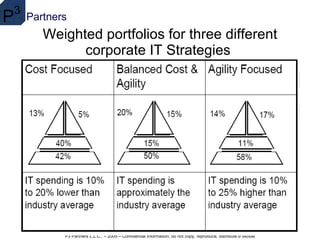
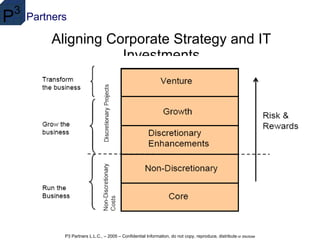
IT governance consists of leadership, organizational structures, processes and relationships to ensure IT supports business strategy and objectives. COBIT is an internationally accepted framework for IT controls that focuses on objectives rather than implementation. Internal controls aim to provide assurance for effective operations, reliable financial reporting, and compliance, and have five components: control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information/communication, and monitoring. Portfolio management tools are needed to align IT investments with business goals and strategies to maximize returns.