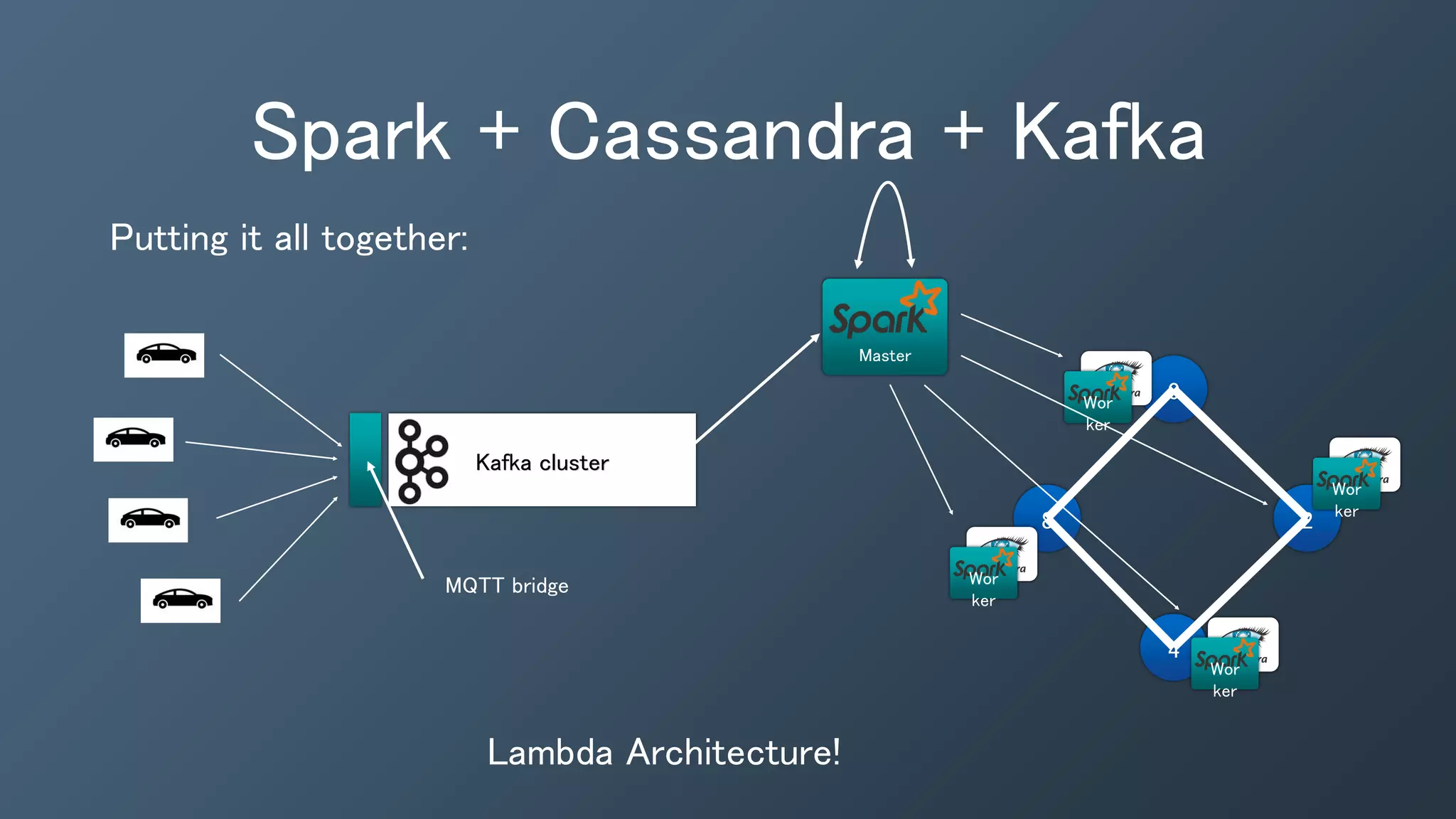
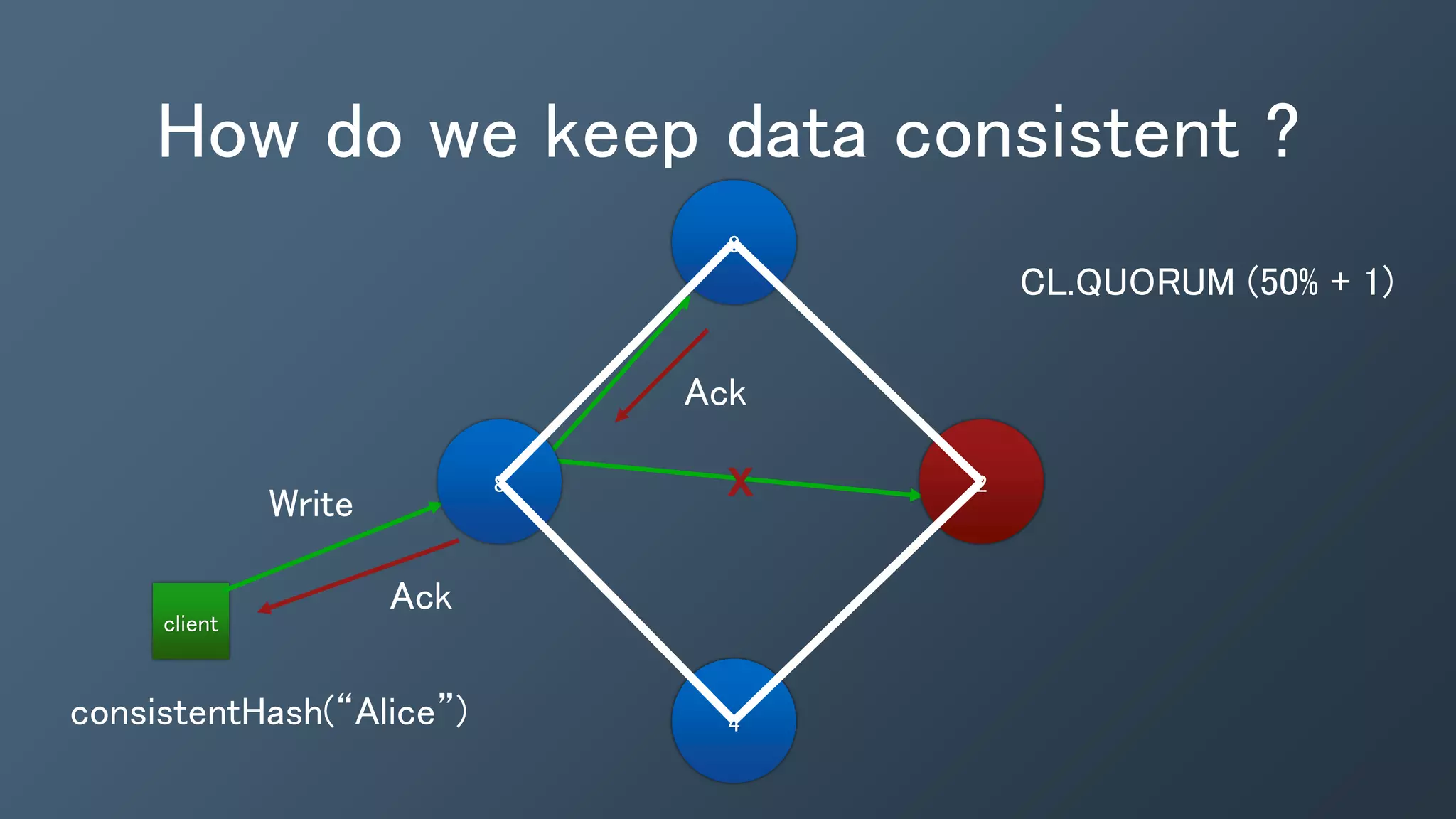
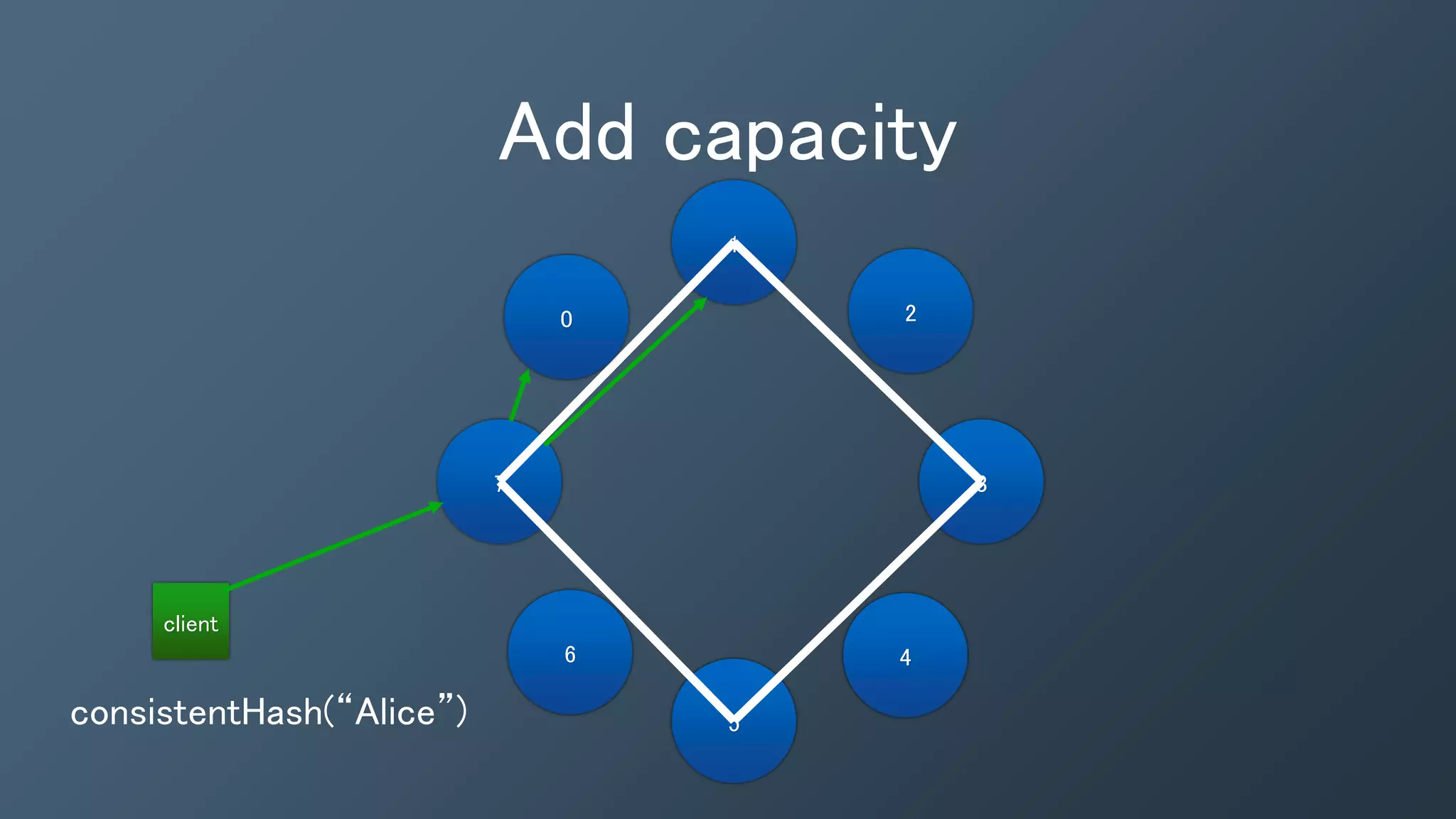
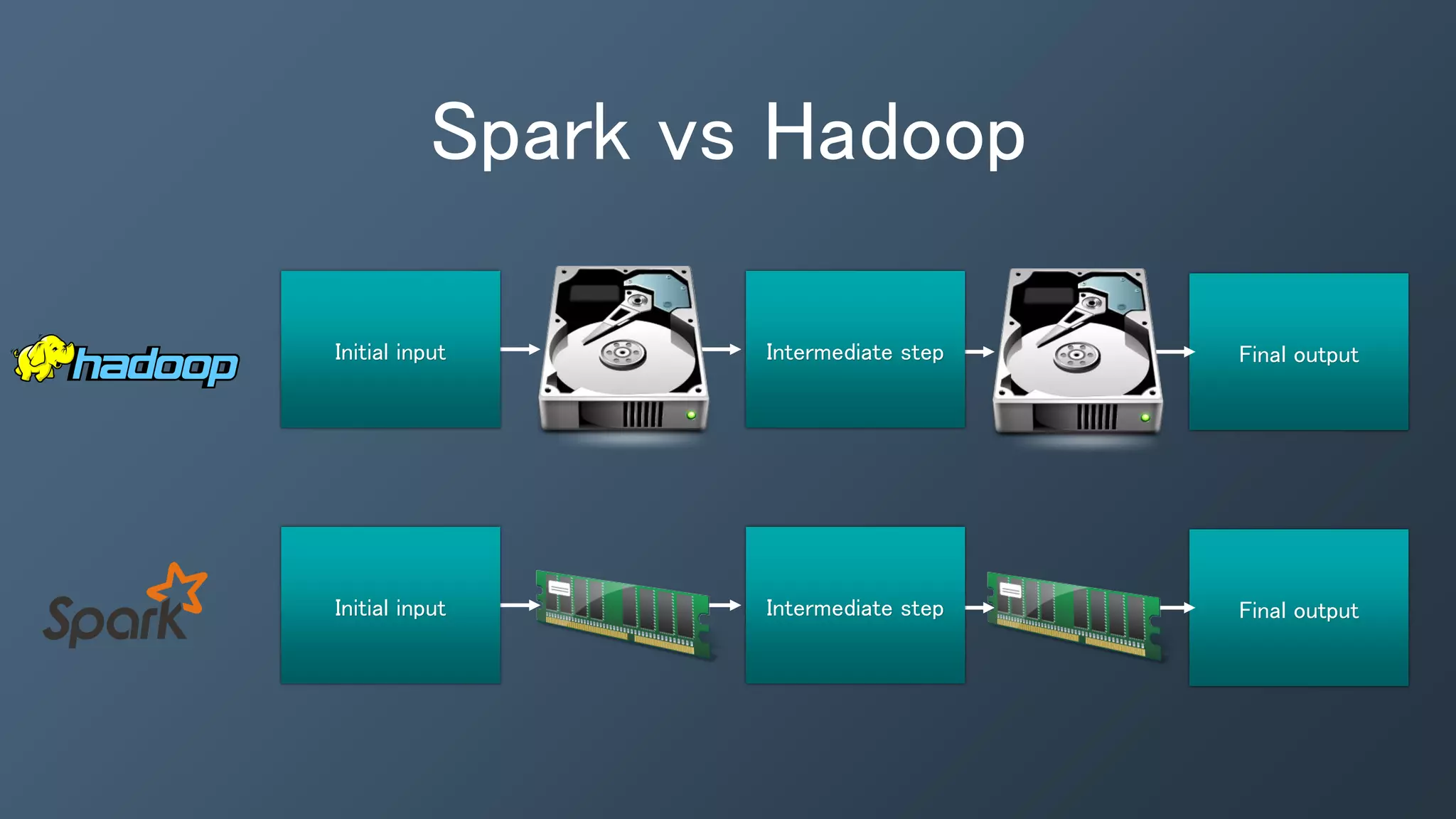
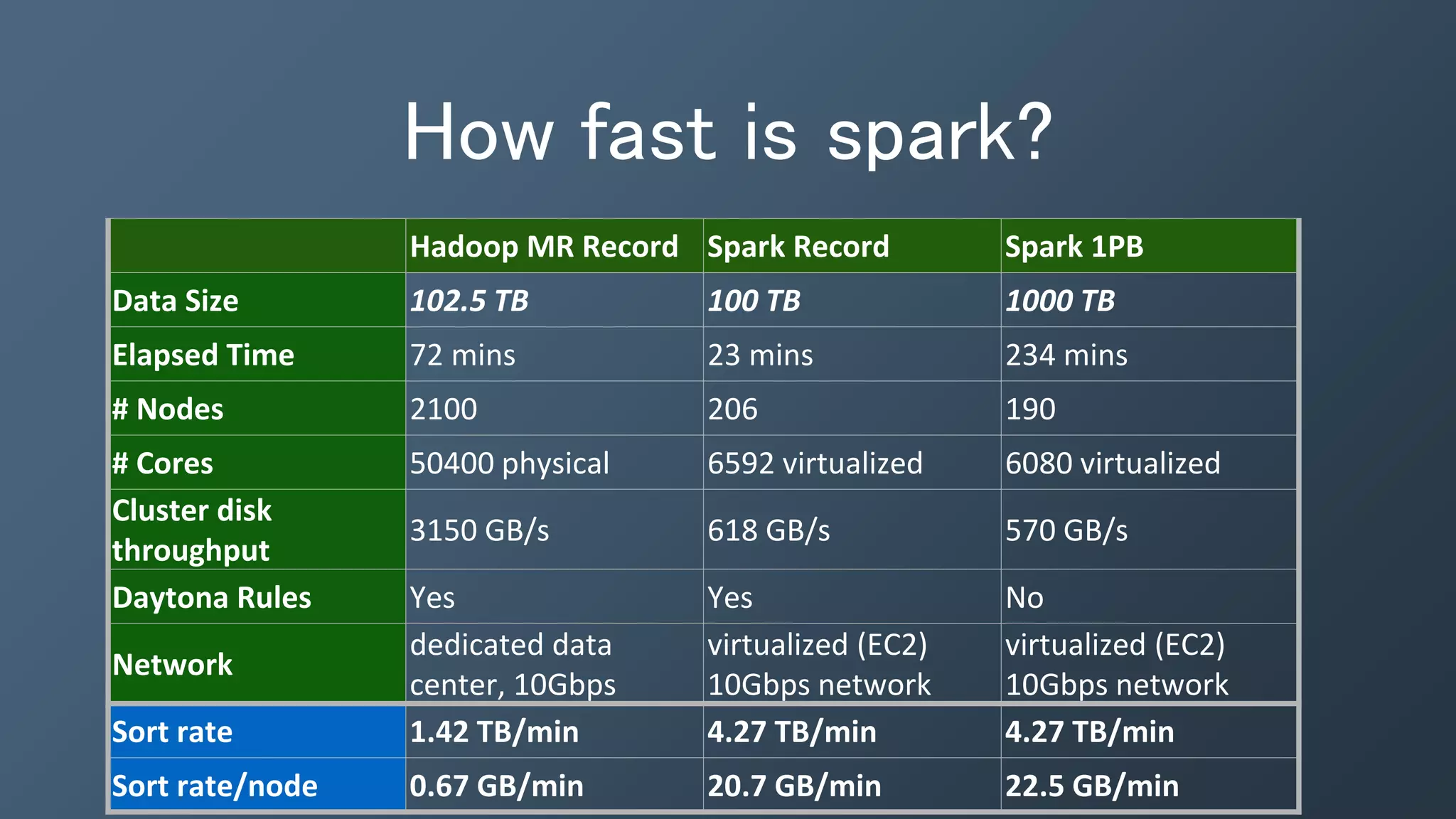
This document provides an introduction and overview of Kafka, Spark and Cassandra. It begins with introductions to each technology - Cassandra as a distributed database, Spark as a fast and general engine for large-scale data processing, and Kafka as a platform for building real-time data pipelines and streaming apps. It then discusses how these three technologies can be used together to build a complete data pipeline for ingesting, processing and analyzing large volumes of streaming data in real-time while storing the results in Cassandra for fast querying.















![Spark
Hadoop word count
public class WordCount {
public static class TokenizerMapper extends
Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>
{
private final static IntWritable one =
new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value,
Context context)
throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new
StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class IntSumReducer extends
Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text,
IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new
IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key,
Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new
Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new
GenericOptionsParser(conf, args)
.getRemainingArgs();
Job job = new Job(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new
Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new
Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true)
? 0 : 1);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kafka-spark-cassandra-webinar-feb-16-2016-160216235246/75/Kafka-spark-cassandra-webinar-feb-16-2016-27-2048.jpg)
![Spark
public class WordCount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JavaRDD<String> textFile = spark.textFile("hdfs://...");
JavaRDD<String> words = textFile.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() {
public Iterable<String> call(String s) { return Arrays.asList(s.split(" ")); }
});
JavaPairRDD<String, Integer> pairs = words.mapToPair(new PairFunction<String, String, Integer>() {
public Tuple2<String, Integer> call(String s) { return new Tuple2<String, Integer>(s, 1); }
});
JavaPairRDD<String, Integer> counts = pairs.reduceByKey(new Function2<Integer, Integer, Integer>() {
public Integer call(Integer a, Integer b) { return a + b; }
});
counts.saveAsTextFile(“hdfs://...");
}
}
Spark word count](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kafka-spark-cassandra-webinar-feb-16-2016-160216235246/75/Kafka-spark-cassandra-webinar-feb-16-2016-28-2048.jpg)