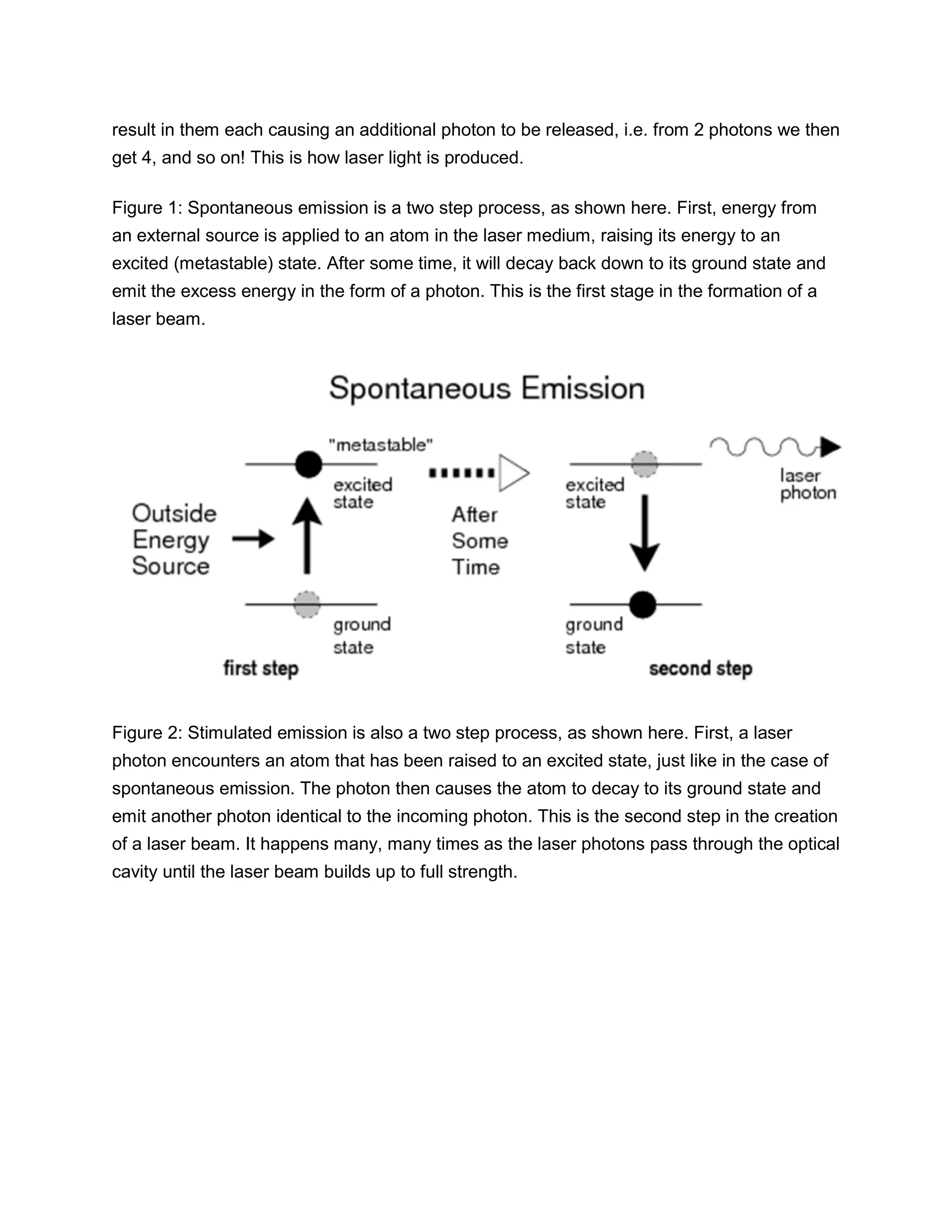
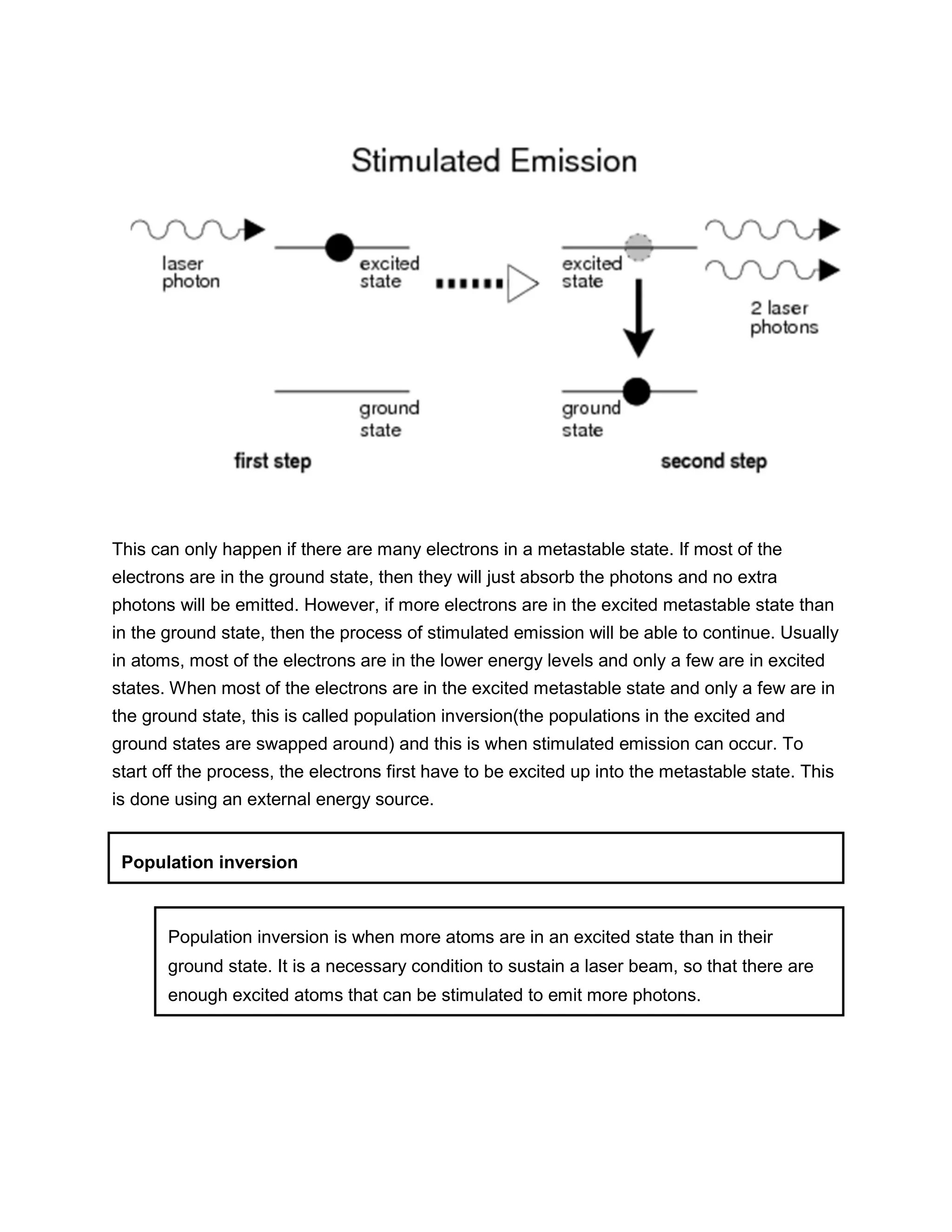
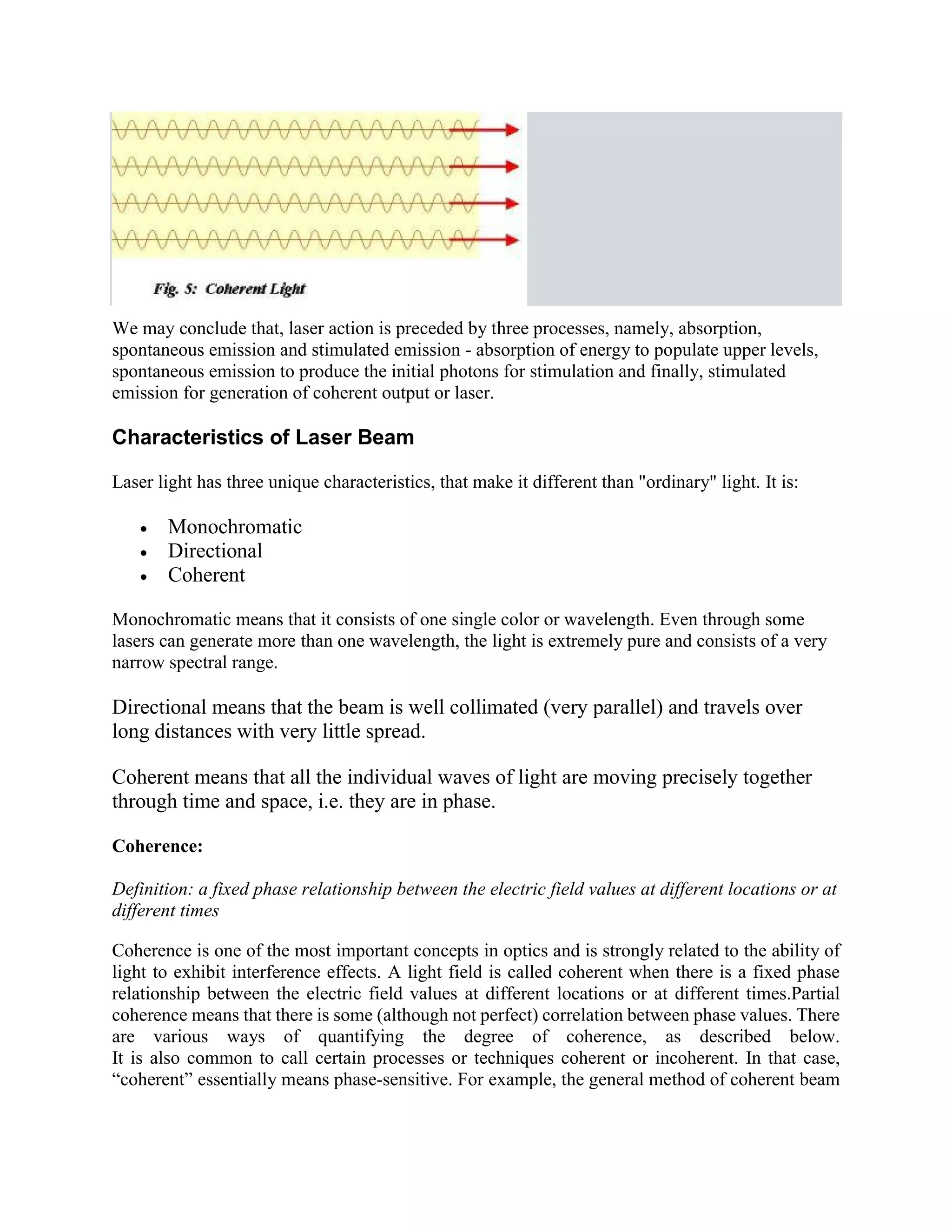
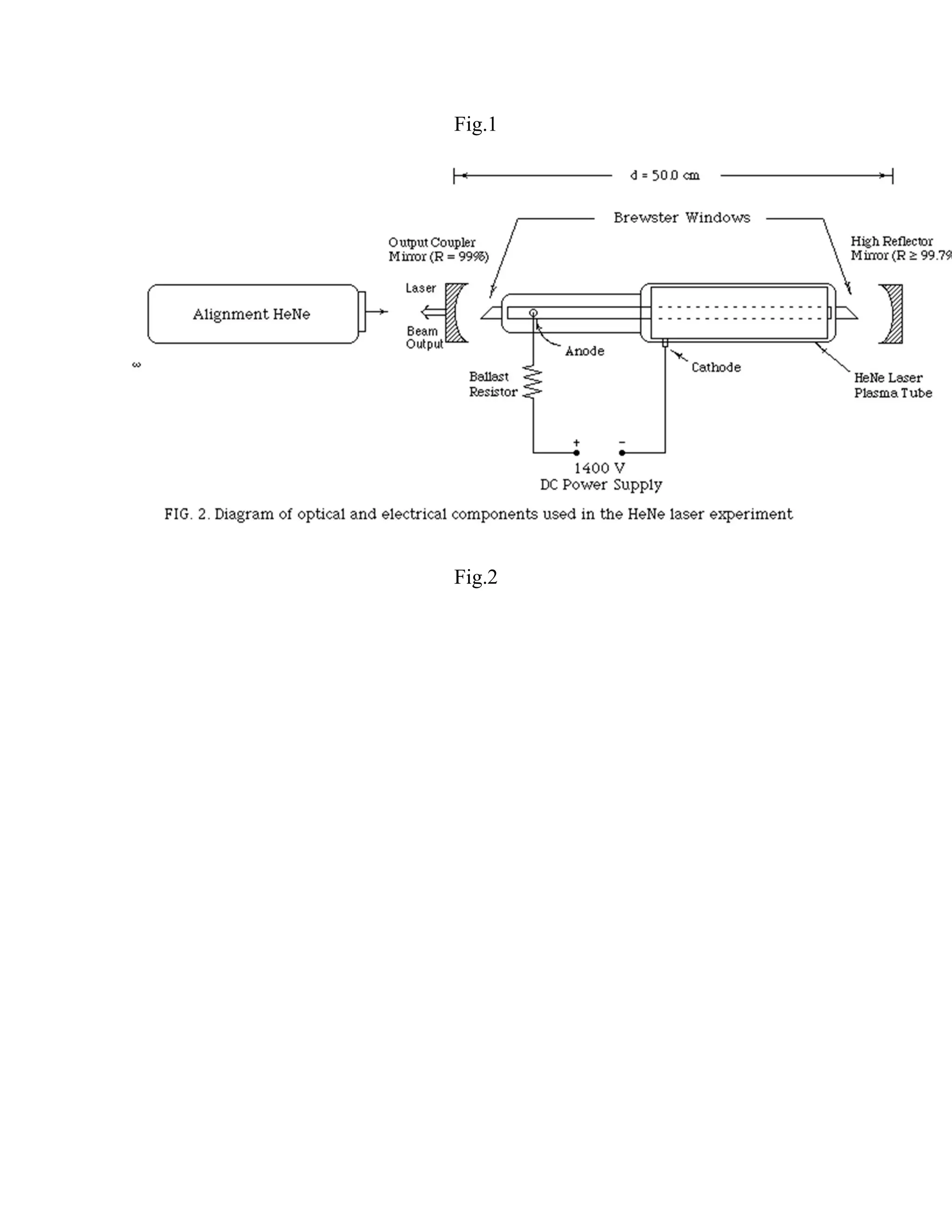
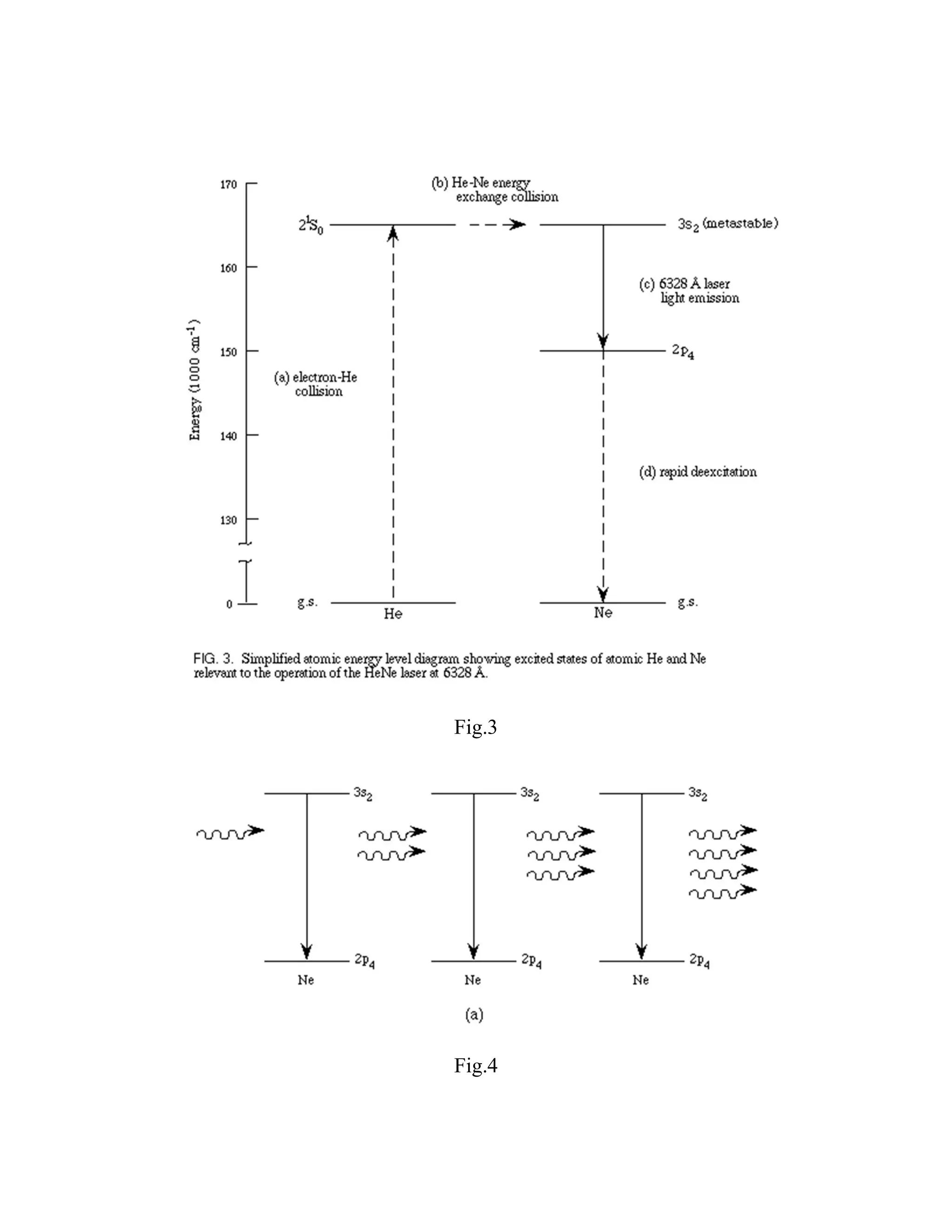
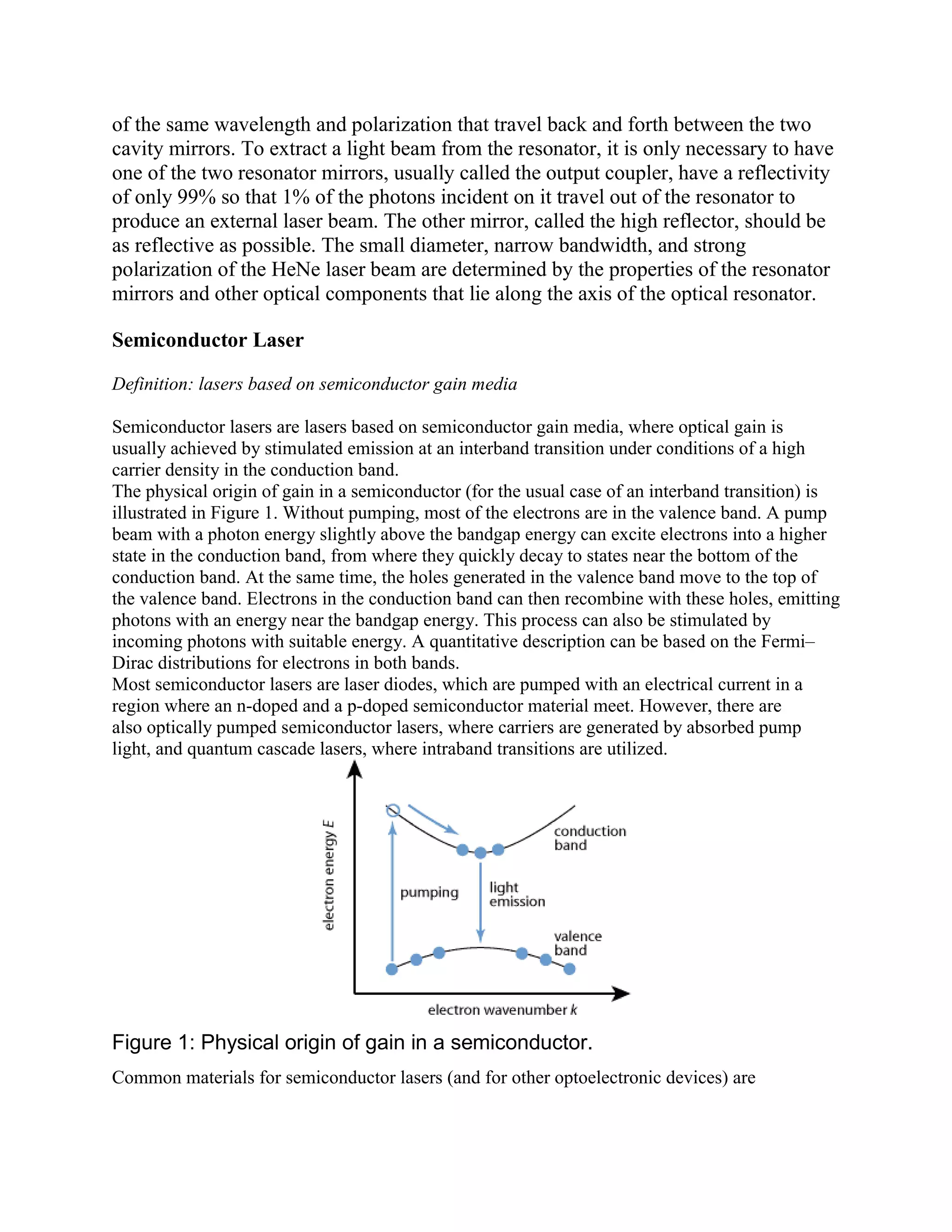
This document provides information about lasers, specifically discussing spontaneous emission, stimulated emission, how lasers work, population inversion, and characteristics of laser beams. It then describes the Helium-Neon laser in detail, including how it is pumped through electron collisions, its gain medium of Helium and Neon gases, and the optical resonator that allows stimulated emission to produce coherent laser light. Key points are that lasers require population inversion to produce stimulated emission of coherent, monochromatic, and directional laser light.