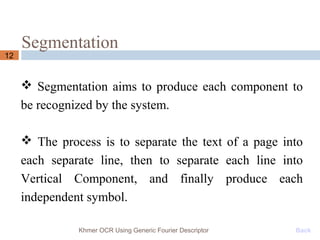
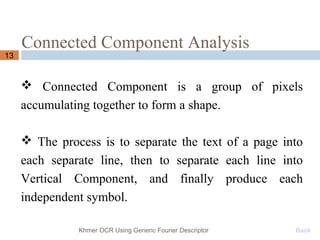
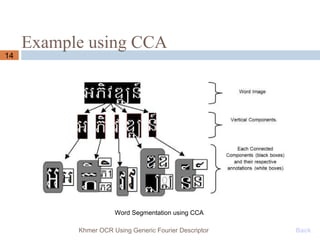
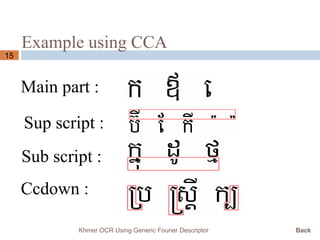
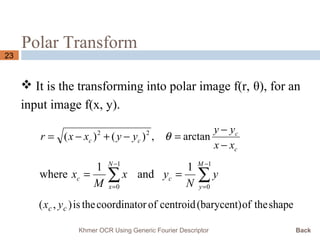
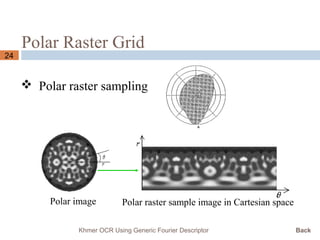
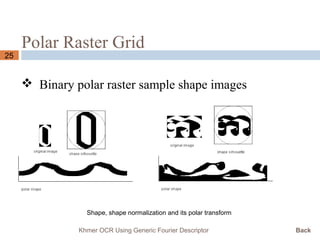
This document presents a Khmer optical character recognition system that uses generic Fourier descriptors for feature extraction and recognition. It discusses pre-processing techniques like binarization and noise removal, segmentation using connected component analysis, and extracting generic Fourier descriptors to represent each character as a feature vector. During recognition, the system compares feature vectors of input characters to those in a database to find the closest match and output the recognized text. The goal is to build a reliable Khmer OCR system that is independent of font and size.














![2D- Fourier Transform
26
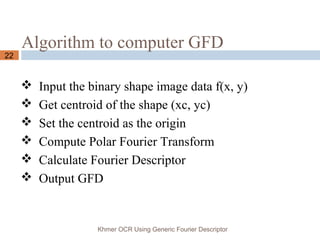
2-D Fourier transform on polar raster sample
image f(r, θ ):
where 0≤r<R and θi
= i(2π/T) (0≤ i<T); 0≤ρ<R,
0≤φ<T. R and T are the radial frequency resolution and
angular frequency resolution respectively.
∑∑ +−=
r i
i
T
i
R
r
jrfPF )]
2
(2exp[),(),( φ
π
ρπθφρ
Khmer OCR Using Generic Fourier Descriptor Back](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/khmerocrusinggfd-150627155124-lva1-app6892/85/Khmer-ocr-using-gfd-26-320.jpg)


![Reference
30
Khmer OCR Using Generic Fourier Descriptor Back
[1] V. Kruy. Preliminary Experiment on Khmer OCR. Kameyama Laboratory,
Waseda Univerisy, Japan.
[2] Thesis for master degree, Khmer OCR, Vanna Kruy.
[3] D. Zhang and G. Lu. Shape-based image retrieval using generic Fourier descriptor.
Gippsland School of Computing and Information
Technology. Monash University. Churchill, Victoria 3842, Australia.
[4] Thesis for Doctoral Degree, chapter 6: Generic Fourier Descriptor, Dengsheng
Zhang.
[5] J.C.Rupe. Vision-Based Hand Shape Identification for Sign Language
Recognition. Department of Computer Engineering Kate Gleason College of
Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology Rochester, NY.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/khmerocrusinggfd-150627155124-lva1-app6892/85/Khmer-ocr-using-gfd-30-320.jpg)
![Reference
31
Khmer OCR Using Generic Fourier Descriptor Back
[6] D. Dimov. A polar-Fourier-Wavelet’s Transform for Effective CBIR. 3rd
ADBIS
workshop on Data mining & Knowledge Discovery
[7] I. Lengieng, K. Sochenda and C. Sokhour. , Khmer OCR for Limon R1 Size 22
Report, PAN Localization Cambodia (PLC) of IDRC.er OCR
[8] A. Averbuch, R.R. Coifmany , D.L. Donohoz M. Eladx M. Israeli. Fast and
Accurate Polar Fourier Transform.
Department of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv 69978, Israel.
Department of mathematics, Yale University, New Haven CT 06520-8283 USA
Department of Statistics, Stanford University, Stanford 94305-9025 CA. USA.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/khmerocrusinggfd-150627155124-lva1-app6892/85/Khmer-ocr-using-gfd-31-320.jpg)