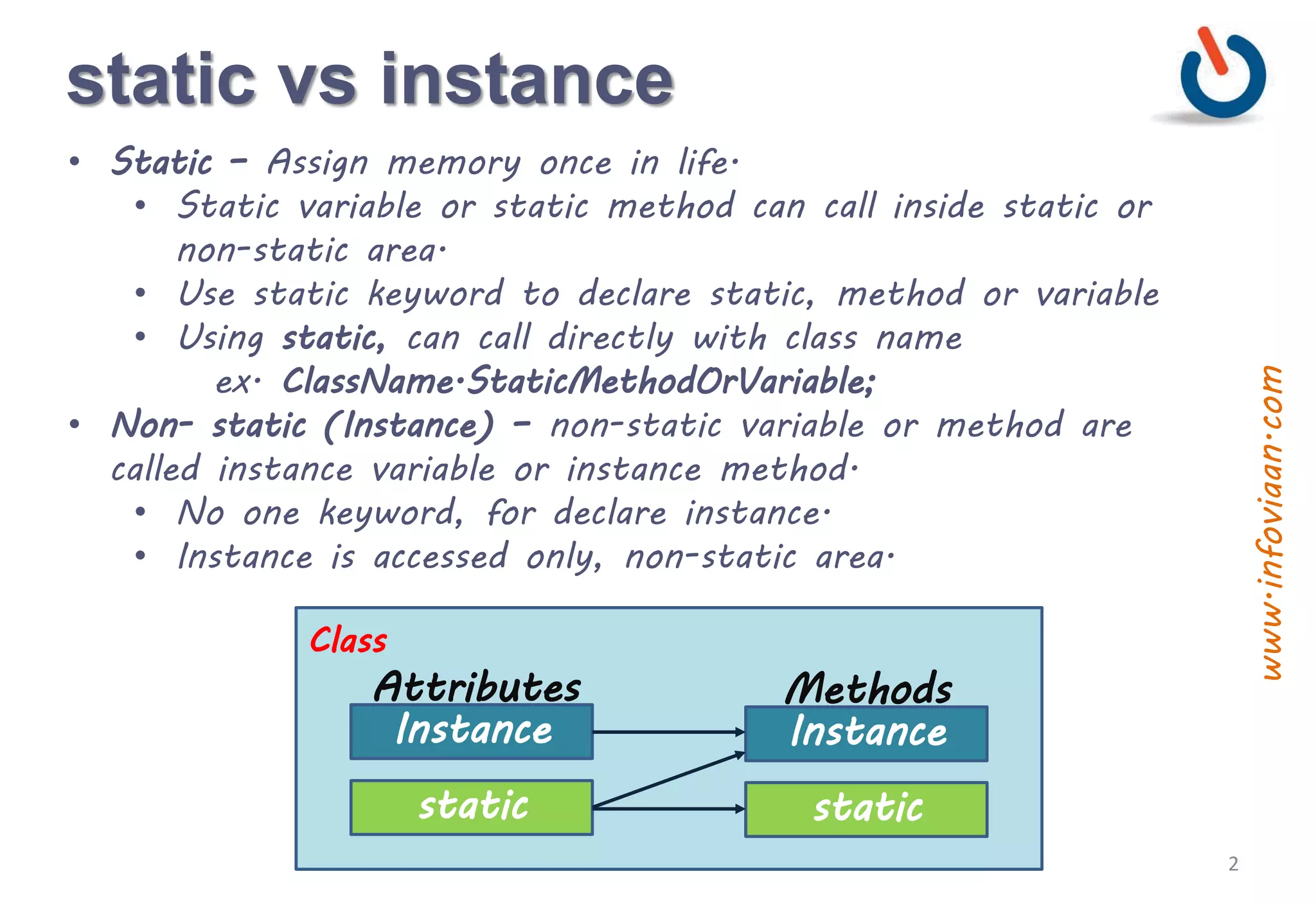
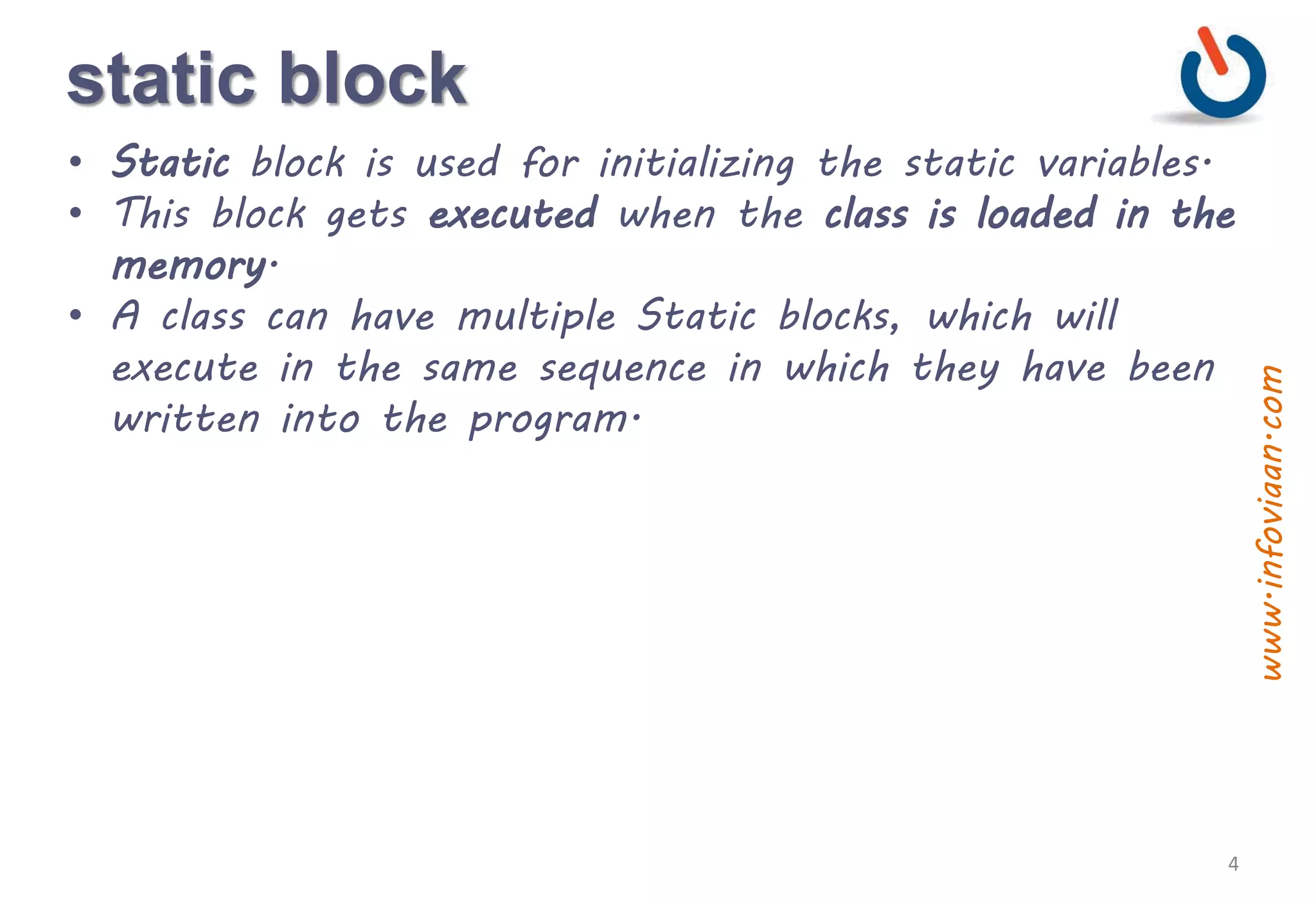
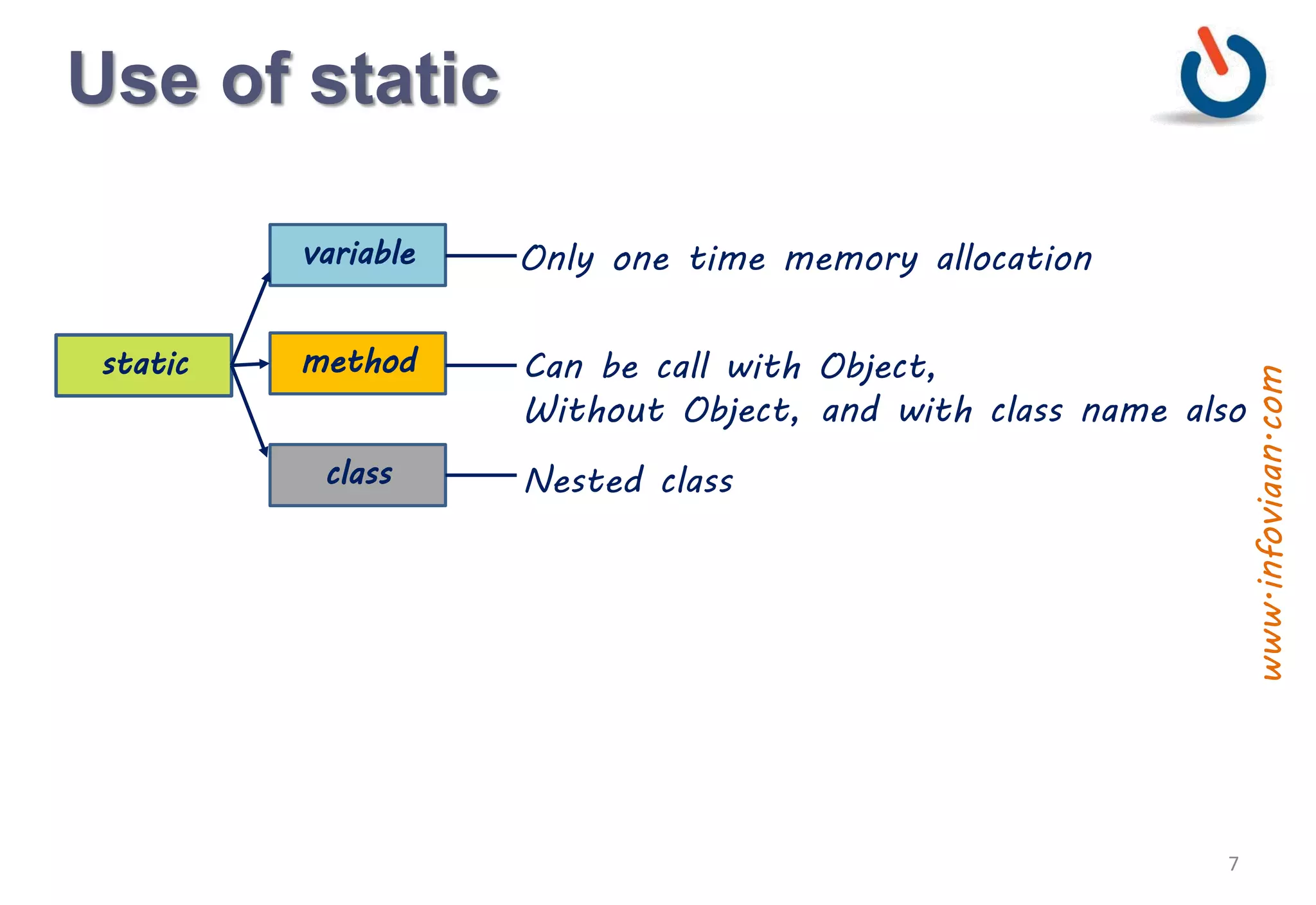
The document discusses static vs instance methods and variables in Java. Static methods and variables have a single copy associated with the class, while instance methods and variables are associated with each object. Static blocks allow initialization of static variables and run when the class is loaded. Static classes cannot be inherited and can only contain a static constructor. Methods are functions in object-oriented programming that perform operations on objects or classes.

![static with variable
public class StaticVariable{
static int x = 789; //static variable
String name = “Laddu”; //non-static (instance) variable
public static void main(String args[]) {
StaticVariable sv = new StaticVariable();
System.out.println(sv.x);
System.out.println(StaticVariable.x);
System.out.println(sv.name);
System.out.println(StaticVariable.name);
//Compile Time Error
}
}
3
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java6-functionmethodstatic-200323053848/75/Java-Method-Static-Block-3-2048.jpg)
![Program - static block
public class TestStaticBlock {
static int x = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(x+10 +" From Main Method");
}
static {
System.out.print(x + " From Static block n");
}
}
10 From Static block
20 From Main Method
// Executes before main method
// Executes After static block
5
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java6-functionmethodstatic-200323053848/75/Java-Method-Static-Block-5-2048.jpg)


![No Return value and No Arguments
void display( )
{
System.out.println(“Hello! This is Display method”);
}
static void sum()
{
int a,b,c; // Local variable
a = 45;
b = 35;
c = a + b;
System.out.println(“Sum Result is : ”+ c);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
sum(); //No CE, static method
display(); //Compilation error, method is not static
} 9
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java6-functionmethodstatic-200323053848/75/Java-Method-Static-Block-9-2048.jpg)
![No Return value with Arguments
public class MethodArgument{
static void info(int age, String name ) {
System.out.println(“Hello! My name is: ”+ name + “n My
age is: ”+ age);
}
void div(double x, int y){
double z = x/y;
System.out.println(“Division Result is: ”+ z);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
info(25, “Ramdev”);
MethodArgument obj; //object declaration
obj = new MethodArgument(); //object instantiation
obj.div(1123.50, 50); //method calling, used with
object
}
} 10
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java6-functionmethodstatic-200323053848/75/Java-Method-Static-Block-10-2048.jpg)
![Return Value but No Arguments
public class MethodReturn{
String info() {
String fullInfo = “Hello! My name is: Ramdev n My age
is: 60 ”
return fullInfo;
}
int multilply(){
int x=78, y=10;
return x*y;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
MethodReturn m = new MethodArgument();
String s = m.info();
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(“Result of Multiplication: ” +m.multiply());
}
} 11
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java6-functionmethodstatic-200323053848/75/Java-Method-Static-Block-11-2048.jpg)
![Return Value with Arguments
public class A {
double area(double radius){
return 3.1415*radius*radius;
}
String details(String name, String address, int age, double salary){
String complete = “Name is : ”+name + “n Age is :”+age + “n
Salary is : ”+ salary+ “n Address is: ”+address;
return complete;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
A a = new A();
A ob = new A();
System.out.println (“Area of Circle is : ” +a.area(2.5));
System.out.println (“Area of Circle is : ” +b.area(3.2));
System.out.println(a.details(“Mark jukerburg”, “USA”,
32, 36872782.8907));
}
} 12
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java6-functionmethodstatic-200323053848/75/Java-Method-Static-Block-12-2048.jpg)
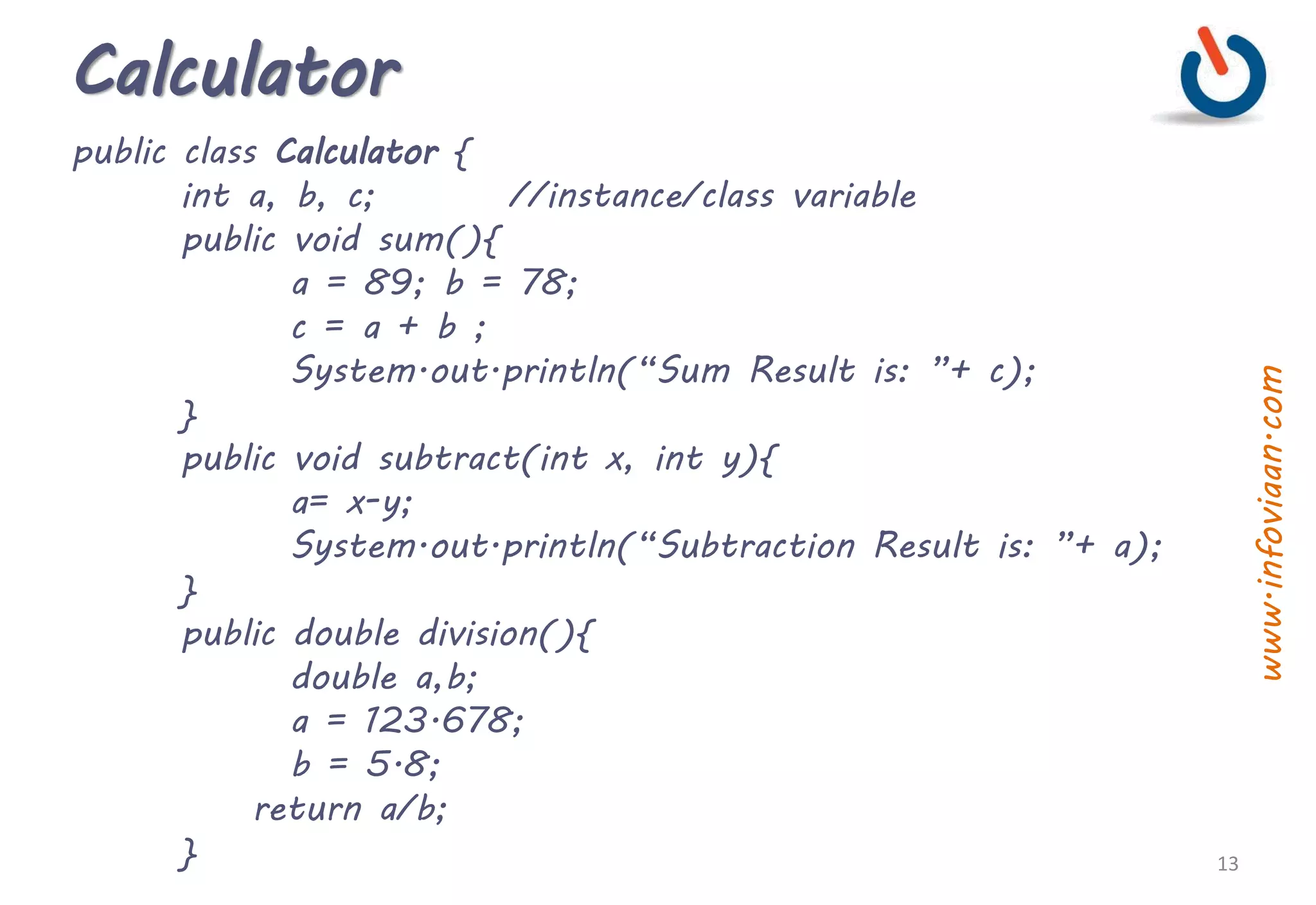
![Calculator cont.
public double multiply(double d1, double d2){
return d1*d2;
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Calculator obj = new Calculator();
int choice;
do{
System.out.println(“Enter a for Additionn Enter s for
Subtraction n Enter m for Multiplication n Enter d
for Division n Enter e for Exit ”);
choice = System.in.read();
switch(choice){
case ‘a’ : obj.sum(); break;
case ‘s’ : obj.subtract(356, 89 ); break;
case ‘d’ : System.out.println(“Division Result: ”+obj.div(); break;
case ‘m’: System.out.println(“Multiplication Result:
” + obj.multiply(123.34, 78.90); break;
case ‘e’: break; }
}while(choice!=‘e’);
}
} 14
www.infoviaan.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java6-functionmethodstatic-200323053848/75/Java-Method-Static-Block-14-2048.jpg)

