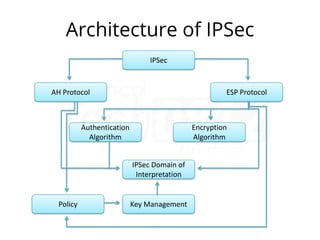
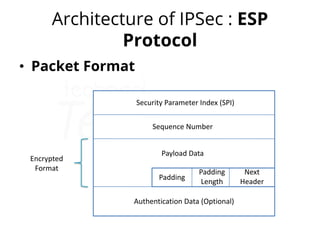
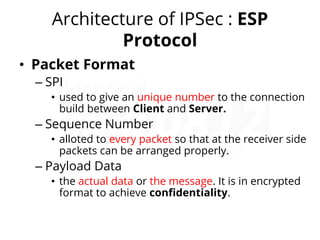
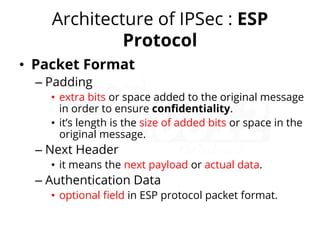
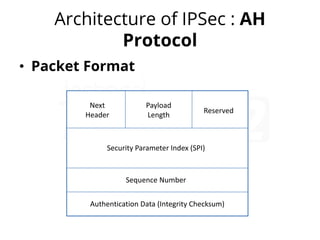
IPsec (IP Security) is a framework used to secure IP traffic by providing confidentiality, integrity, and authentication through various protocols and algorithms. It employs encryption methods like AES and DES, hashing protocols like MD5 and SHA, and authentication techniques such as RSA digital signatures and pre-shared keys. The architecture of IPsec includes protocols like AH (Authentication Header) and ESP (Encapsulation Security Payload) for ensuring data security during transmission.