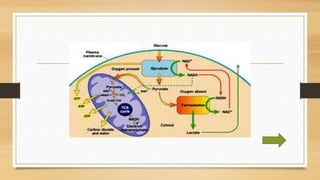
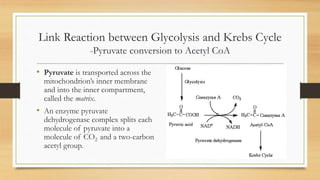
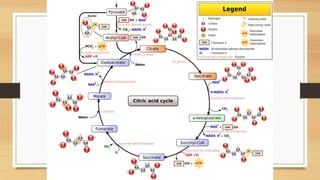
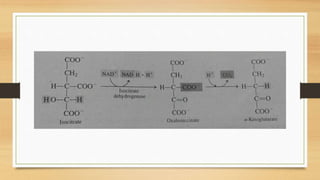
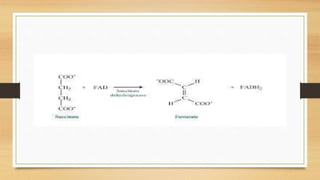
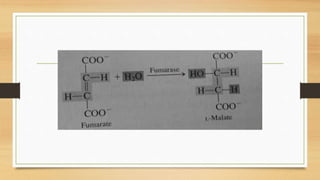
The Krebs Cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix and is a series of chemical reactions that generates energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into carbon dioxide. It was discovered by Hans Adolf Krebs in 1937 and is also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle. Each turn of the cycle produces one GTP or ATP, three NADH molecules, and one FADH2 molecule which will be used in cellular respiration to produce ATP.