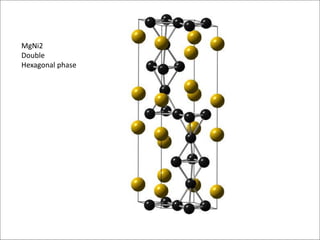
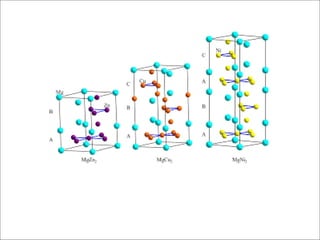
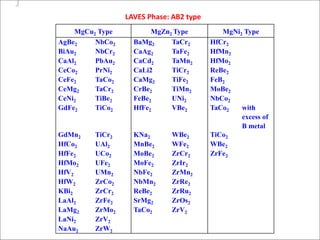
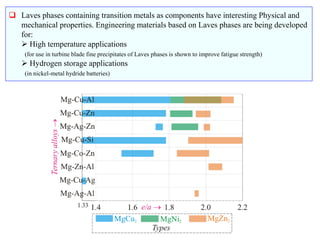
The document discusses Laves phases, which have the chemical formula AB2 and typically a radius ratio of rA/rB between 1.1-1.6. There are three common crystal structures for Laves phases - hexagonal (MgZn2), face-centered cubic (MgCu2), and double hexagonal (MgNi2). Laves phases can have interesting physical and mechanical properties and are being developed for high temperature applications like turbine blades and hydrogen storage in battery materials.


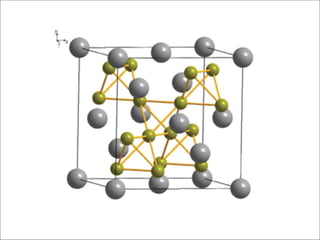
![Mg (8a) Cu (16d)
MgCu2 (Laves)
Lattice parameter(s) a = 7.048 Å
Space Group Fd-3m (227)
Strukturbericht notation C15
Pearson symbol cF24
Other examples with this
structure
Au2Pb
MgCu2 Laves Phase Cubic
[001]
Wyckoff
position
Site
Symmetry
x y z Occupancy
Cu 16d -3m 0.625 0.625 0.625 1
Mg 8a -43m 0 0 0 1
C15
Very
frequent
structural
type
Unit cell formula: Mg8Cu16
Mg: Vertex-1, FC-3, Inside cell-4 → 8
Cu: Inside cell-16 → 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lavesphase-240406194936-6085a9cf/85/Laves-phase-Laves-phase-Laves-phase-Laves-phase-4-320.jpg)
![Mg (8a) Cu (16d)
MgCu2 (Laves)
Lattice parameter(s) a = 7.048 Å
Space Group Fd-3m (227)
Strukturbericht notation C15
Pearson symbol cF24
Other examples with this
structure
Au2Pb
MgCu2 Laves Phase Cubic
[001]
Wyckoff
position
Site
Symmetry
x y z Occupancy
Cu 16d -3m 0.625 0.625 0.625 1
Mg 8a -43m 0 0 0 1
C15
Very
frequent
structural
type
Unit cell formula: Mg8Cu16
Mg: Vertex-1, FC-3, Inside cell-4 → 8
Cu: Inside cell-16 → 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lavesphase-240406194936-6085a9cf/85/Laves-phase-Laves-phase-Laves-phase-Laves-phase-6-320.jpg)
![Size Factor compounds: (i) Laves phases (ii) Frank-Kasper Phases
D
❑ These phases have a formula: AB2
❑ Laves phases can be regarded as Tetrahedrally Close Packed (TCP)* structures with an
ideal ratio of the radii (rA/rB) = (3/2)1/2 ~1.225 [or usually rA/rB (1.1, 1.6)]
❑ If rA/rB = 1.225 then a high packing density is achieved with the chemical formula AB2
with a average coordination number of 13.3
❑ Crystal structures:
➢ Hexagonal → MgZn2 (C15), MgNi2 (C36)
➢ FCC → MgCu2 (C14)
❑ There are more than 1400 members belonging to the ‘Laves family’
❑ Many ternary and multinary representatives of the Laves phases have been reported with
excess of A or B elements. Some ternary Laves phases are known in systems with no
corresponding binary Laves phases.
❑ The range of existence of the three phases (C15, C36, C14) in ternary Laves phases is
influenced by the e/a ratio
D(i) Laves Phases
* Also called Topologically Close Packed structures?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lavesphase-240406194936-6085a9cf/85/Laves-phase-Laves-phase-Laves-phase-Laves-phase-8-320.jpg)
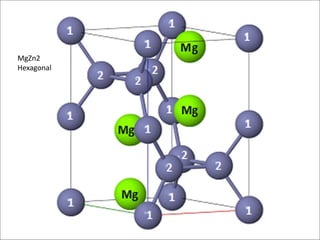
![MgZn2 (Laves)
Lattice parameter(s) a = 5.18 Å, c = 8.52 Å
Space Group P 63/mmc (194)
Strukturbericht notation C14
Pearson symbol hP12
Other examples with this
structure
NbCr2
Wyckoff
position
Site
Symmetry
x y z Occupancy
Mg 4f 3m 0.33 0.67 0.062 1
Zn1 2a -3m 0 0 0 1
Zn2 6h mm2 0.83 0.66 0.25 1
MgZn2 Laves Phase
Mg
Zn2
Zn1
[0001]
Hexagonal
C14
Zn: Vertex-1, Edge-1, Inside cell-6 → 8
Mg: Inside cell-4 → 4
Unit cell formula: Mg4Zn8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lavesphase-240406194936-6085a9cf/85/Laves-phase-Laves-phase-Laves-phase-Laves-phase-10-320.jpg)