Ismanam2013 for cs_poster
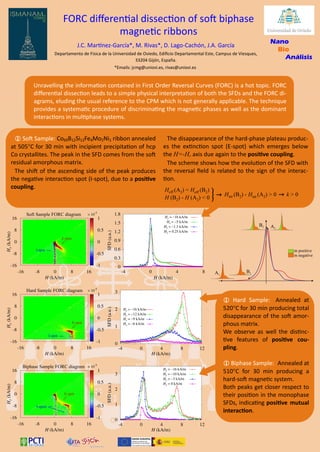
- 1. FORC differential dissection of soft biphase magnetic ribbons J.C. Martínez-García*, M. Rivas*, D. Lago-Cachón, J.A. García Departamento de Física de la Universidad de Oviedo, Edificio Departamental Este, Campus de Viesques, 33204 Gijón, España. *Emails: jcmg@uniovi.es, rivas@uniovi.es Unravelling the information contained in First Order Reversal Curves (FORC) is a hot topic. FORC differential dissection leads to a simple physical interpretation of both the SFDs and the FORC di- agrams, eluding the usual reference to the CPM which is not generally applicable. The technique provides a systematic procedure of discriminating the magnetic phases as well as the dominant interactions in multiphase systems. Soft Sample: Co69B12Si12Fe4Mo2Ni1 ribbon annealed at 505C for 30 min with incipient precipitation of hcp Co crystallites. The peak in the SFD comes from the soft residual amorphous matrix. The shift of the ascending side of the peak produces the negative interaction spot (I-spot), due to a positive coupling. The disappearance of the hard-phase plateau produc- es the extinction spot (E-spot) which emerges below the H=-Hr axis due again to the positive coupling. The scheme shows how the evolution of the SFD with the reversal field is related to the sign of the interac- tion. Nano Bio Análisis Hard Sample: Annealed at 520C for 30 min producing total disappearance of the soft amor- phous matrix. We observe as well the distinc- tive features of positive cou- pling. Biphase Sample: Annealed at 510C for 30 min producing a hard-soft magnetic system. Both peaks get closer respect to their position in the monophase SFDs, indicating positive mutual interaction. Soft Sample FORC diagram Hard Sample FORC diagram Biphase Sample FORC diagram I-spot E-spot I-spot E-spot I-spots E-spot
