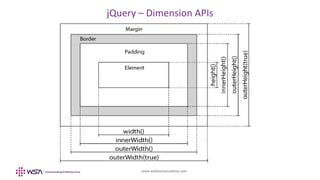
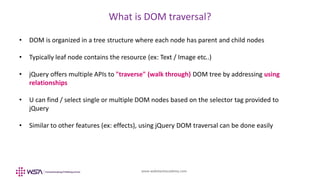
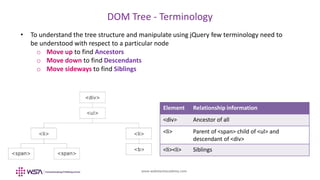
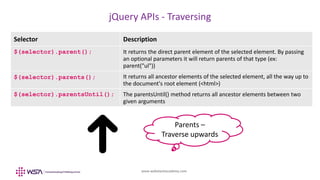
The document provides an overview of jQuery and its use for manipulating the Document Object Model (DOM). It details various jQuery methods for accessing, modifying, and traversing DOM elements, as well as handling styles and dimensions. Example code snippets illustrate how to implement these methods in practice, showcasing functionalities like inserting and removing elements, obtaining dimensions, and traversing parent, child, and sibling relationships.