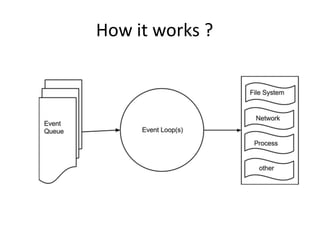
Javascript uses an event loop model to perform asynchronous operations even though it is single-threaded. Callbacks are used to handle asynchronous operations but can make code complex. Promises were introduced to simplify asynchronous code. A Promise represents the eventual completion (or failure) of an asynchronous operation, and allows consuming code to define callbacks instead of nesting callbacks. Promises are constructed by calling new Promise(), which takes a resolver function with resolve and reject parameters. The state of a Promise can be pending, fulfilled, or rejected.


![First-class functions
function sqr(x) {
return x * x; }
// a function may be assigned to a variable
var func = sqr;
// a function may have properties or be a property
func.doubleMe = function (x) {
return x + x;
};
// a function may be used as a parameter
[1, 2, 3].map(func.doubleMe); OR
[1, 2, 3].map(func);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jspromises-140304044613-phpapp01/85/Java-Script-Promise-3-320.jpg)