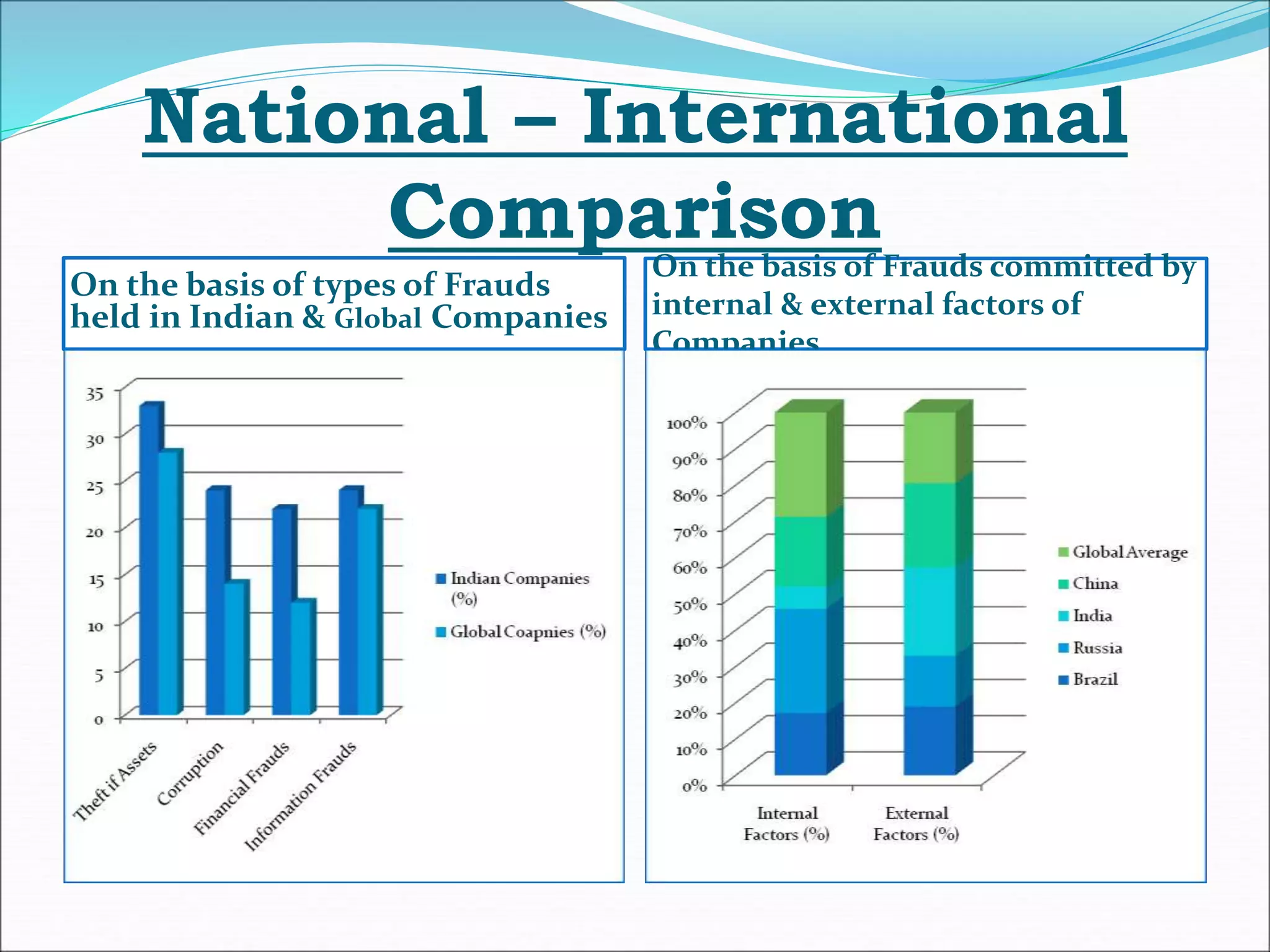
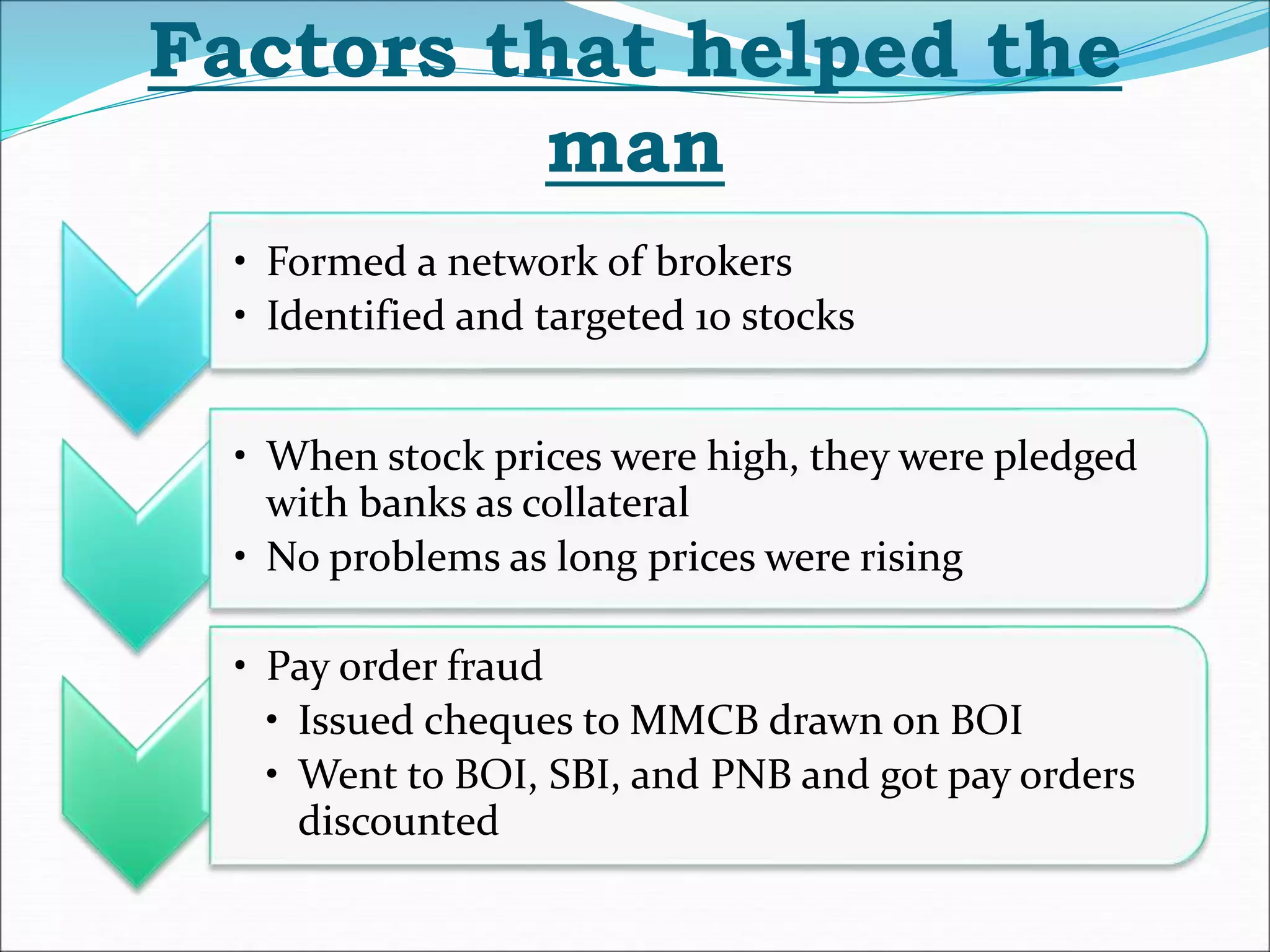
This document summarizes the Ketan Parekh scam, a major corporate fraud that occurred in India in 1999-2001. Ketan Parekh, a stockbroker, manipulated the prices of 10 stocks ("K-10 stocks") by heavily investing in them, which caused a stock market bubble. When the scam was revealed in 2001, the stock market crashed, with the Sensex falling 28% in two months, causing losses of Rs. 2000 billion. Key lessons were the need for tighter regulation of brokers and collateralized lending. The retail investors were hit hardest by the scam.