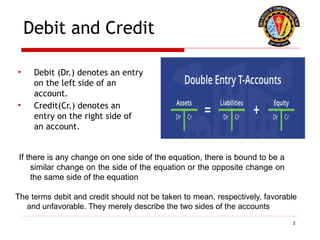
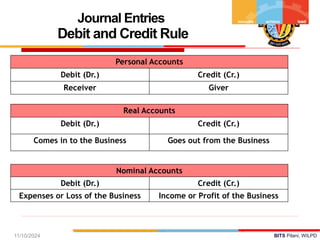
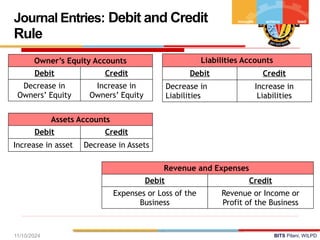
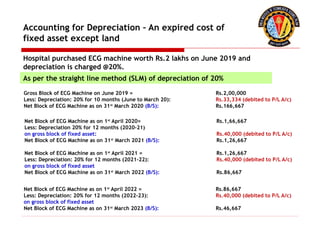
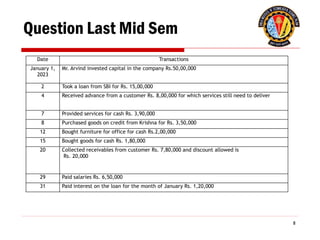
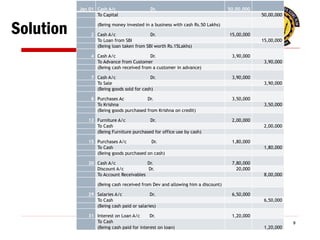
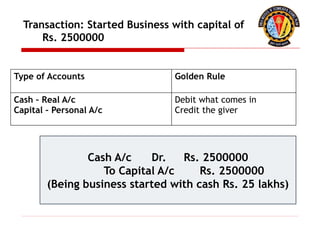
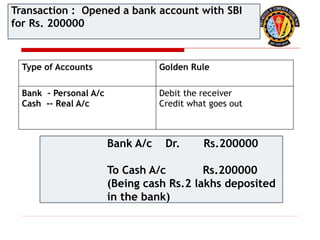
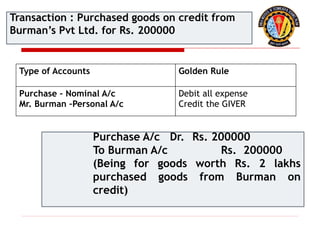
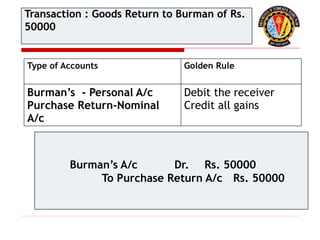
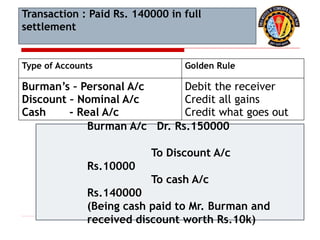
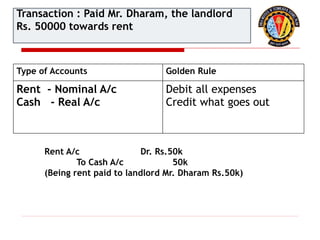
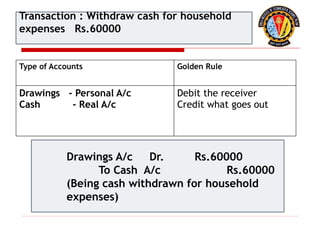
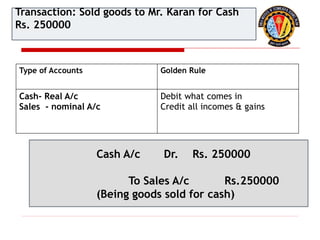
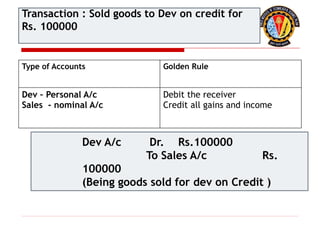
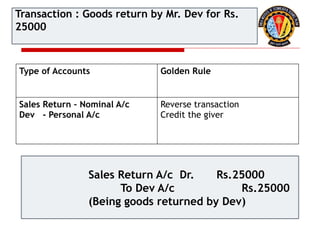
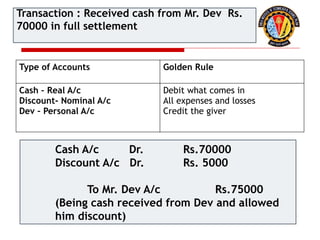
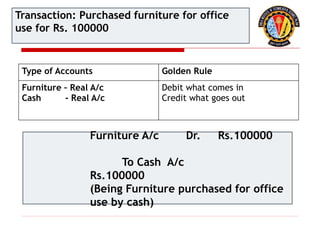
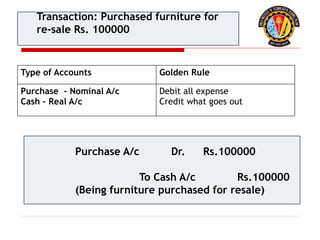
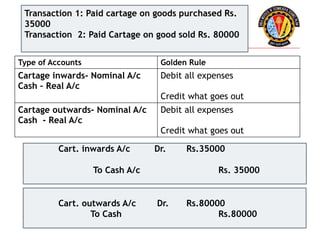
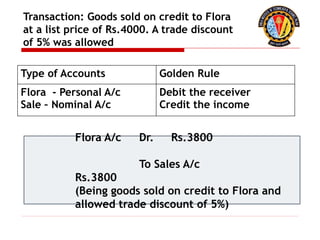
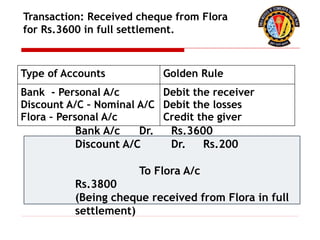
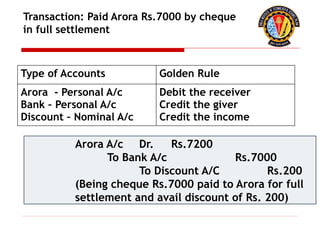
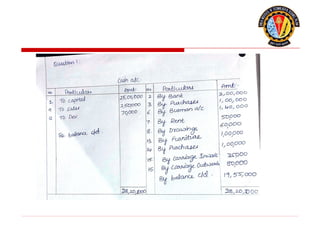
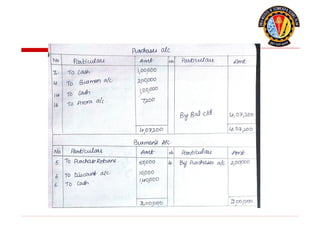
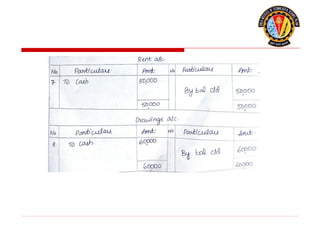
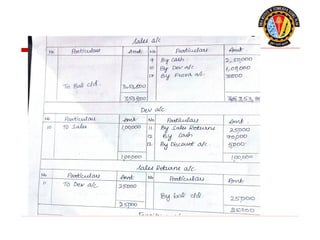
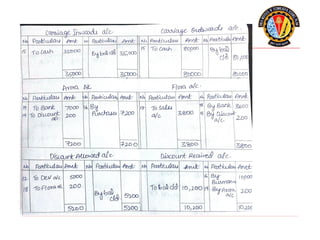
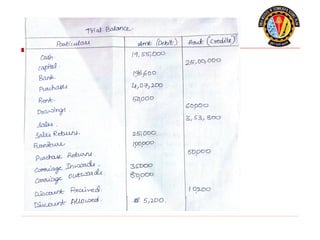
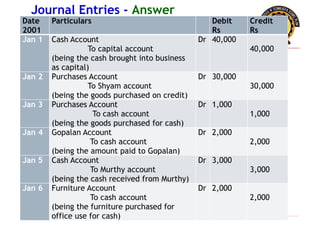
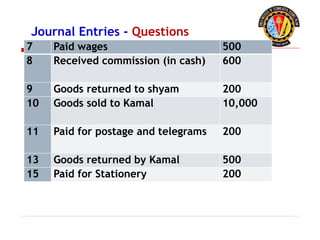
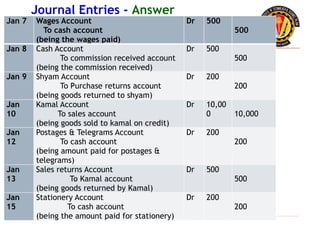
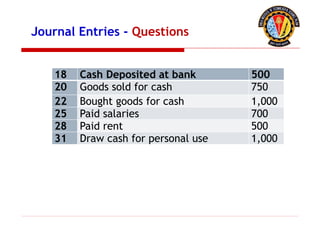
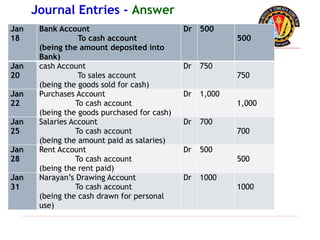
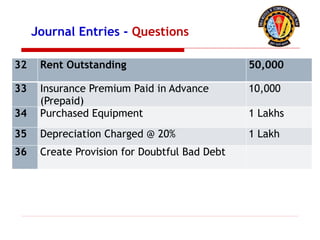
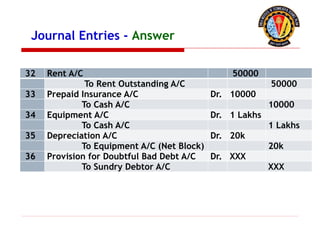
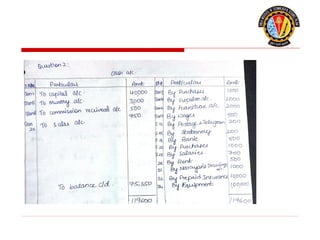
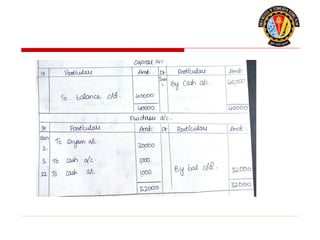
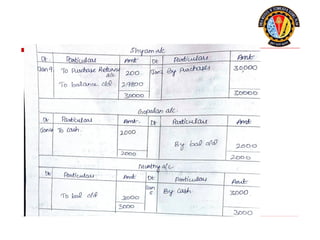
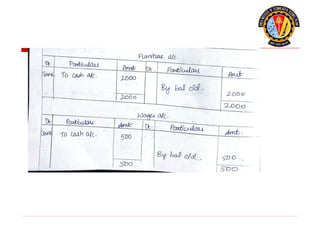
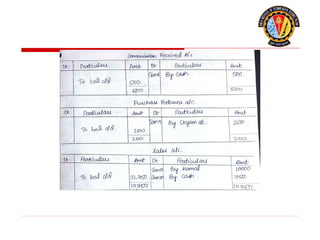
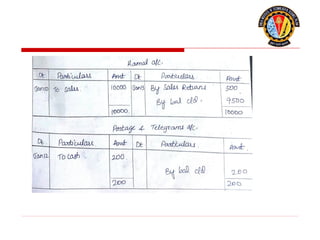
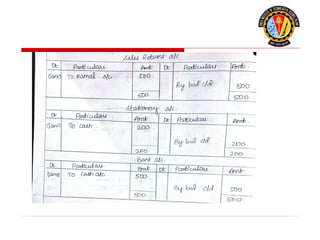
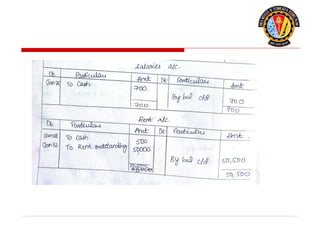
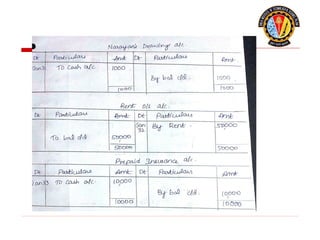
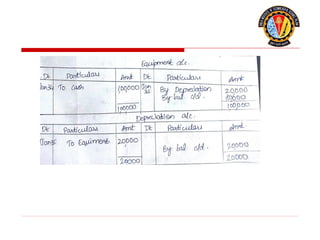
The document outlines the principles of debit and credit in accounting, illustrating how transactions are recorded in various types of accounts, such as personal, real, and nominal accounts. It explains the impact of transactions on assets, liabilities, and owner's equity, along with detailed journal entries for various business transactions. Additionally, the document provides examples of calculating depreciation and creating provisions for doubtful debts, emphasizing the importance of accurate bookkeeping.