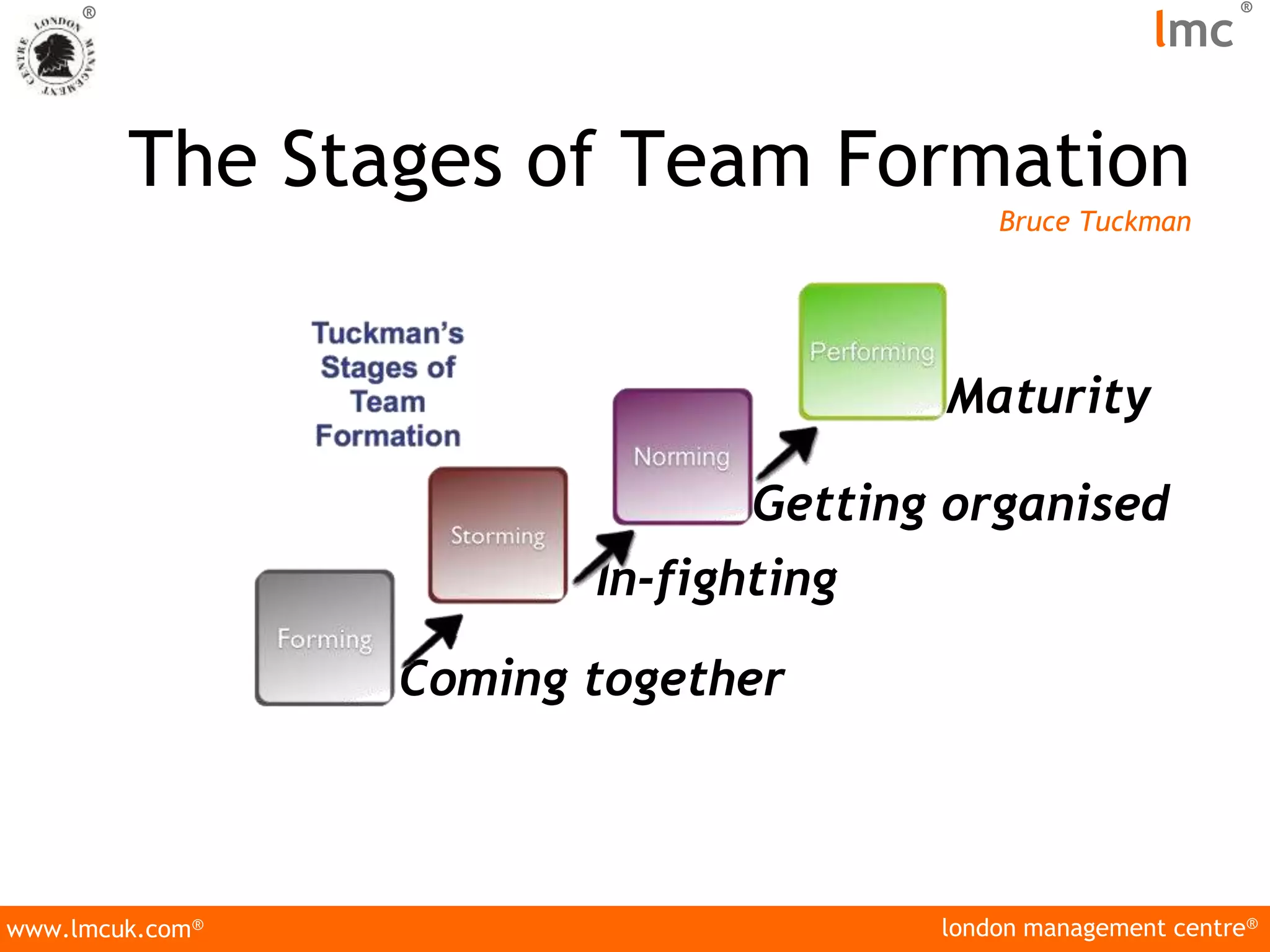
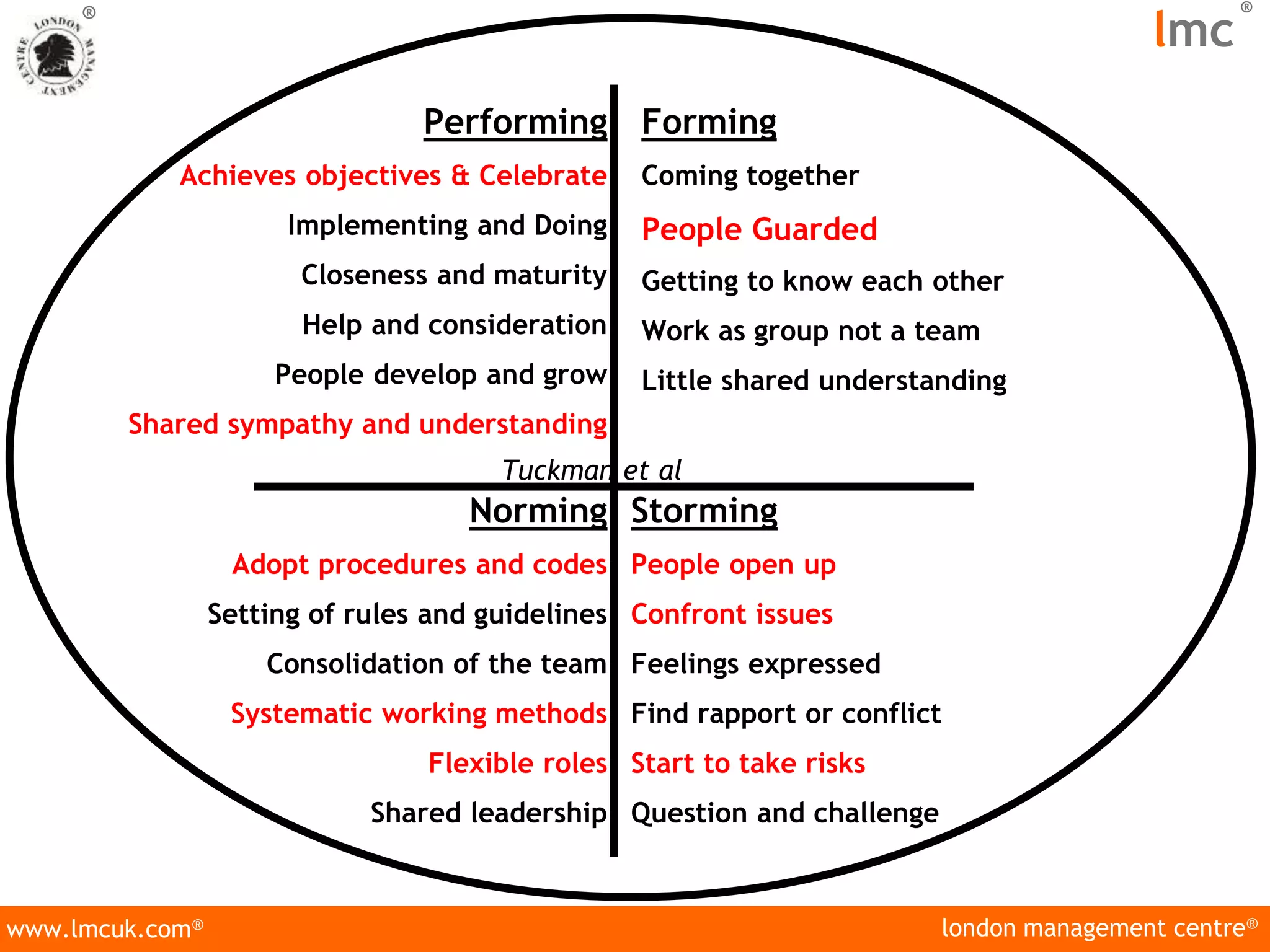
The document discusses two types of organizational change: strategic and operational, outlining their definitions and the reasons organizations need to adapt, such as competition and technology. It highlights the resistance to change among employees due to various fears and emphasizes the importance of management in guiding successful transitions. Additionally, it describes the characteristics of effective teams and the stages of team formation, noting that most major change efforts fail due to a lack of holistic approaches and workforce engagement.