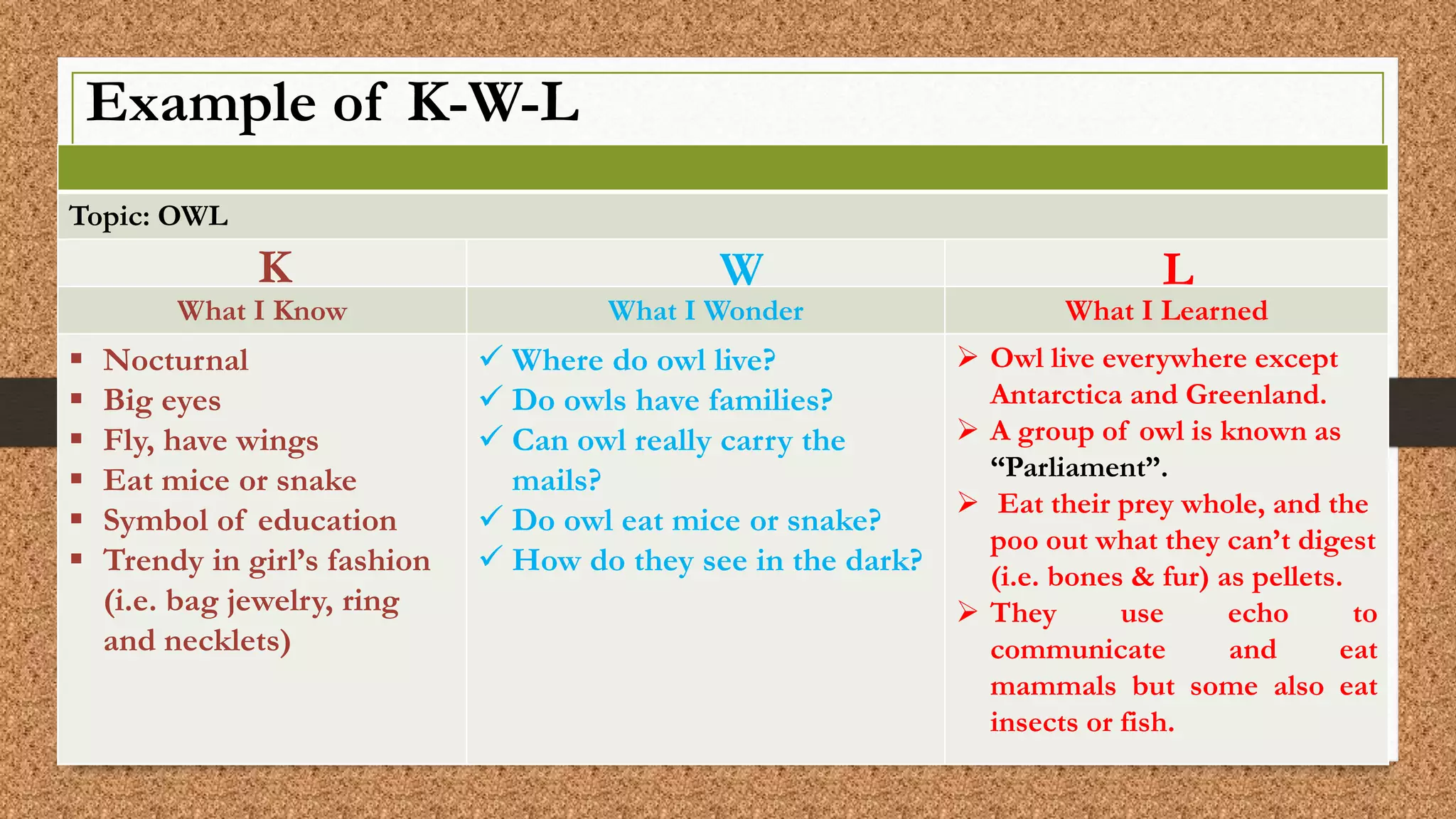
1. The document discusses strategies for activating background knowledge when reading, including using a K-W-L chart.
2. A K-W-L chart has three columns for what readers already Know, what they Wonder, and what they Learn from reading.
3. The process involves brainstorming what you already know about a topic in the K column, asking questions in the W column, and recording what was learned in the L column after reading.