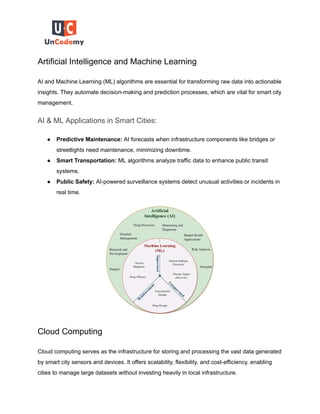
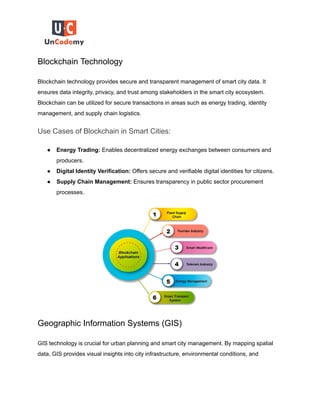
Smart cities leverage data analytics and digital technologies to improve urban living by enhancing resource management, real-time decision making, and citizen services. Key technologies, including IoT, big data analytics, AI, cloud computing, and GIS, play pivotal roles in transforming data into actionable insights, which foster sustainable urban development. As these technologies evolve, they contribute to creating more efficient, resilient, and livable urban environments.