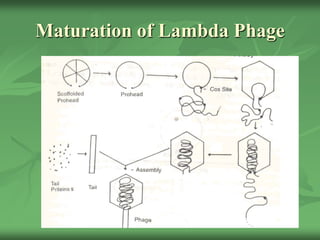
The lambda (λ) phage infects E. coli and can follow two different life cycles - lytic or lysogenic. In the lytic cycle, phage genes are expressed which results in the production of new phage particles and lysis of the host cell. In the lysogenic cycle, the phage genome integrates into the host chromosome where it is replicated along with the host DNA in a process called lysogeny. The prophage can be excised from the host chromosome under certain conditions and enter the lytic cycle.