Embed presentation

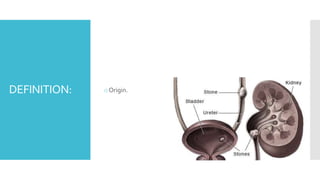
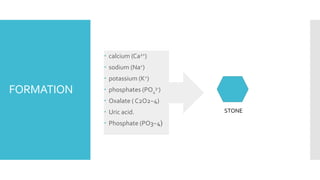

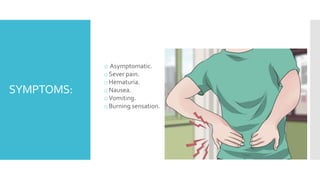

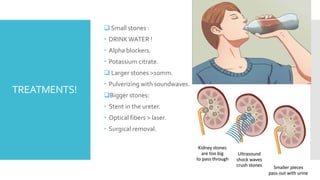

Kidney stones form when minerals and salts in urine crystallize and accumulate in the kidneys or ureters. The most common types are calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate stones, which form due to an imbalance of calcium, oxalate, sodium, and phosphates in urine. Symptoms include severe pain in the back or side, painful or difficult urination, nausea, and vomiting. Left untreated, kidney stones can damage the kidneys. Treatment depends on the size of the stone, ranging from increased fluid intake for small stones to surgical removal for large stones that cannot pass naturally.







