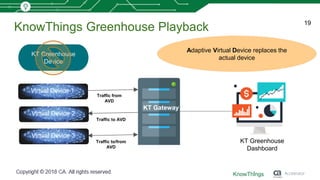
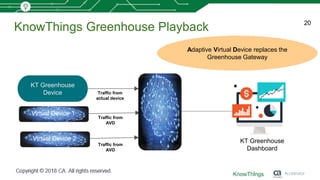
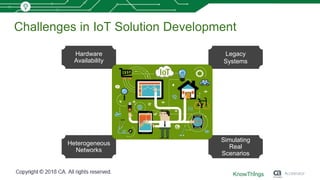
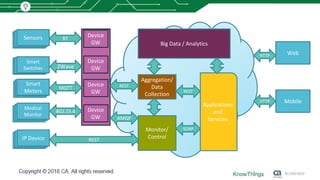
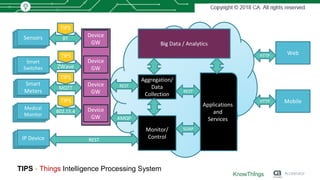
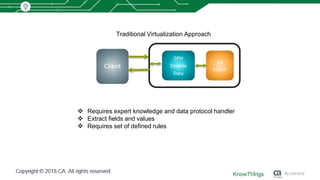
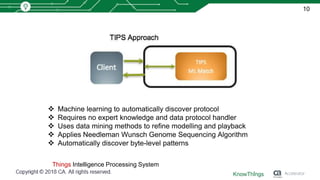
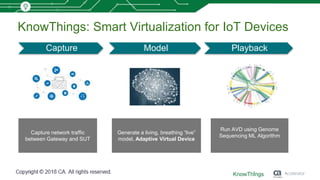
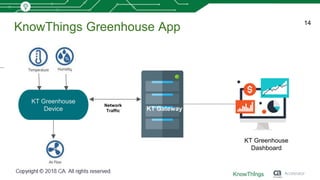
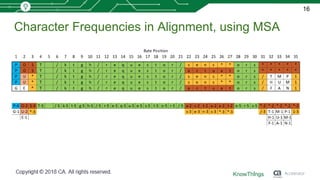
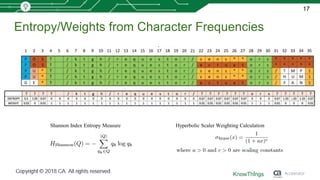
This document discusses using machine learning for IoT device virtualization. It outlines challenges with IoT application development like hardware availability and simulating real scenarios. It then describes how KnowThings uses machine learning to automatically discover data protocols from network traffic and generate adaptive virtual devices without expert knowledge. Their solution captures traffic, generates a "living" model using genome sequencing algorithms, and allows the virtual device to playback responses. This enables more effective testing of IoT applications during development.



![Greenhouse Message Traces
Request Response
POST /ktgh/requestor/sensors
[{"name": "Temperature", "ID": "TMP1"},
{"name": "Humidity", "ID": "HUM1"}]
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
POST /ktgh/requestor/actuators
[{"name": "Fan", "ID": "FAN1"}]
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
PUT /ktgh/requestor/sensors/TMP1
{"dataValue": 37.20527648925781}
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
PUT /ktgh/requestor/sensors/HUM1
{"dataValue": 32.28166961669922}
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
GET /ktgh/requestor/actuators/FAN1 HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{"ID":"FAN1","name":"Fan","value":89.20875276}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iotdevconmenkajun2018share-180608205023/85/IoT-Developer-Confrence-A-Novel-Approach-IoT-Device-Virtualization-using-Machine-Learning-15-320.jpg)
![Cluster to Discover Operation Types
Request Response
POST /ktgh/requestor/sensors
[{"name": "Temperature", "ID": "TMP1"},
{"name": "Humidity", "ID": "HUM1"}]
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
POST /ktgh/requestor/actuators
[{"name": "Fan", "ID": "FAN1"}]
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Request Response
GET /ktgh/requestor/actuators/FAN1 HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{"ID":"FAN1","name":"Fan",
"value":89.20875276}
Request Response
PUT /ktgh/requestor/sensors/TMP1
{"dataValue": 37.20527648925781}
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
PUT /ktgh/requestor/sensors/HUM1
{"dataValue": 32.28166961669922}
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Cluster 1
(POST)
Cluster 2
(PUT)
Cluster 3
(GET)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iotdevconmenkajun2018share-180608205023/85/IoT-Developer-Confrence-A-Novel-Approach-IoT-Device-Virtualization-using-Machine-Learning-18-320.jpg)