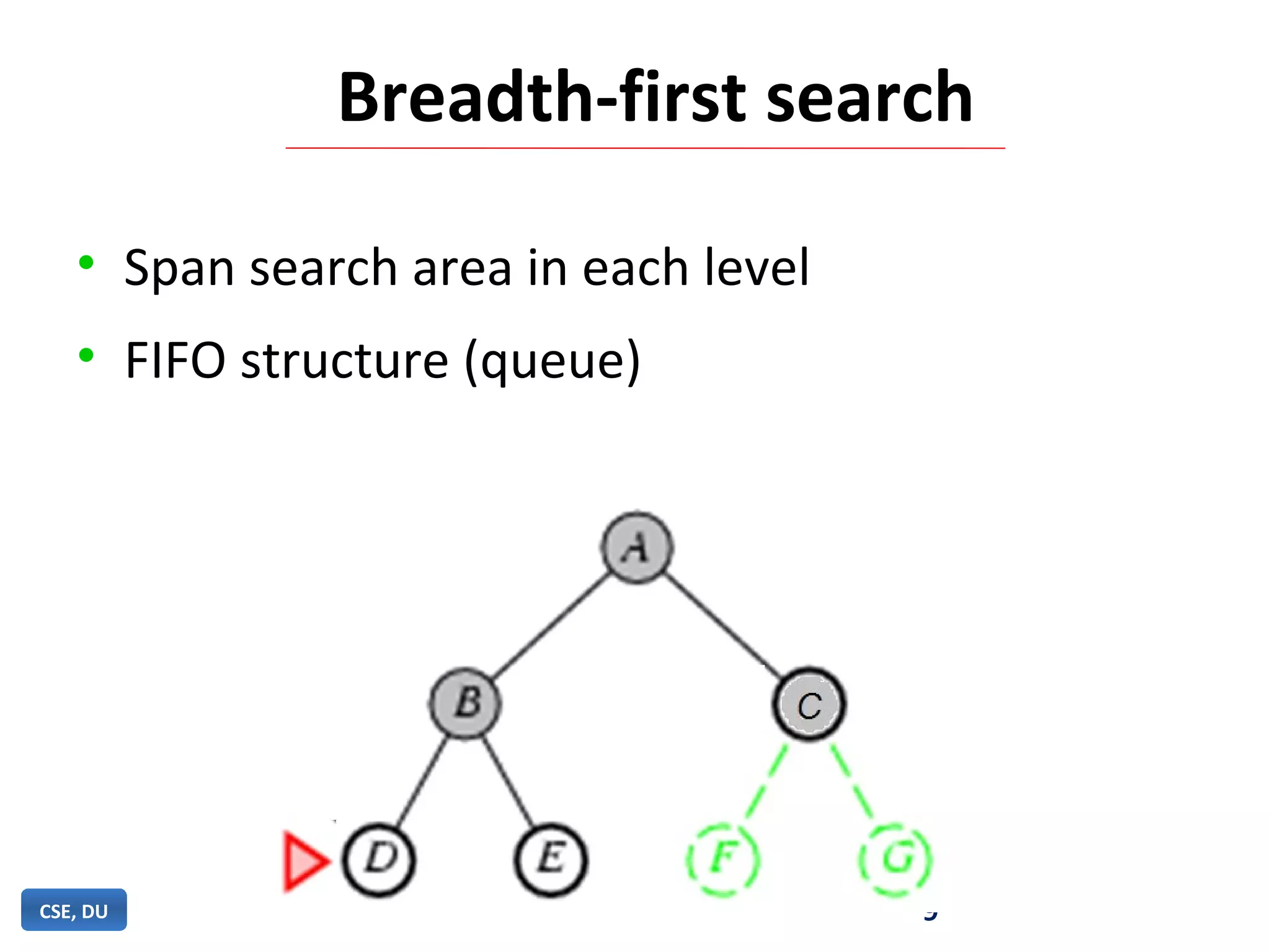
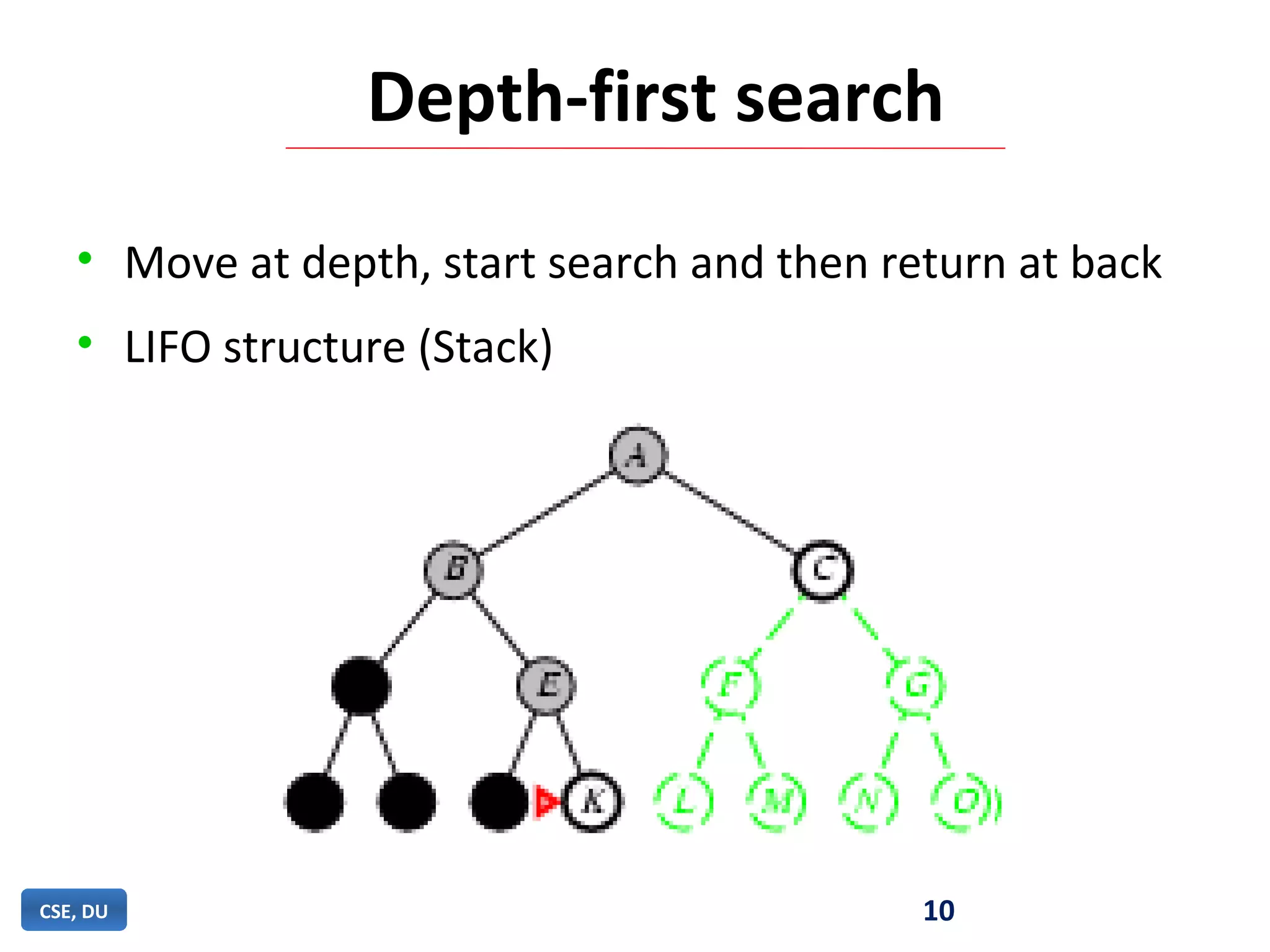
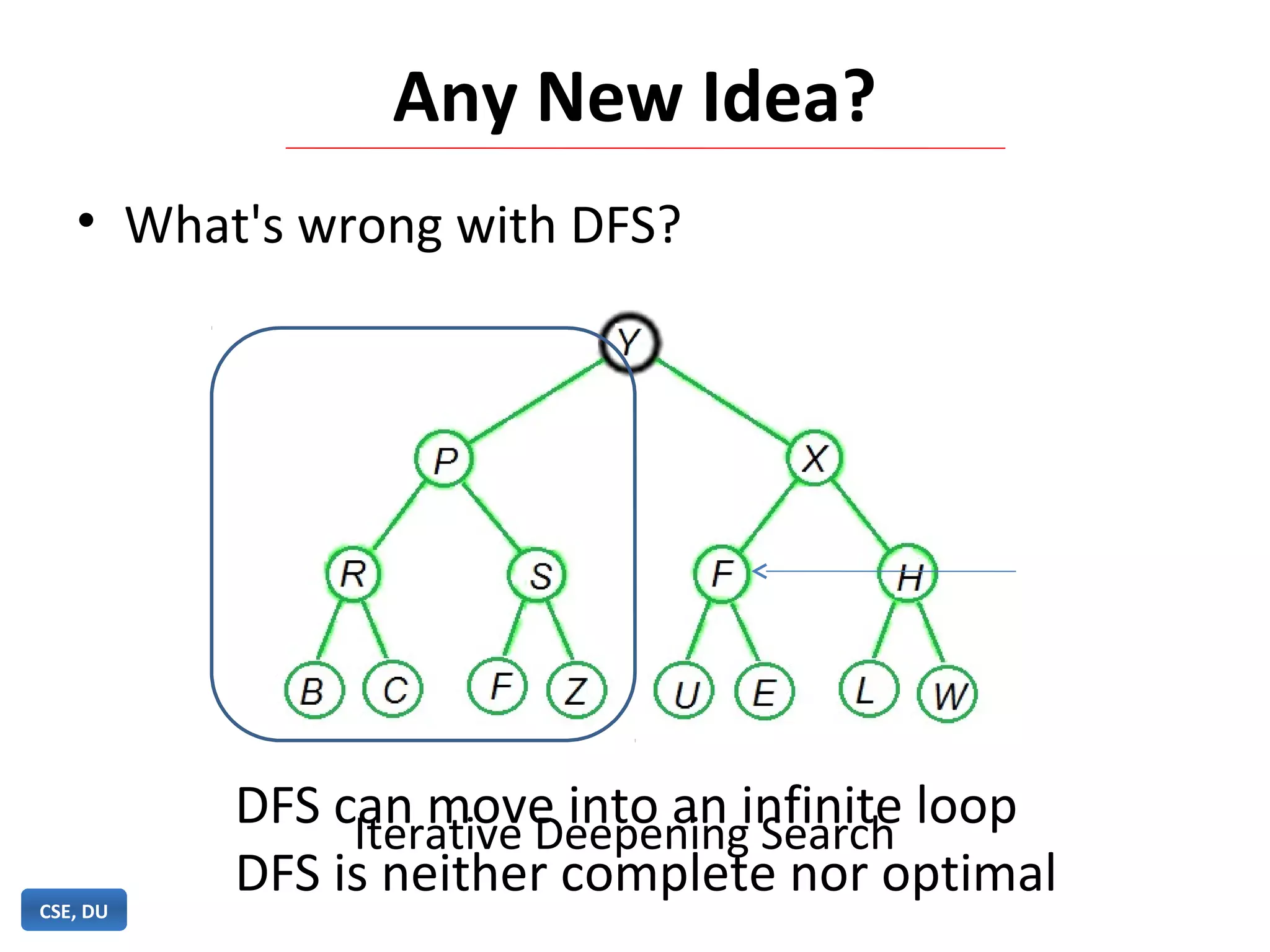
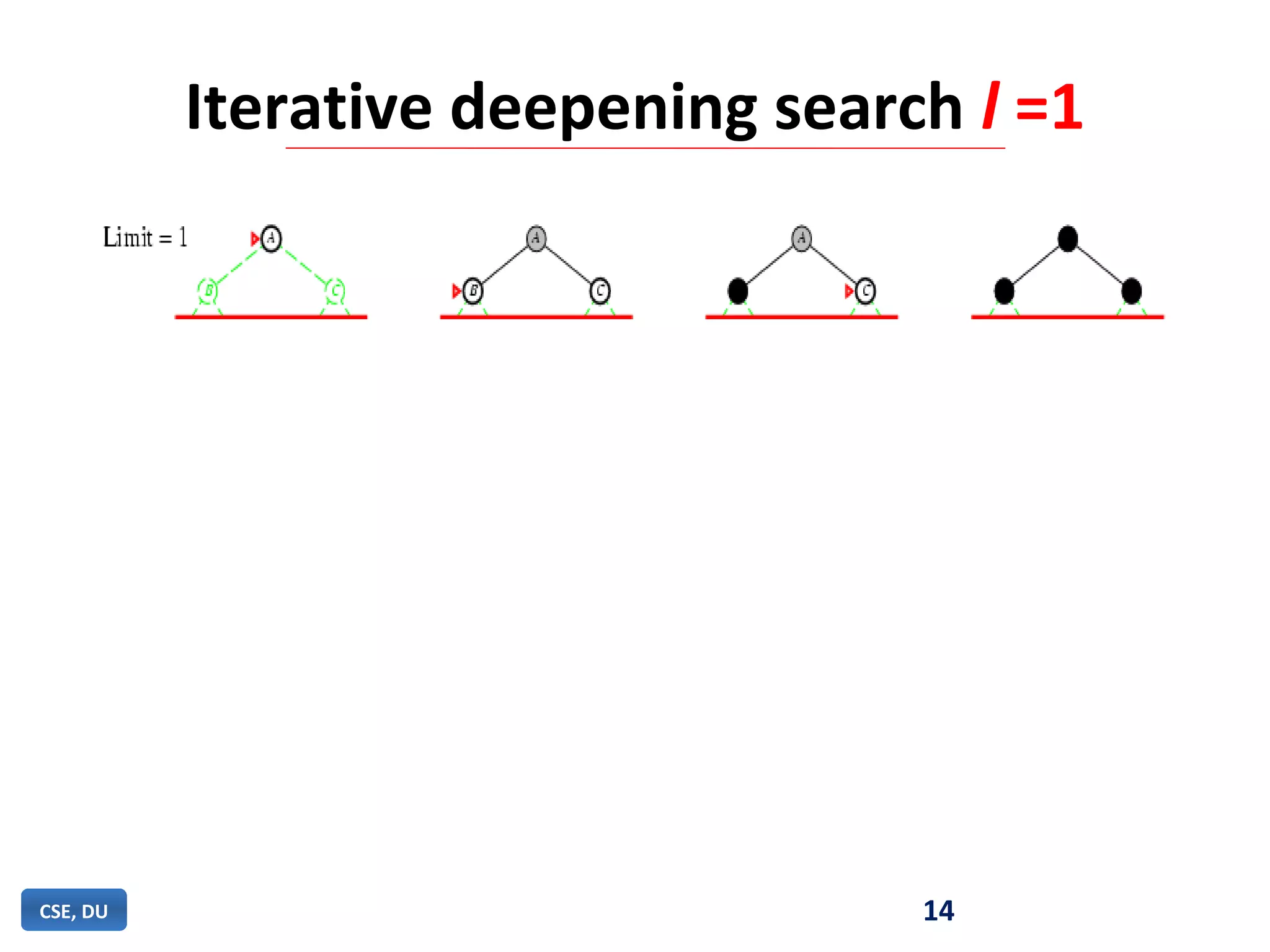
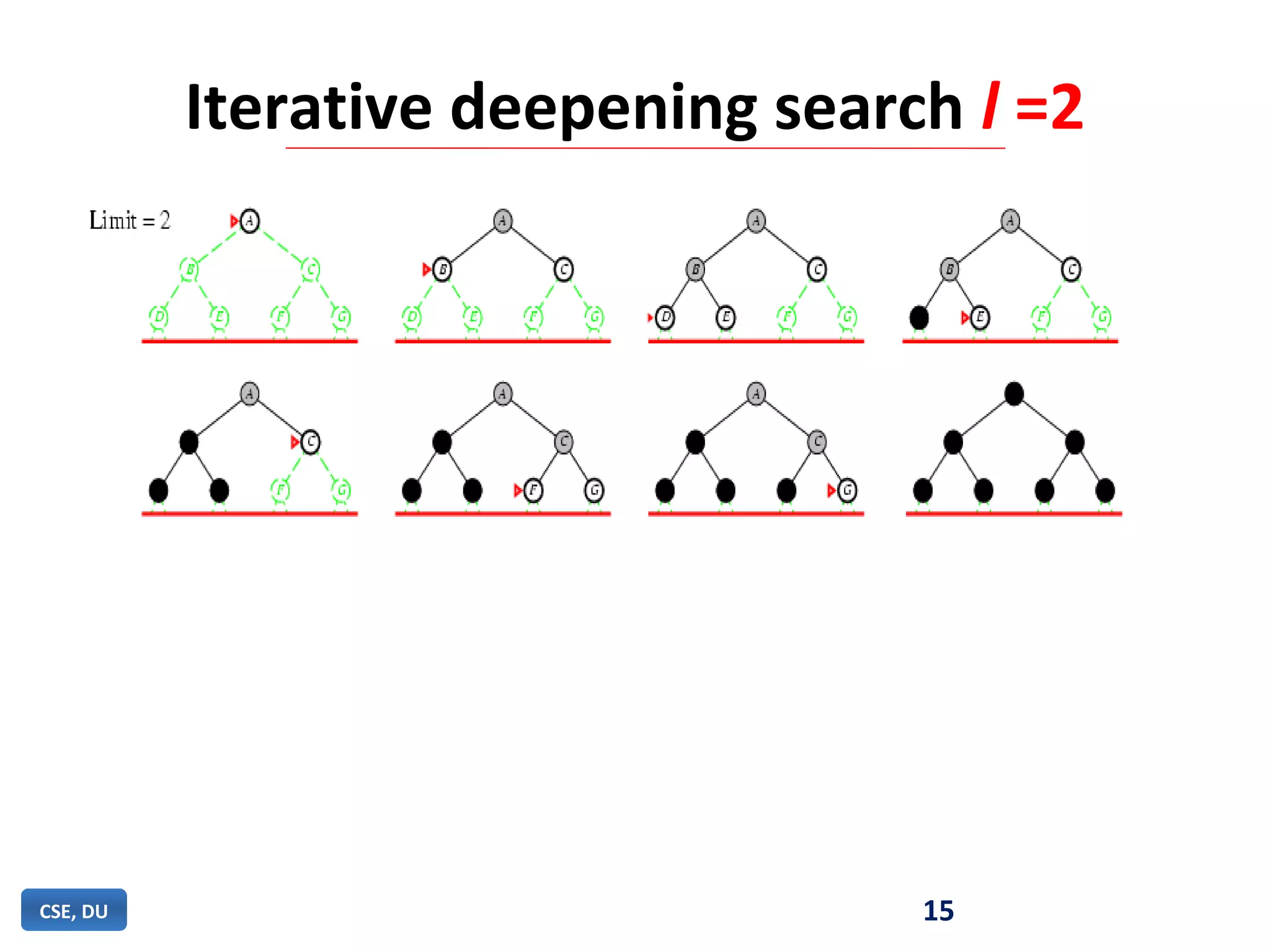
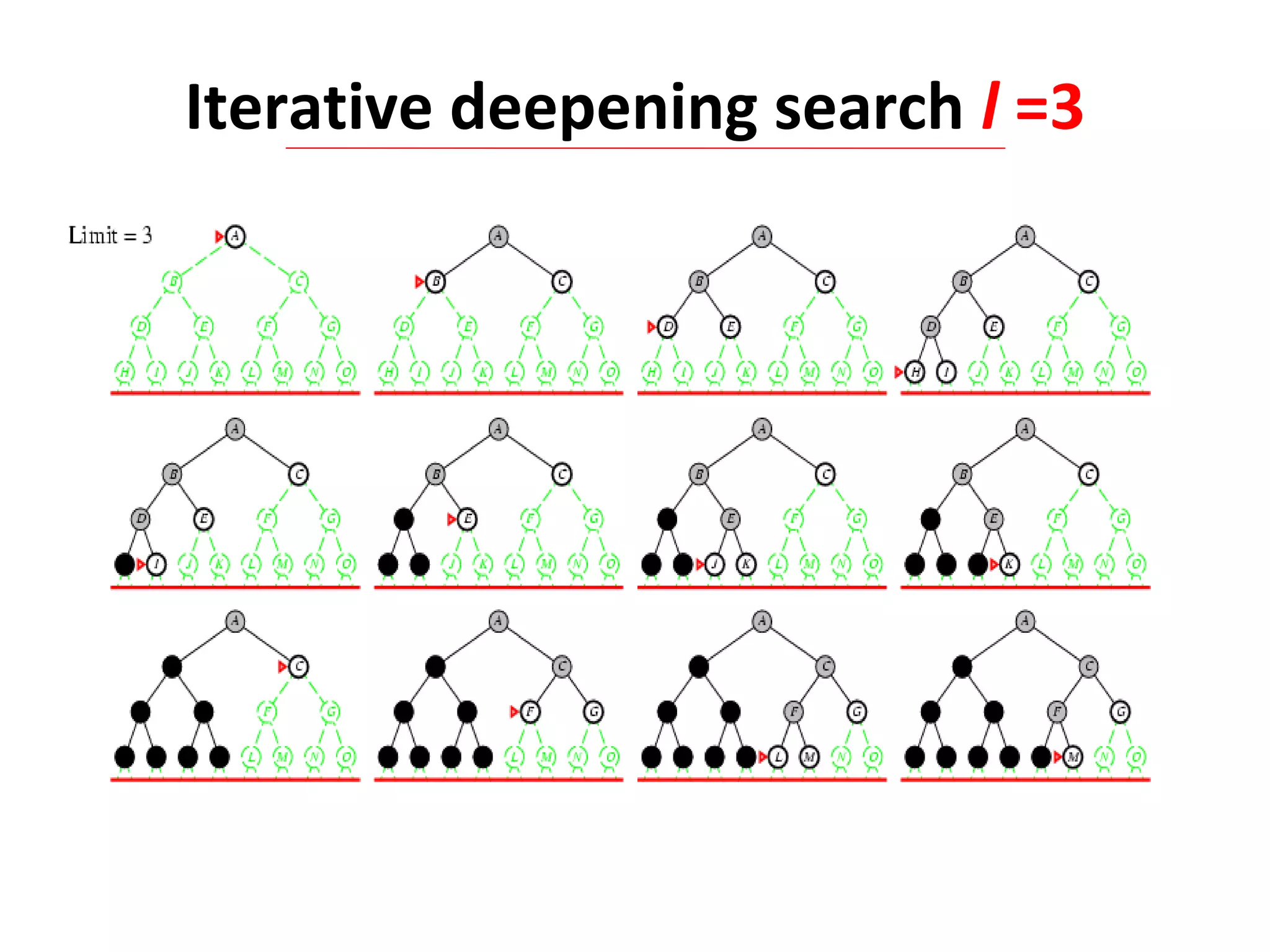
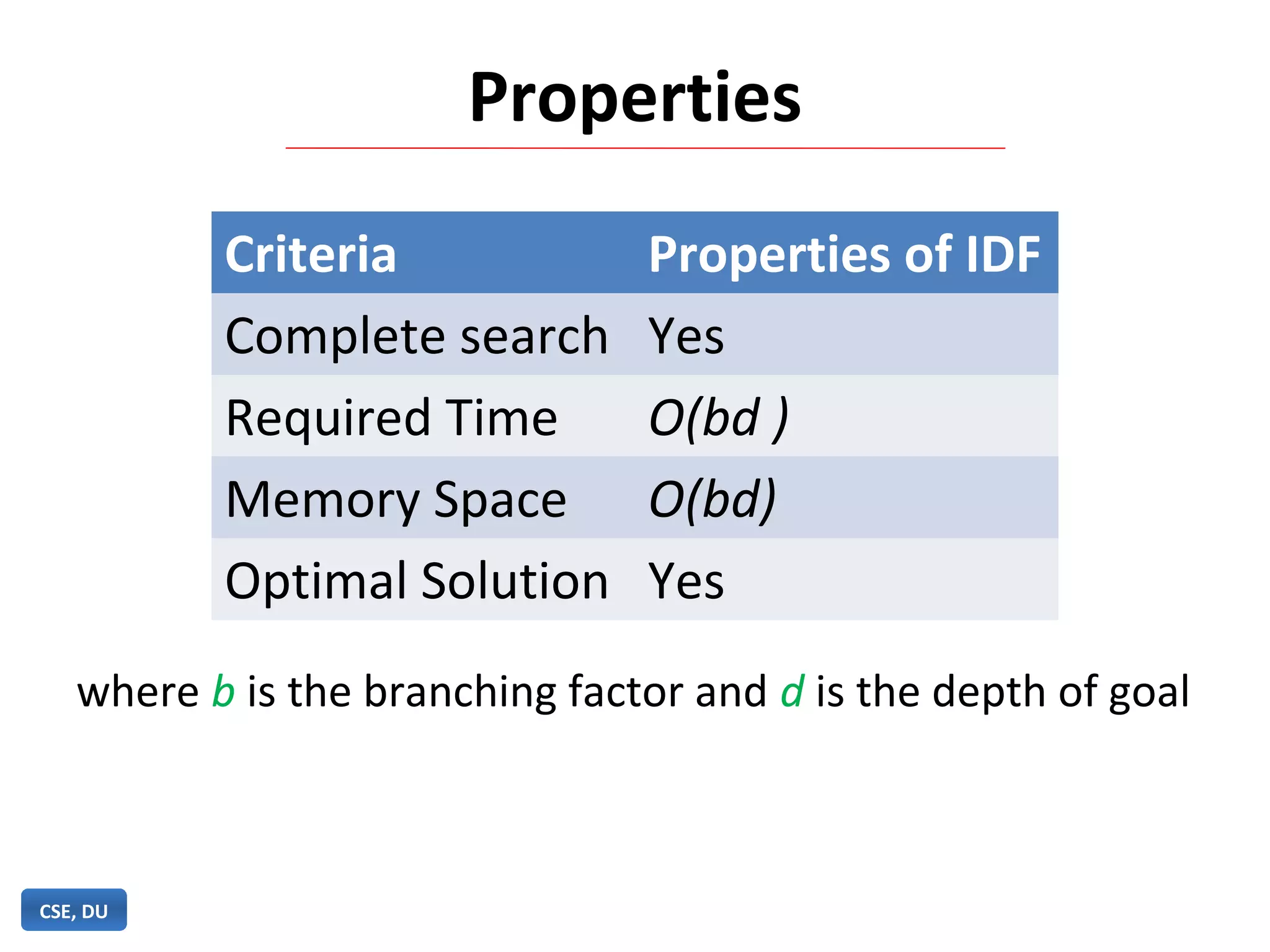
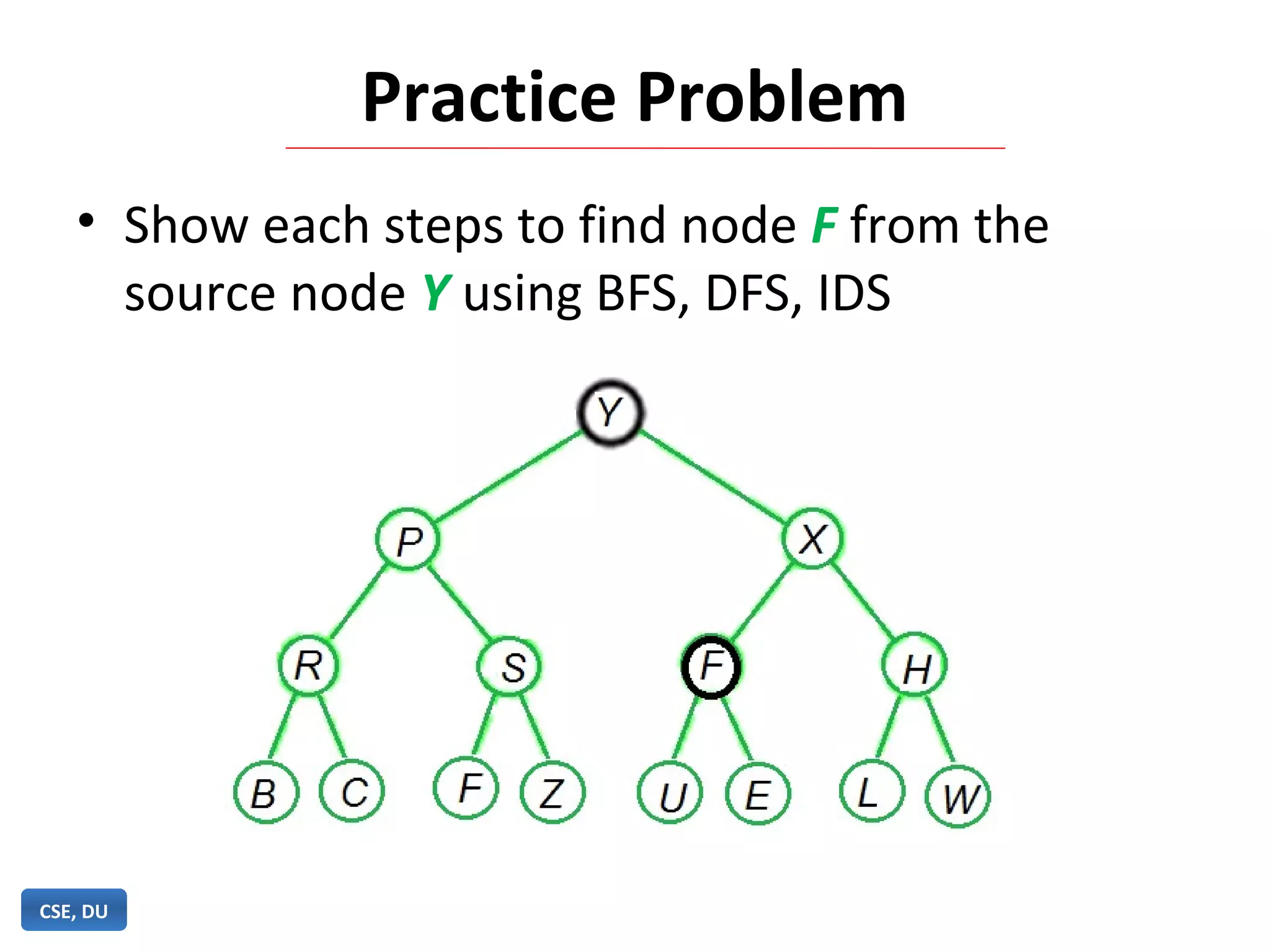
Iterative deepening search (IDS) is an algorithm that combines the completeness of breadth-first search with the memory efficiency of depth-first search. IDS performs an exhaustive depth-first search, increasing the depth limit by one each iteration, until the goal is found. IDS is guaranteed to find a solution if one exists, uses less memory than breadth-first search by limiting the depth of search at each iteration, and is more efficient than depth-first search which can get stuck in infinite loops.


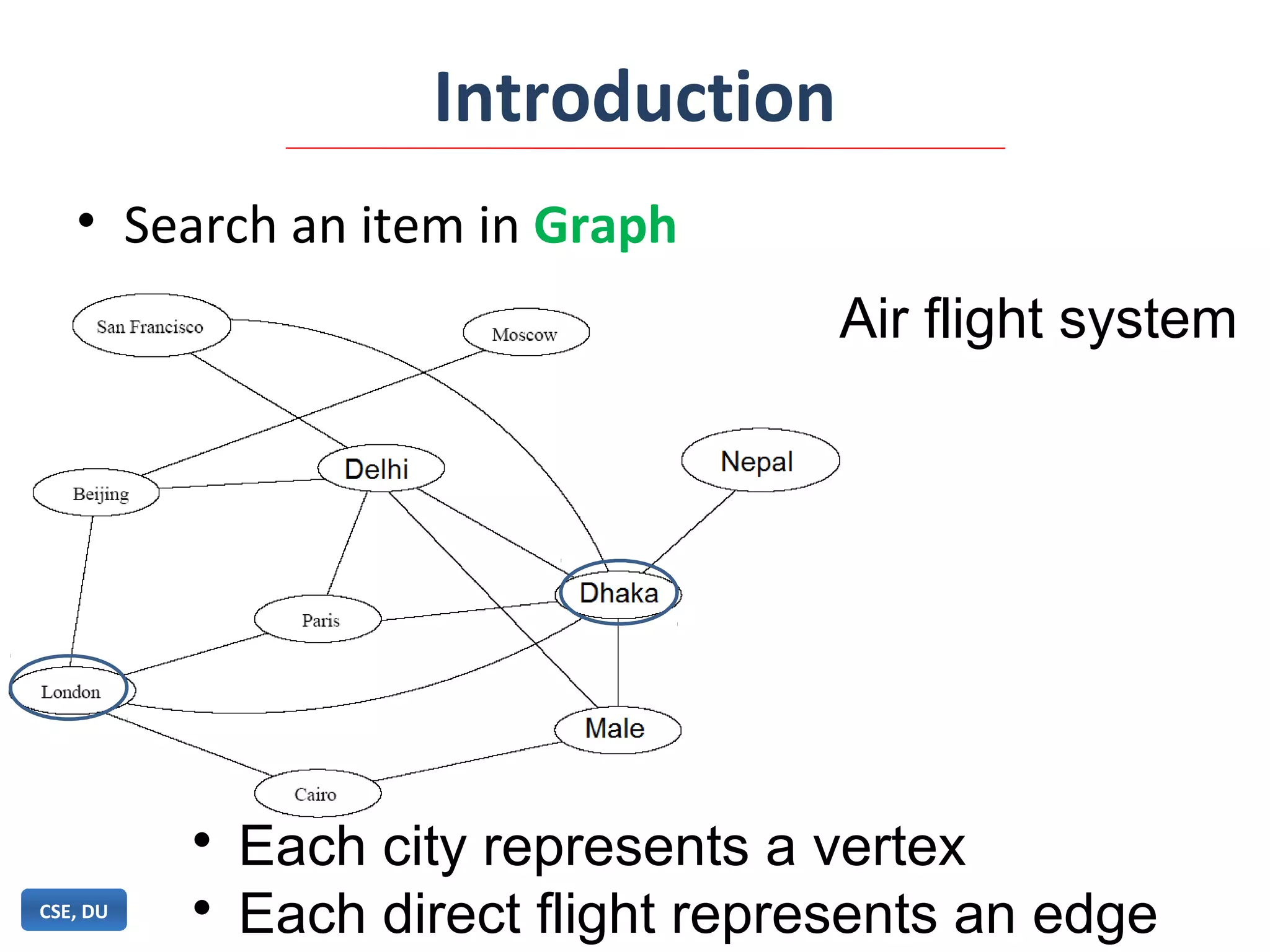
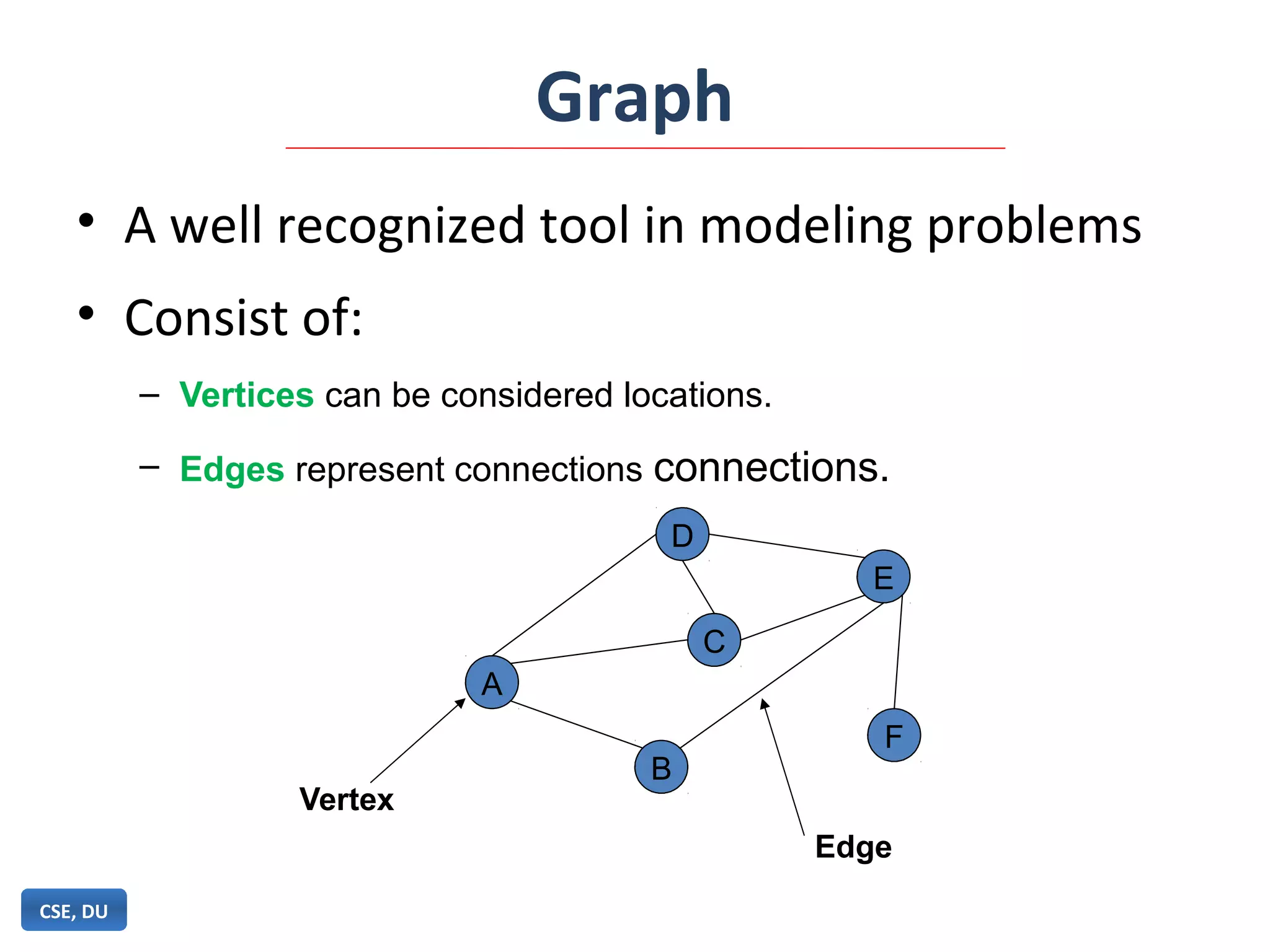
![Adjacency Matrix
A[i][j] = 1 if there is an edge connecting vertices i,j
A[i][j] = 0 otherwise
6CSE, DU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iterativedeepeningsearch-141221081041-conversion-gate01/75/Iterative-deepening-search-6-2048.jpg)
![Adjacency List
The adjacency list is an array A[0..n-1] of lists,
where n is the number of vertices in the graph
7CSE, DU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iterativedeepeningsearch-141221081041-conversion-gate01/75/Iterative-deepening-search-7-2048.jpg)