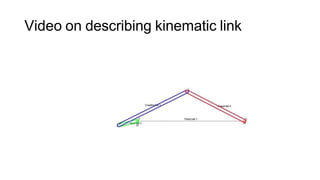
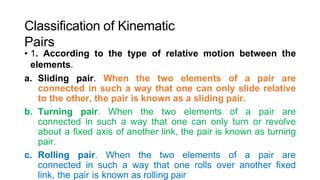
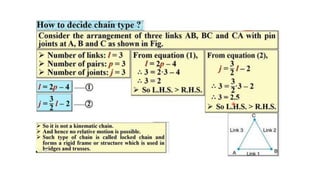
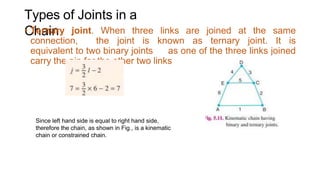
This document provides an overview of kinematics of machinery, which is formally known as the theory of machines. It defines kinematic elements and links, and describes the different types of links including rigid, flexible, and fluid links. It also discusses kinematic pairs and different types of kinematic pairs classified based on relative motion and contact between elements. Additionally, it defines kinematic chains and different types of joints that can be present in kinematic chains.