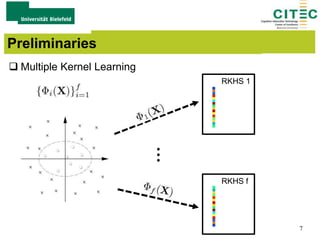
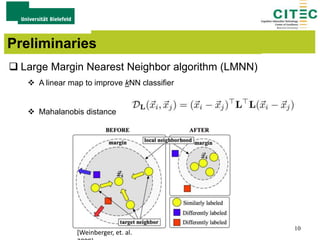
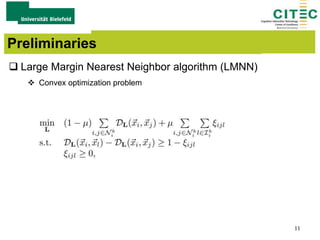
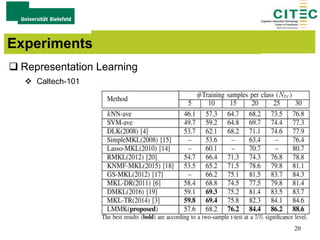
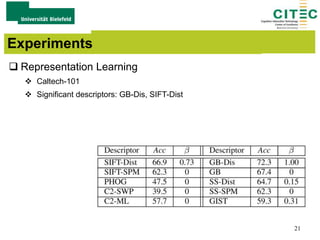
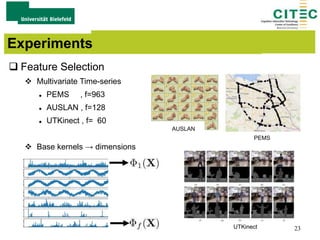
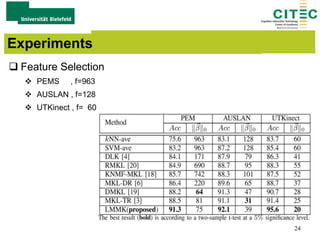
The document outlines a method for large-margin multiple kernel learning (LMMK) aimed at enhancing discriminative feature selection and representation learning in machine learning approaches. It discusses the optimization framework, local class separation in Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space (RKHS), and details various experiments conducted with different datasets. Key techniques include the use of multiple base kernels and non-negative linear programming for effective feature selection and representation.