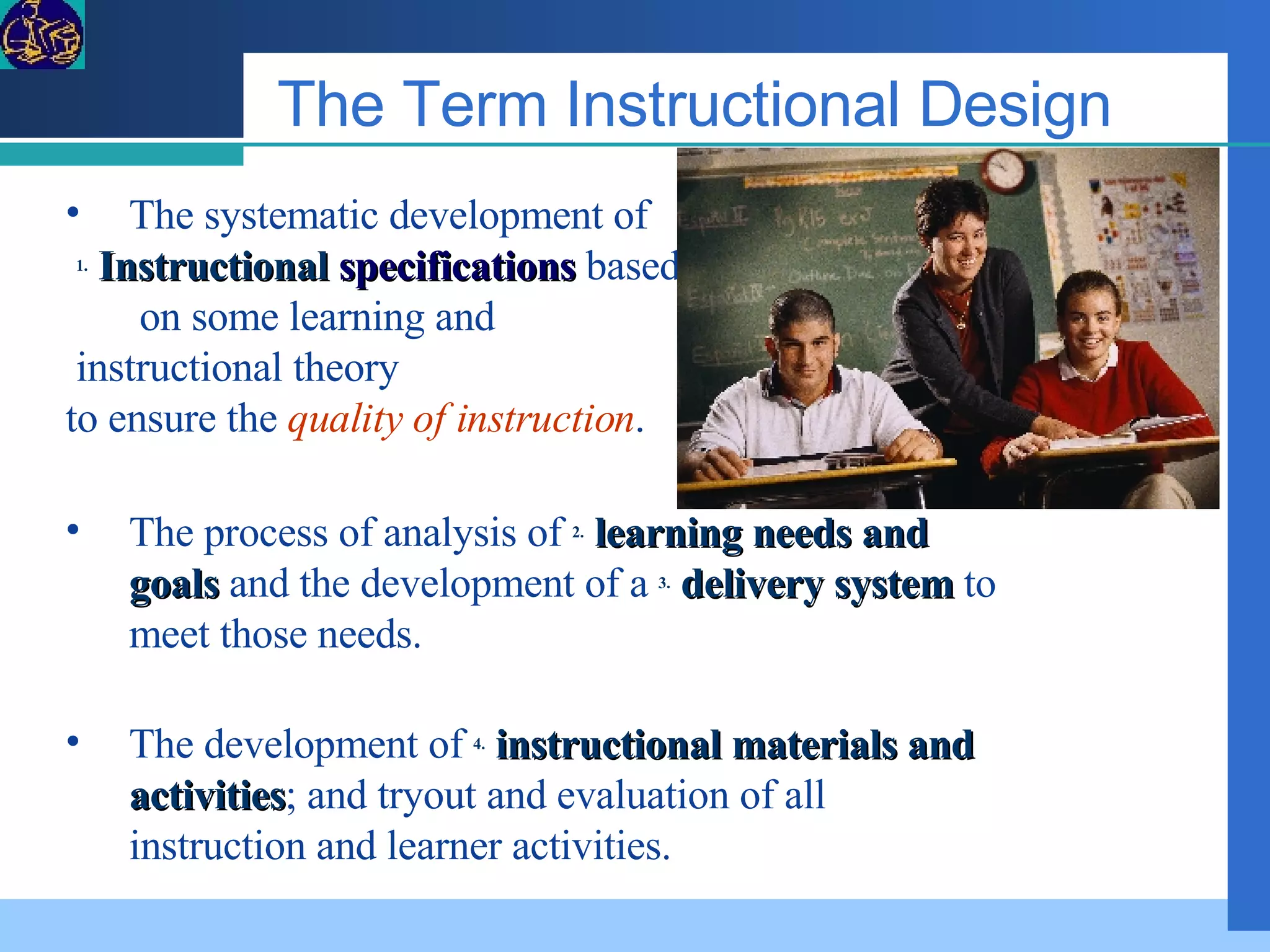
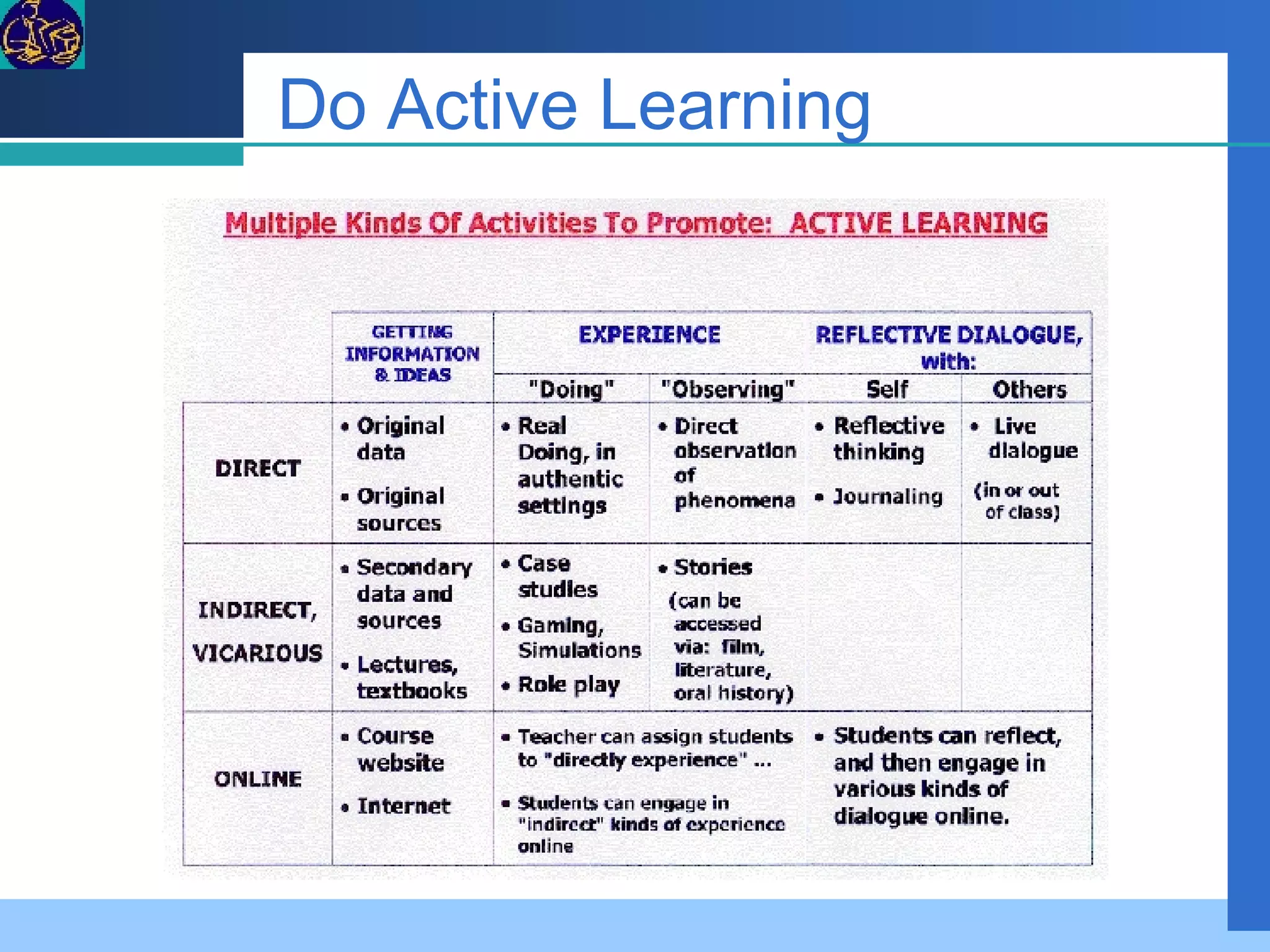
The document provides an overview of a 5-day teacher training workshop on implementing e-learning. It discusses instructional design principles and models, e-learning modalities, open source software, building an online learning platform, and evaluating online content. The objectives are to define common terms and processes for e-learning, build understanding of instructional design, and guide teachers in designing an online course web board and publishing web pages.