Embed presentation
Downloaded 438 times


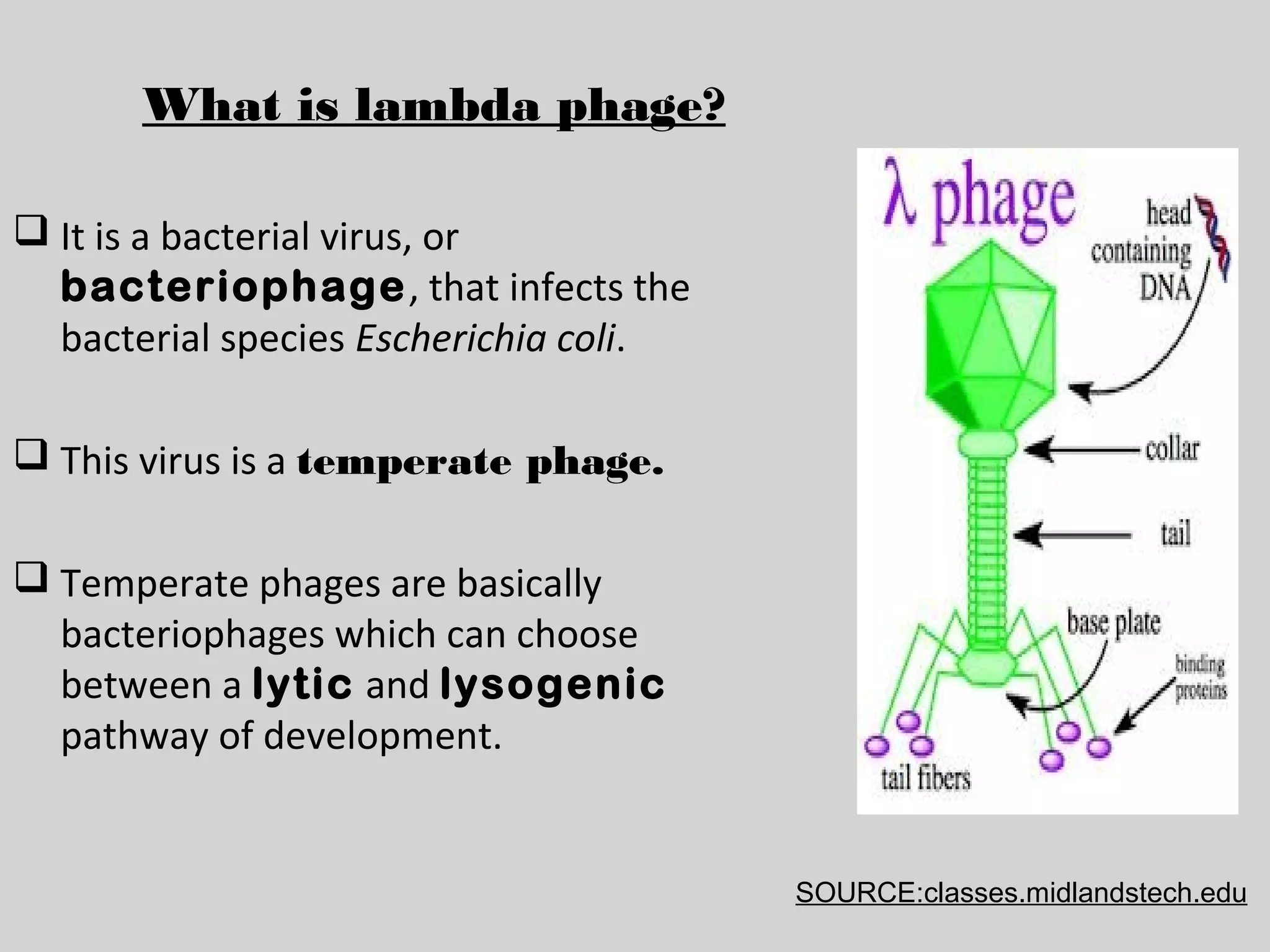
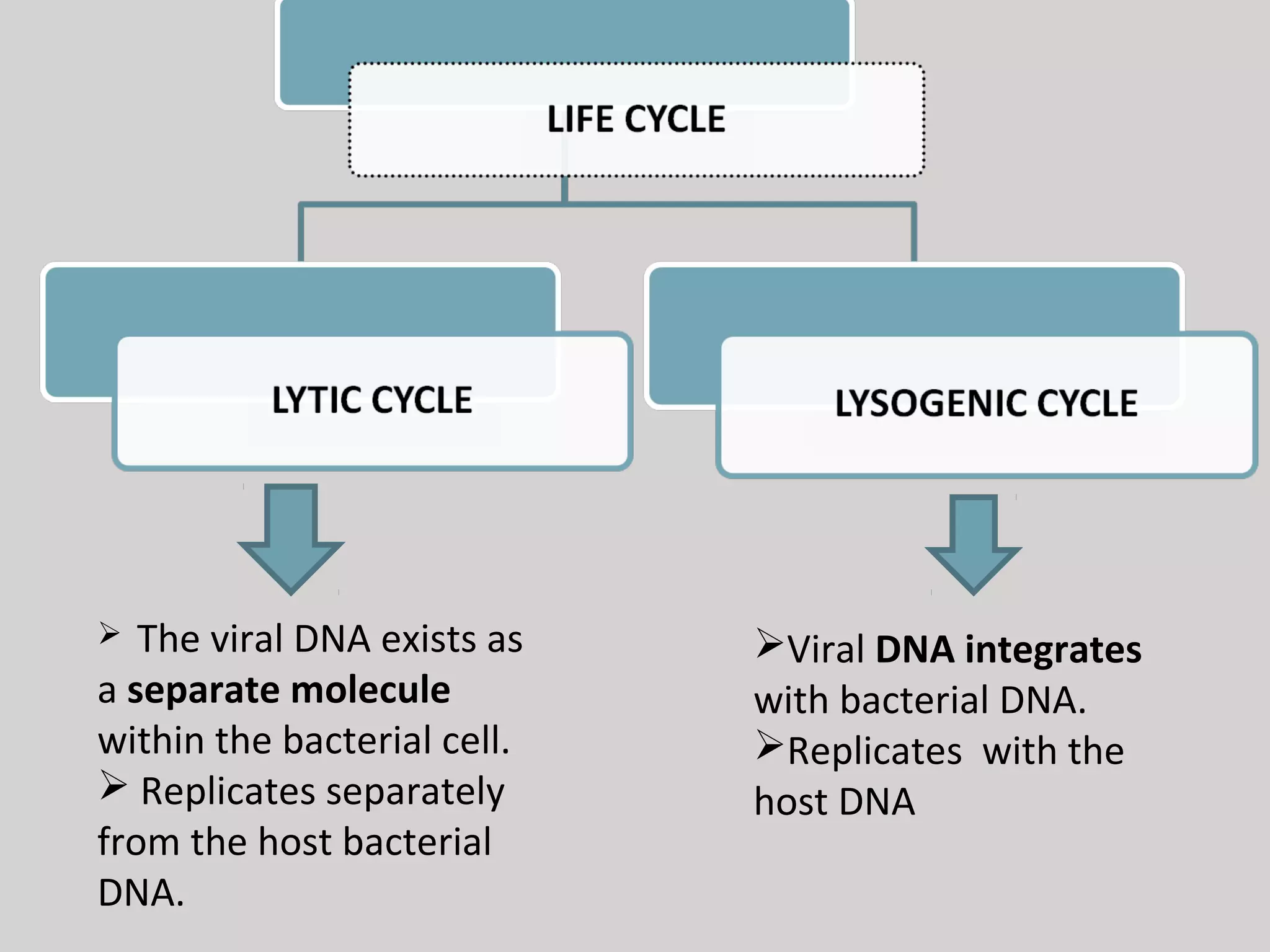
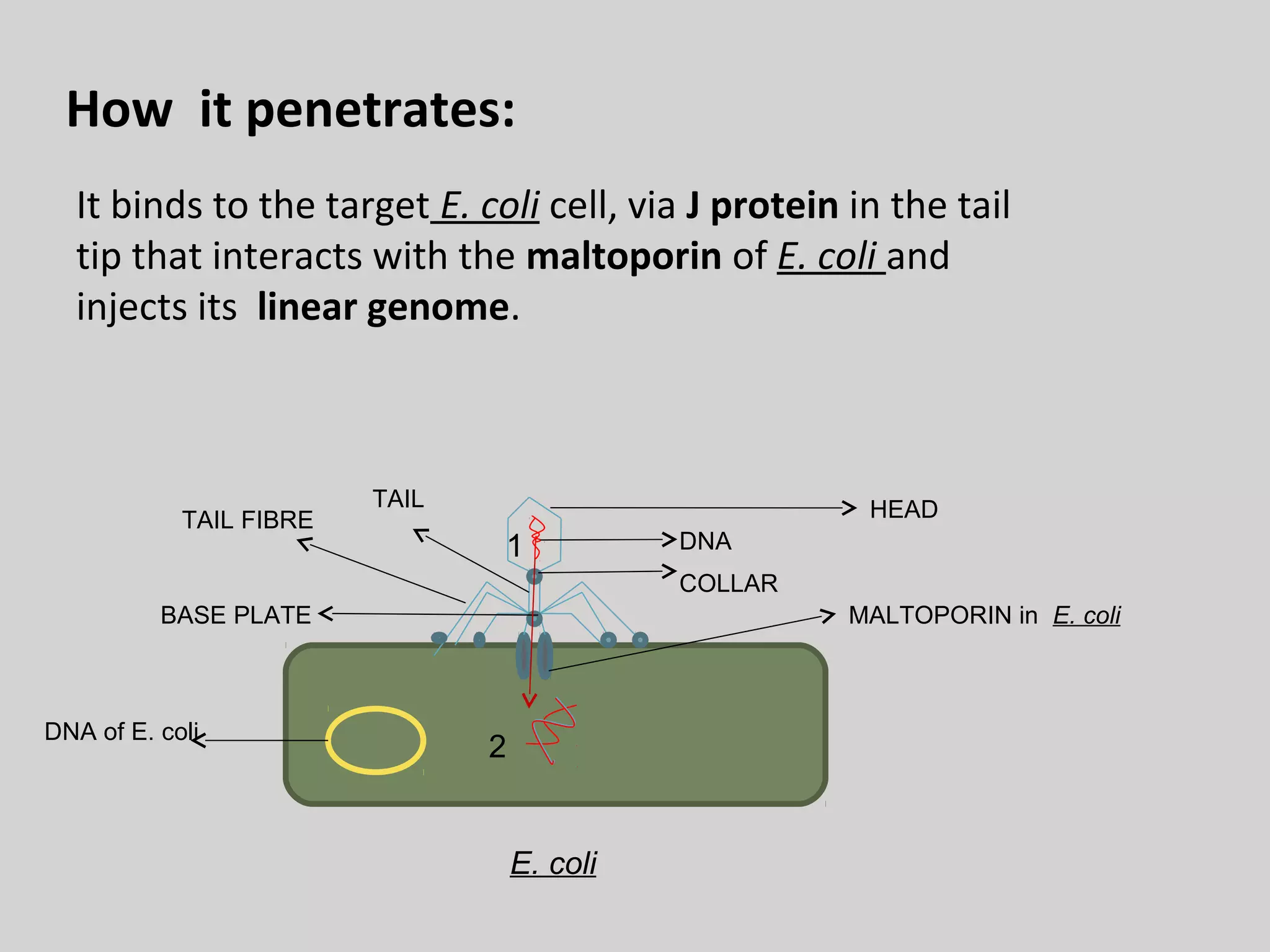
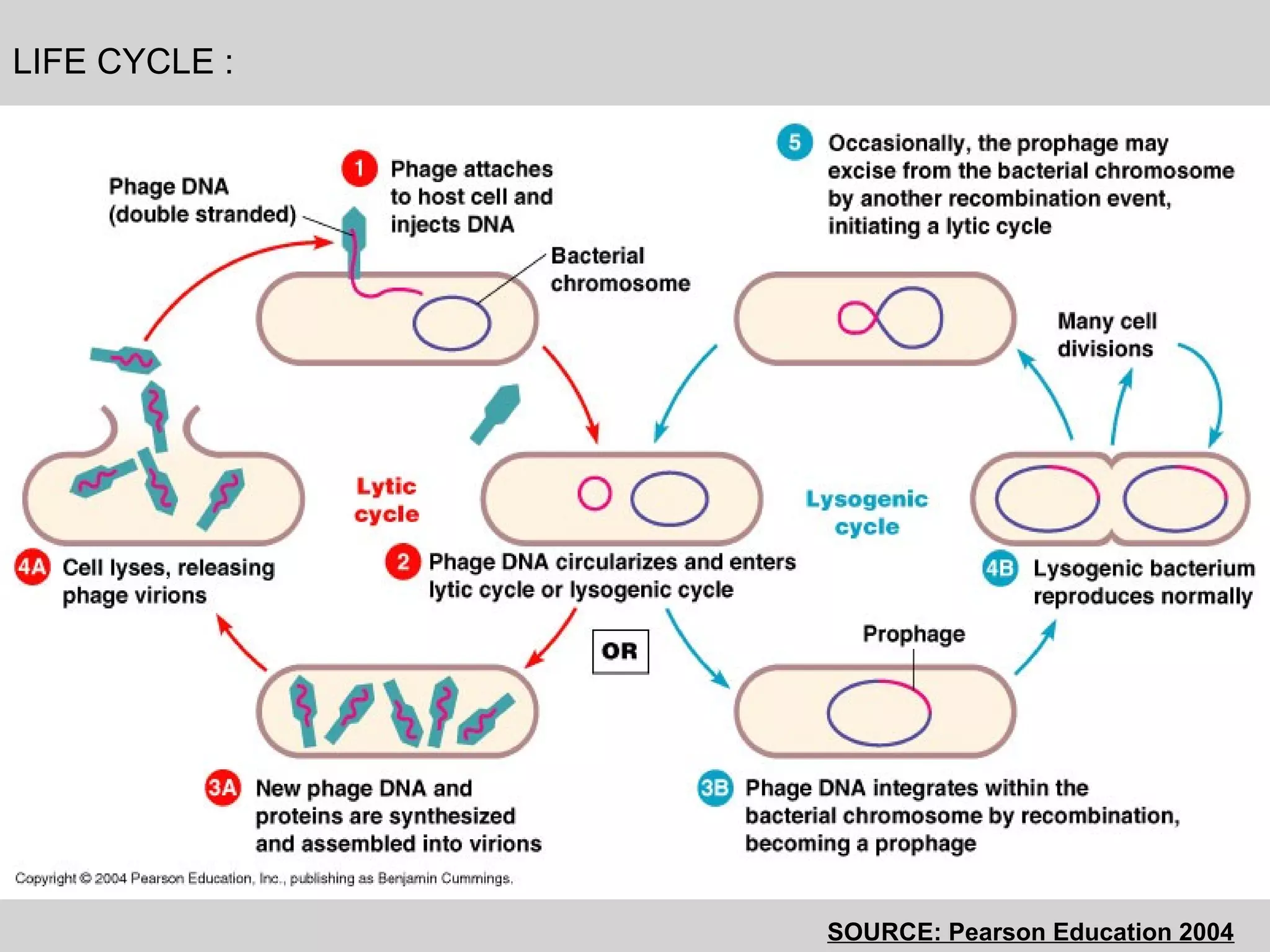


Lambda phage is a bacteriophage that infects E. coli bacteria. It has two life cycles: a lytic cycle and a lysogenic cycle. In the lytic cycle, the phage genome is transferred into the bacterial cell where it replicates and causes the bacterial cell to burst, releasing new phage particles. In the lysogenic cycle, the phage genome integrates into the bacterial chromosome and replicates with the host DNA without killing the cell. The phage can switch between these two cycles depending on environmental conditions inside the infected bacterial cell.







