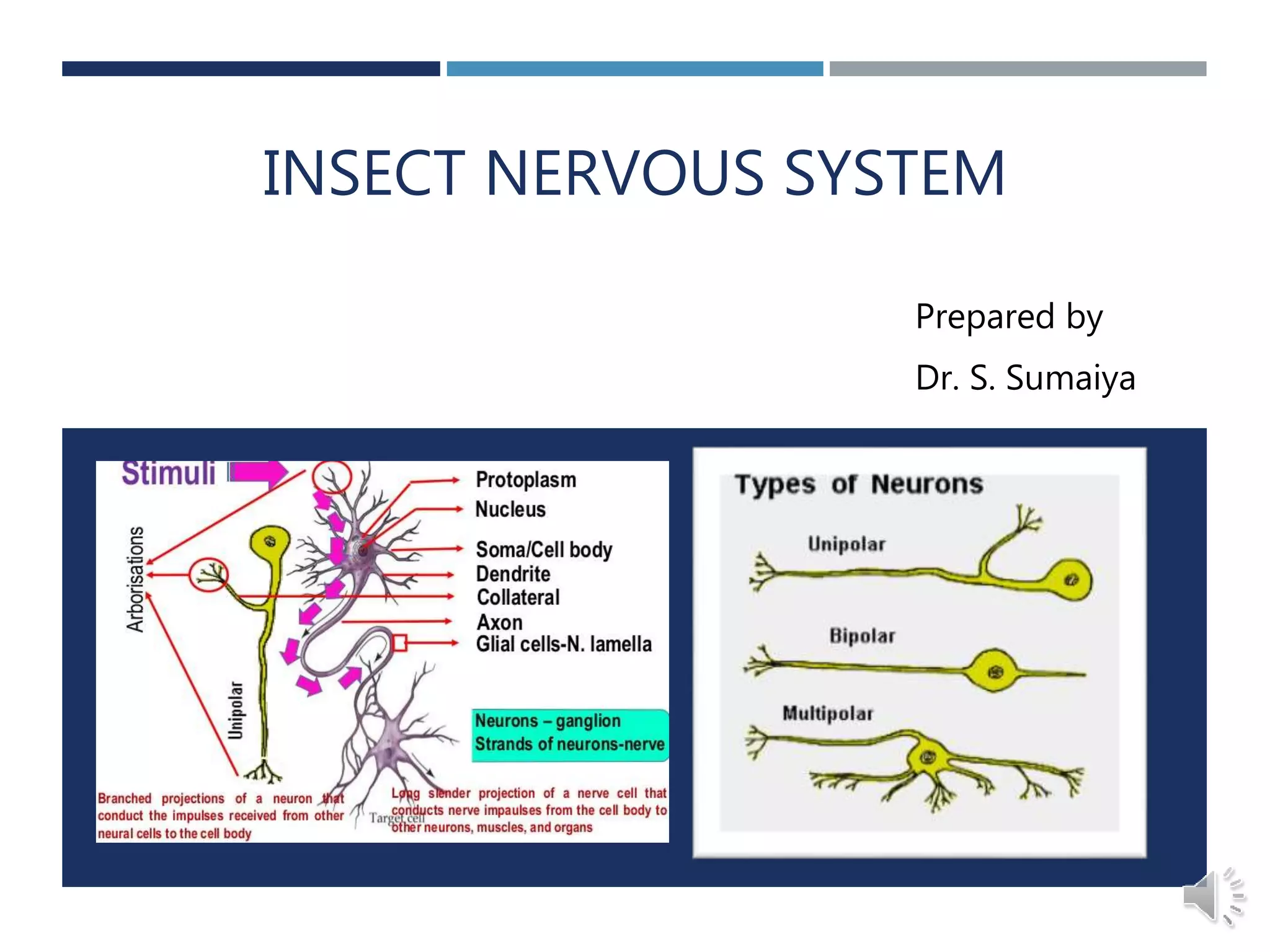
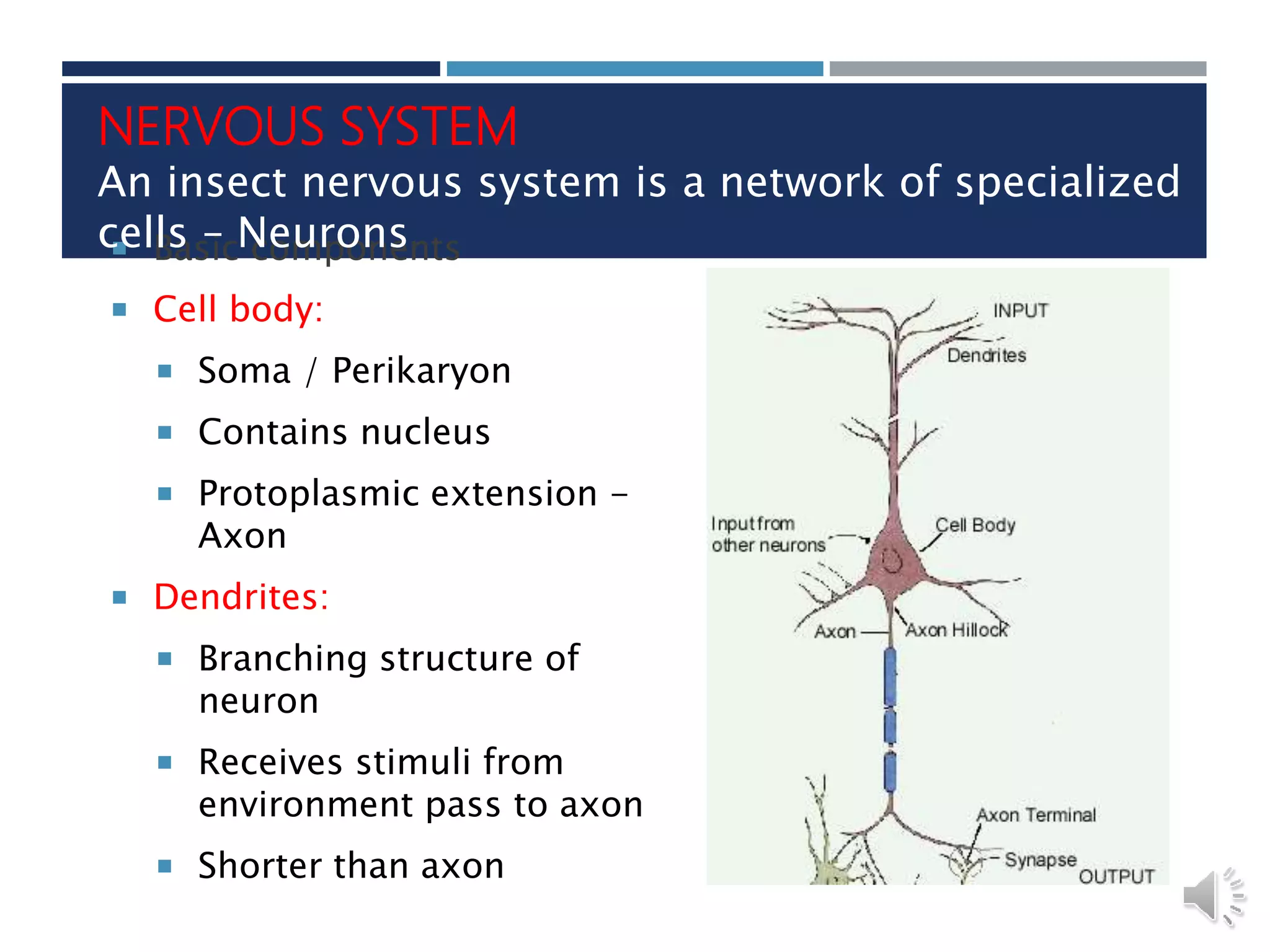
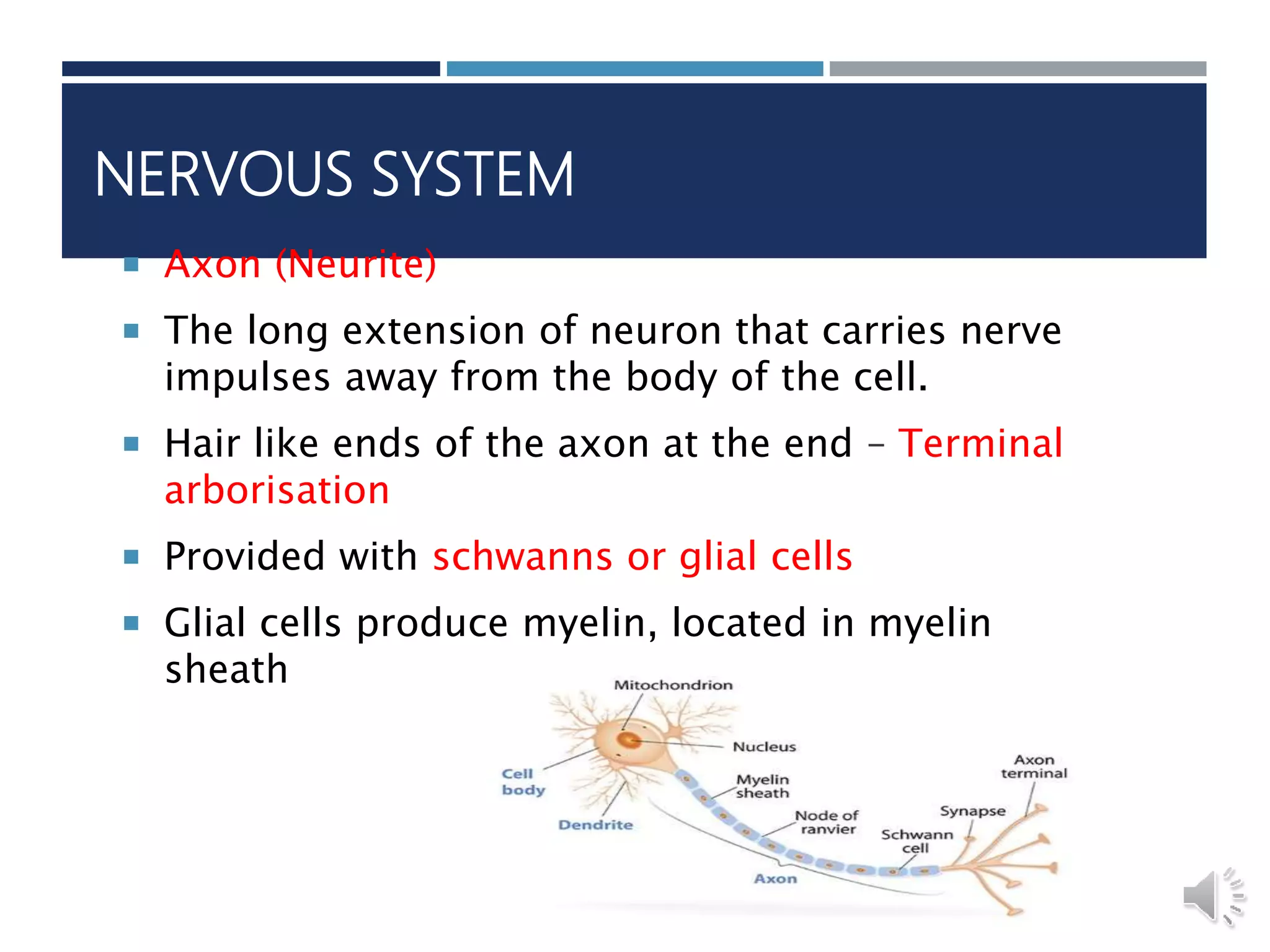
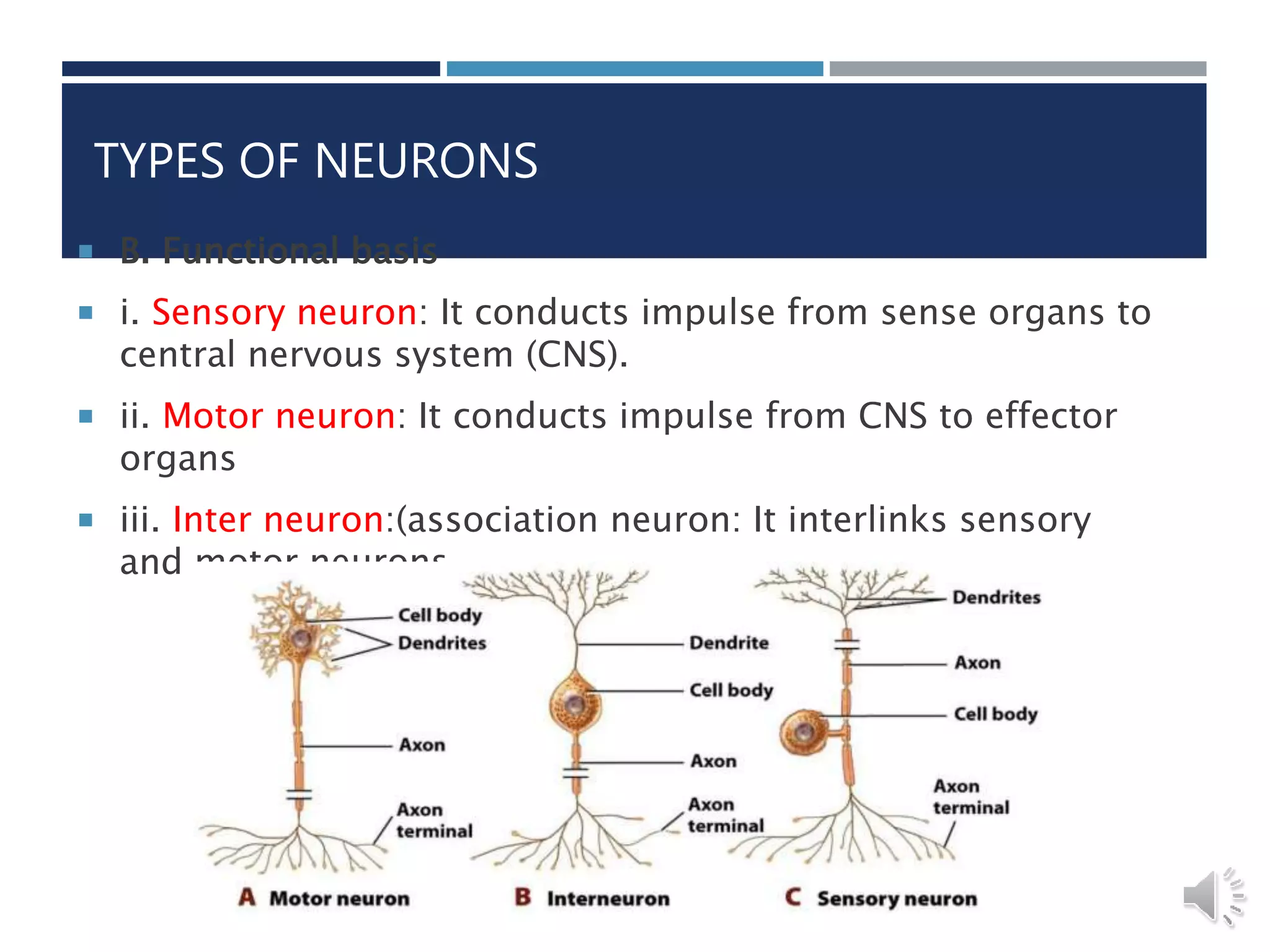
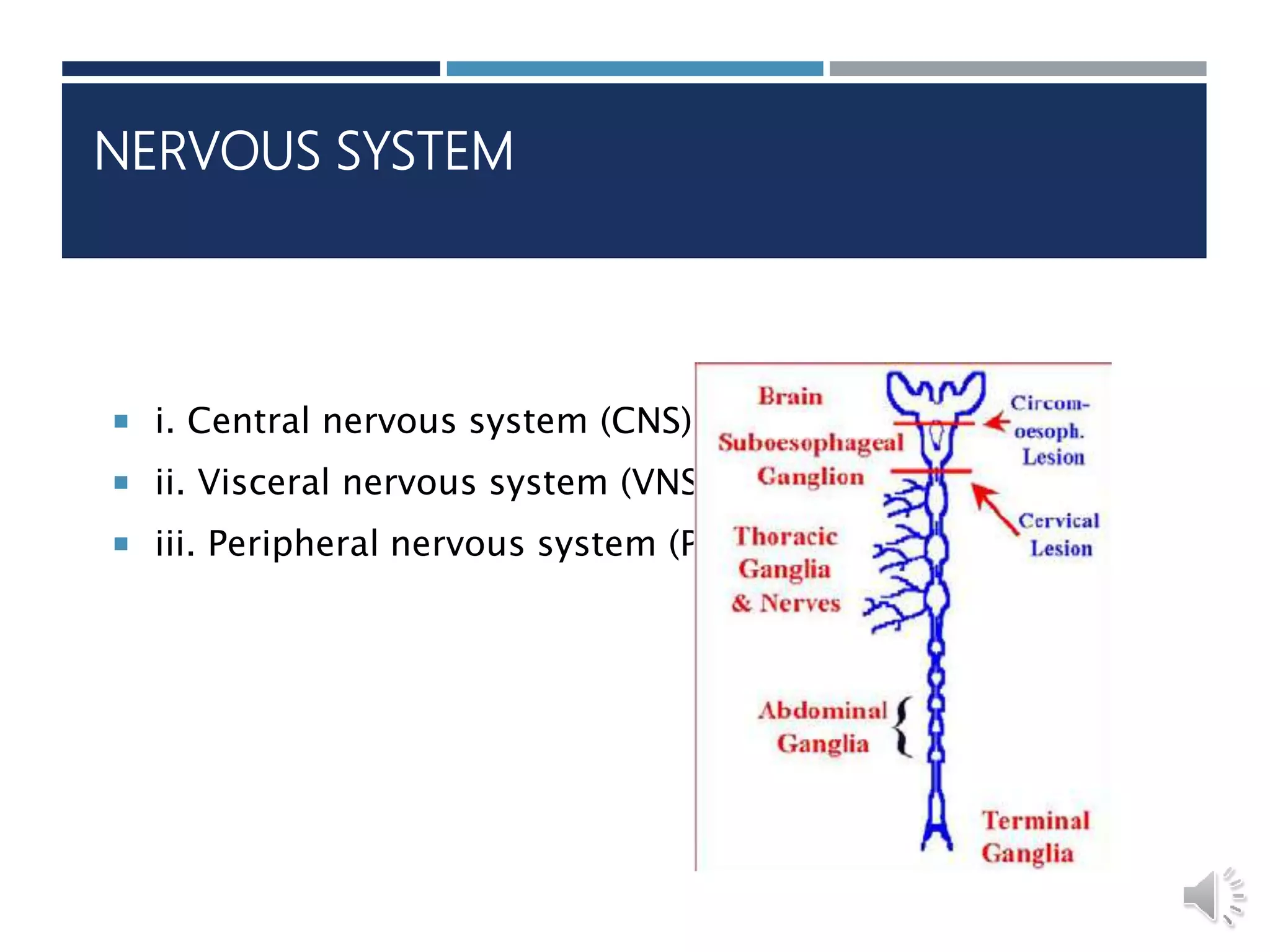
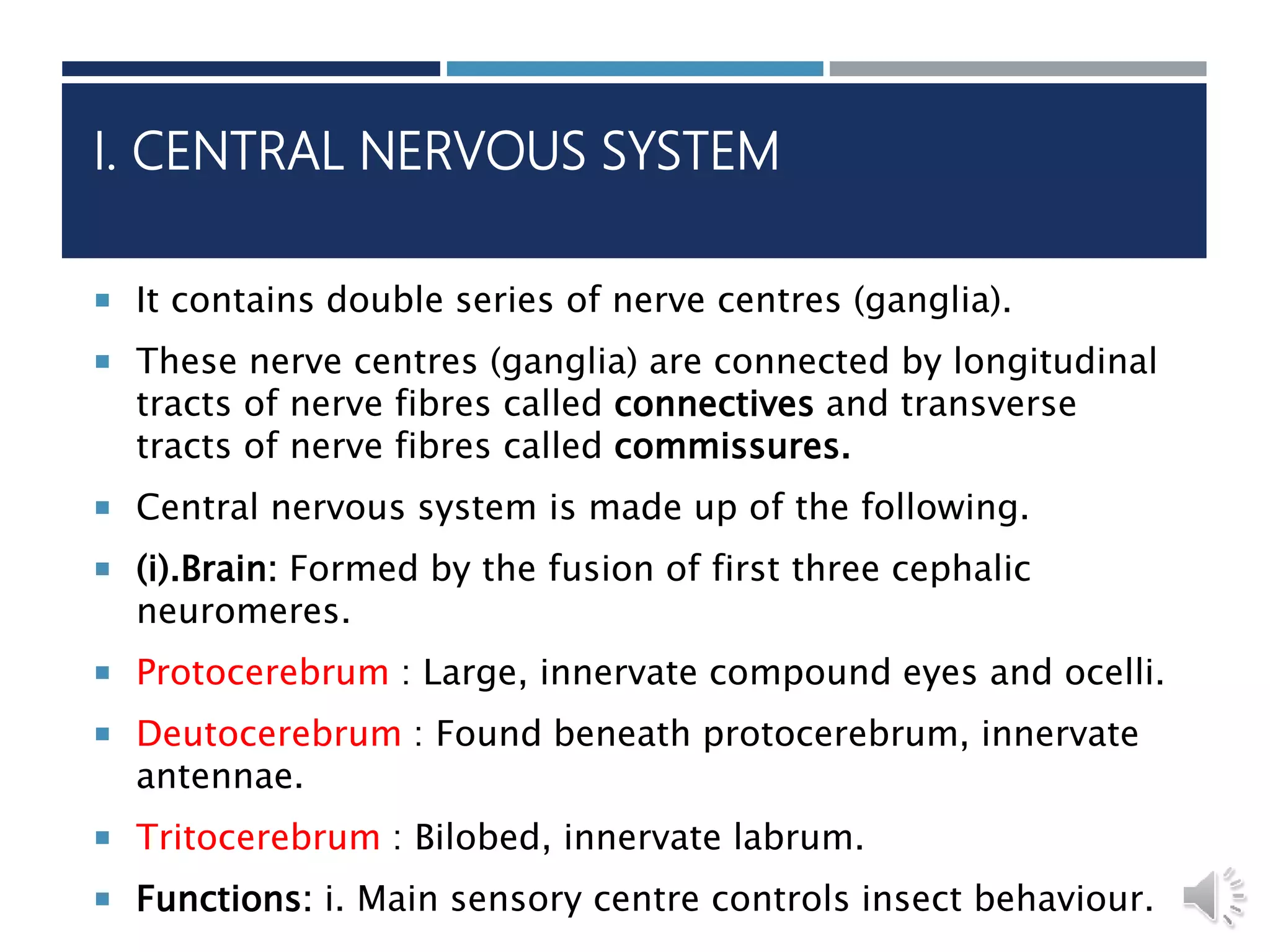
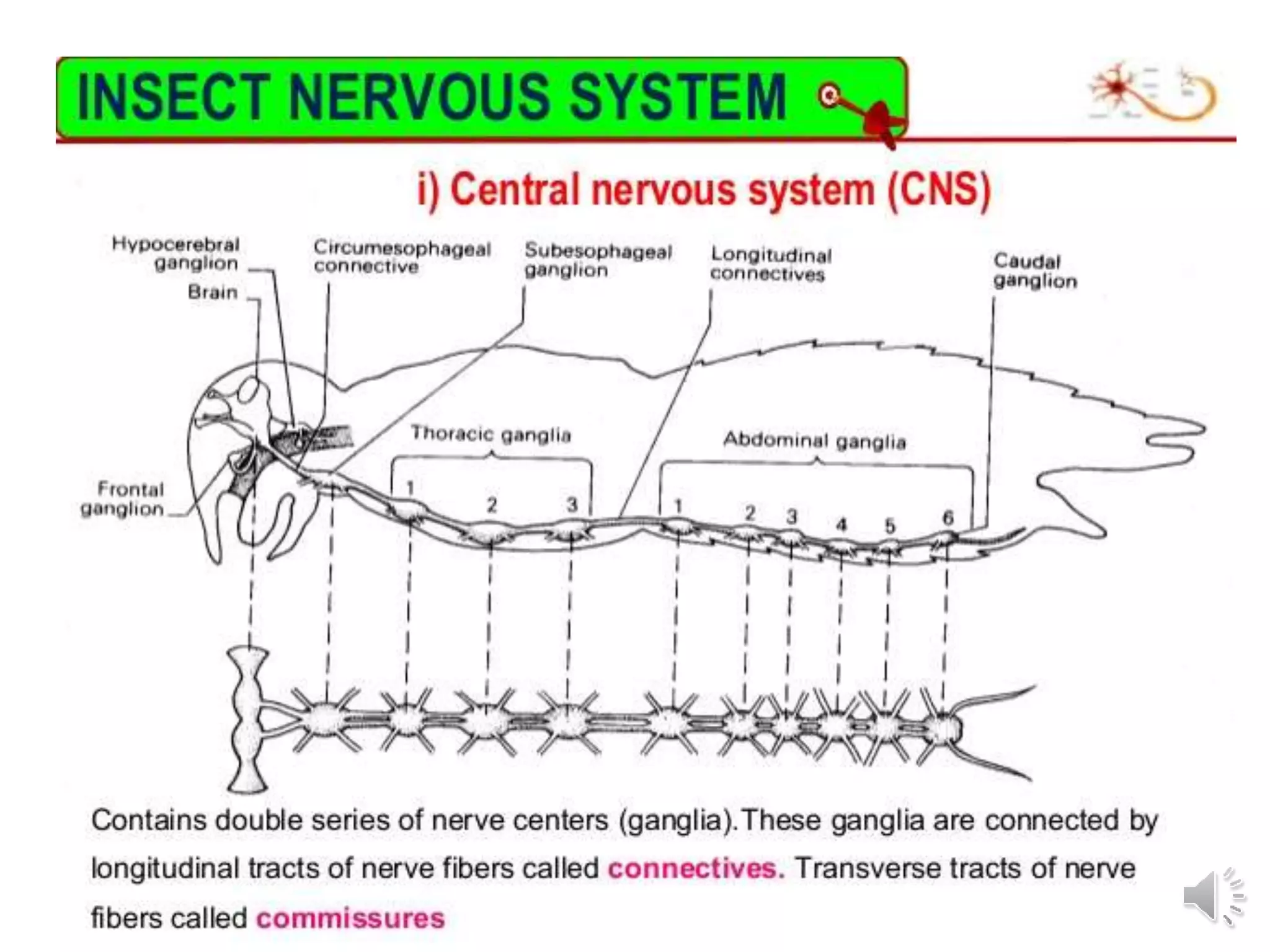
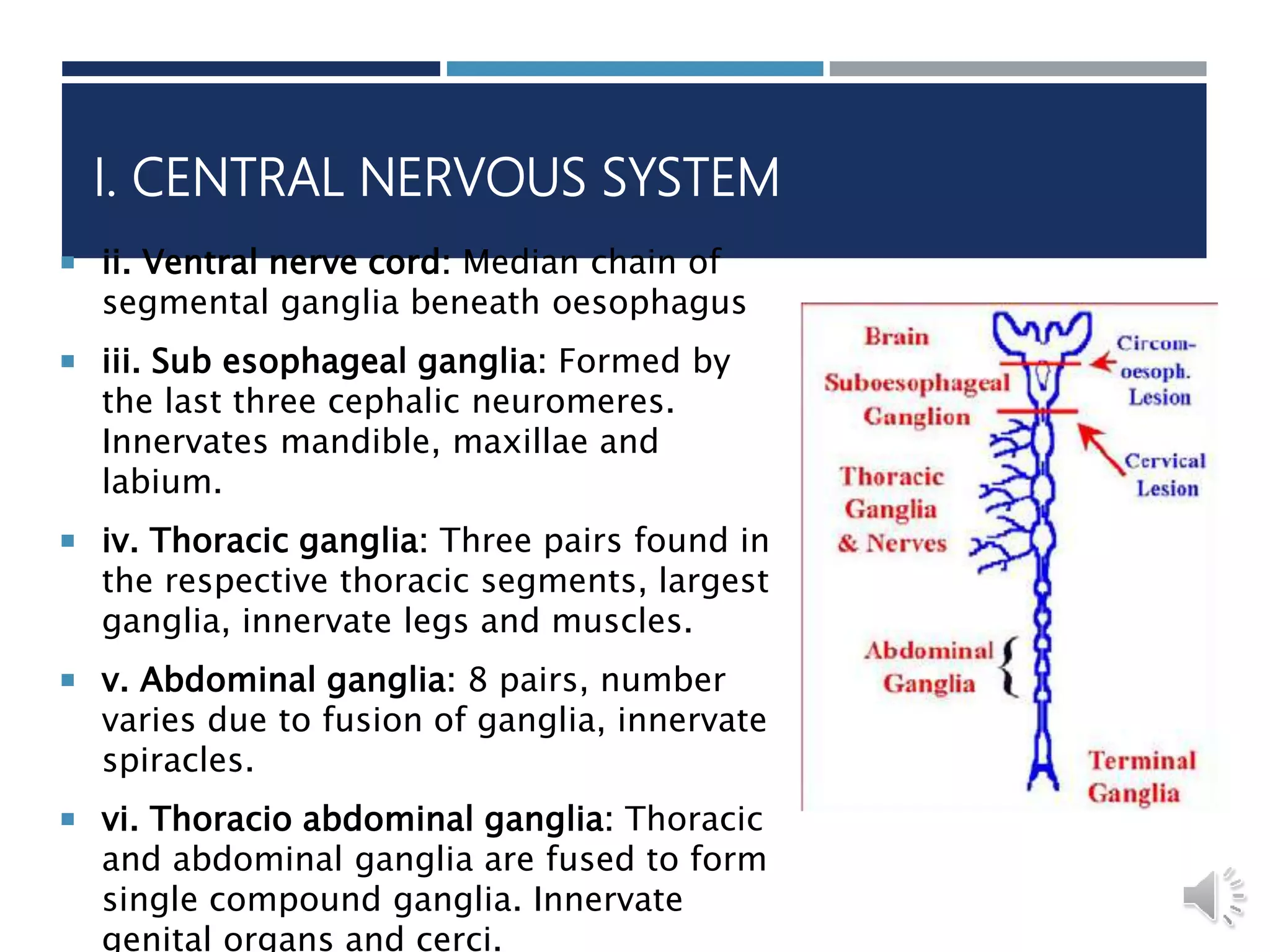
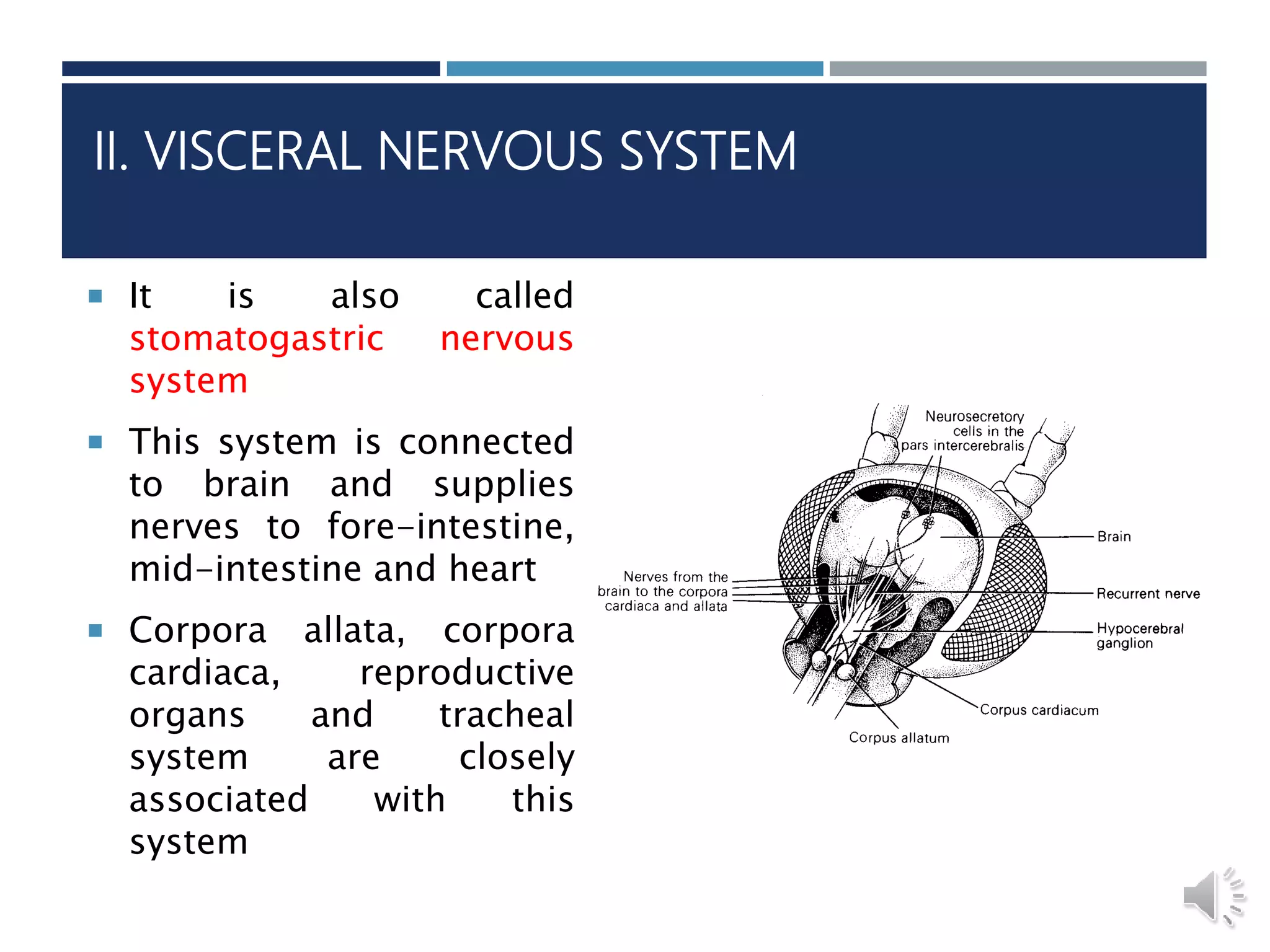
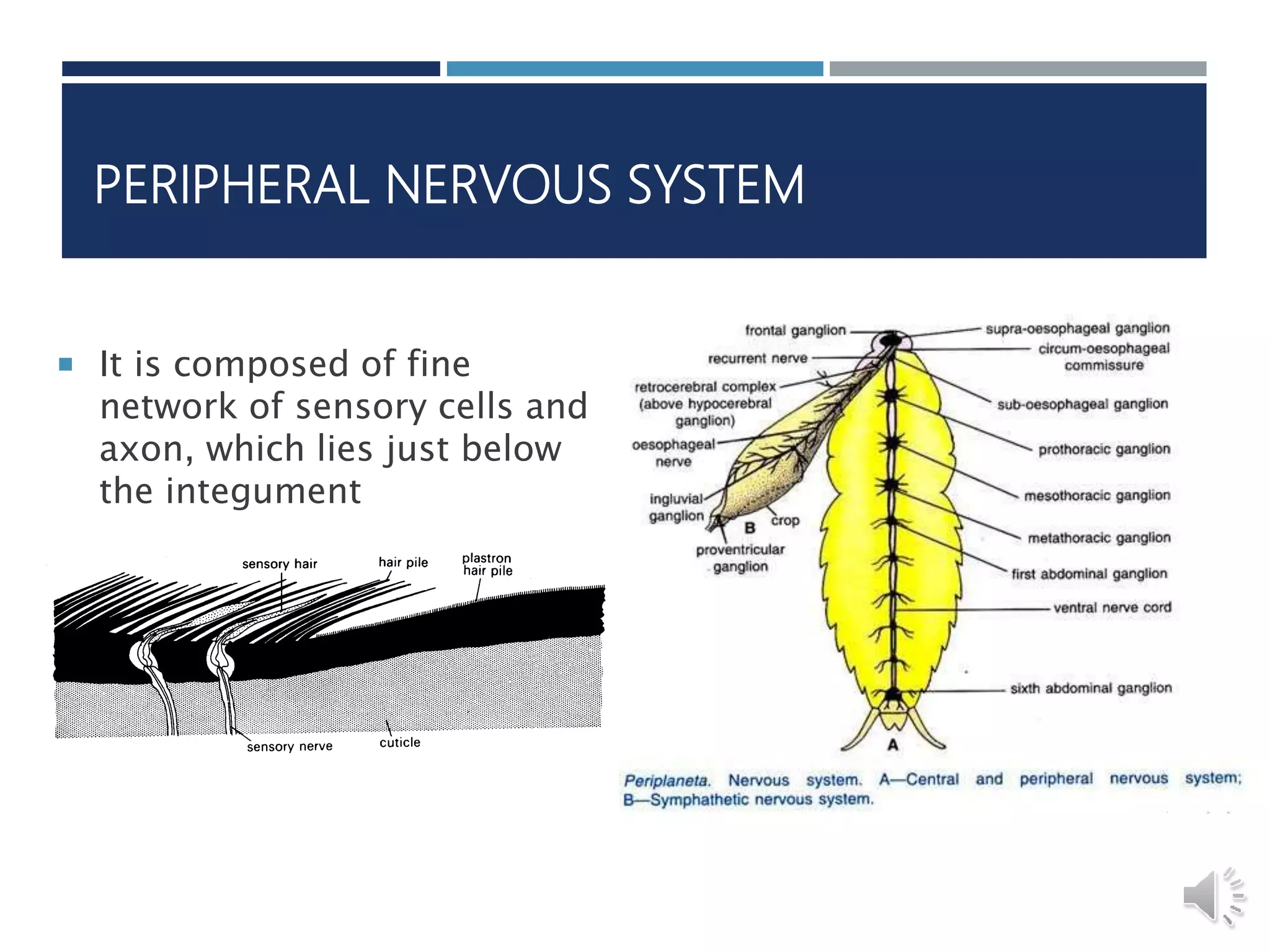
An insect's nervous system consists of three main parts:
1) The central nervous system is a double chain of ganglia connected by nerve fibers that control the insect's behavior and innervate its senses, muscles, and organs.
2) The visceral nervous system connects to the brain and supplies nerves to the foregut, midgut and heart.
3) The peripheral nervous system is a network of sensory cells just below the integument that detects stimuli from the environment.