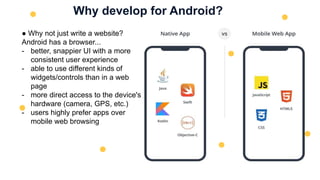
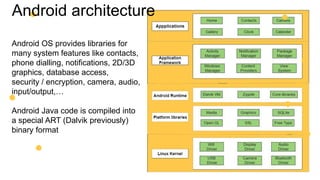
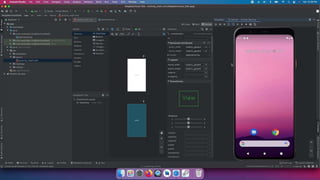
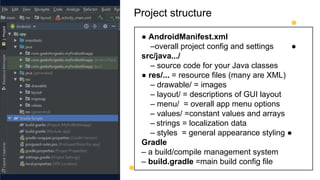
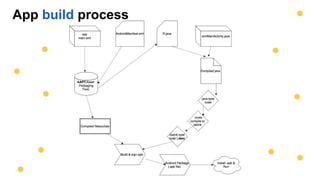
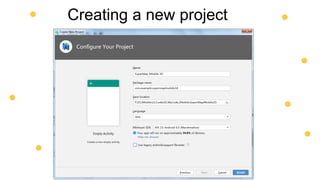
This document is an introduction to mobile application development focused on creating an Android app using Java programming. It discusses Android's architecture, benefits of developing for Android over iOS, and the tools needed like Android Studio and virtual devices for testing. Key concepts include project structure, Android terminology, and a design example for an interactive game app.