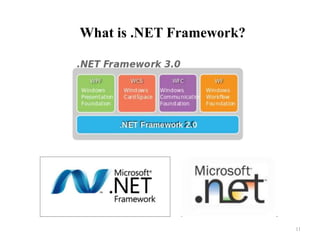
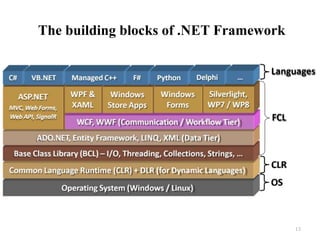
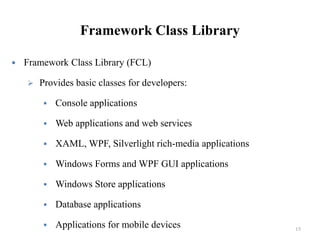
This document provides an introduction and overview of computer programming concepts using C# and .NET. It defines computer programming and the software development process. It then discusses C# as a programming language, the .NET Framework platform, using Visual Studio as an integrated development environment, and MSDN Library for documentation and references. Key topics covered include writing a first C# program, compiling and debugging code, and the components of the .NET Framework like the common language runtime and framework class library.







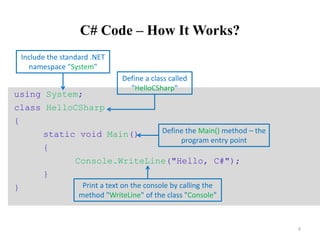
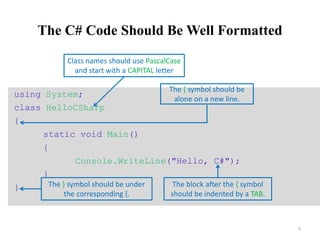
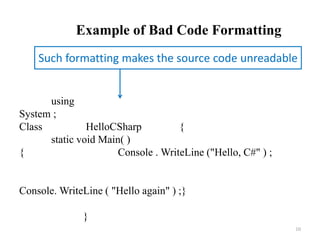





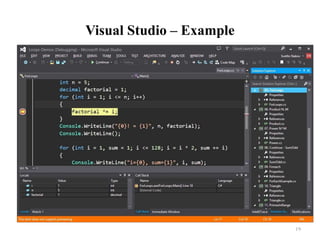

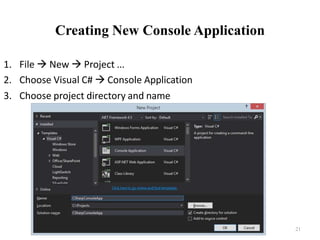
![Compiling the Source Code
• The process of compiling includes:
Syntactic checks
Type safety checks
Translation of the source code to lower level language (MSIL)
Creating executable files (assemblies)
• You can start compilation by
Using Build->Build Solution/Project
Pressing [F6] or [Shift+Ctrl+B]
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1-introductiontoprogramming-240104031649-9cc395e9/85/LECTURE-1-Introduction-to-Programming-pptx-23-320.jpg)
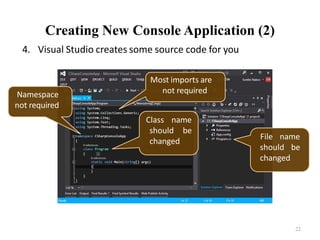
![Running Programs
• The process of running application includes:
Compiling (if project not compiled)
Starting the application
• You can run application by:
Using Debug->Start menu
By pressing [F5] or [Ctrl+F5]
• * NOTE: Not all types of projects are able to be started!
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1-introductiontoprogramming-240104031649-9cc395e9/85/LECTURE-1-Introduction-to-Programming-pptx-24-320.jpg)




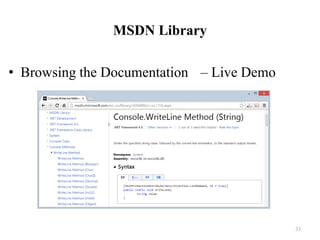
![How to Use MSDN Library?
32
Search in Google for certain class / method / property
E.g.
Or
Or
Use Visual Studio's built-in help system
Press [F1] in Visual Studio in the code
Browse http://msdn.microsoft.com Press [F1] to view
the documentation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1-introductiontoprogramming-240104031649-9cc395e9/85/LECTURE-1-Introduction-to-Programming-pptx-32-320.jpg)