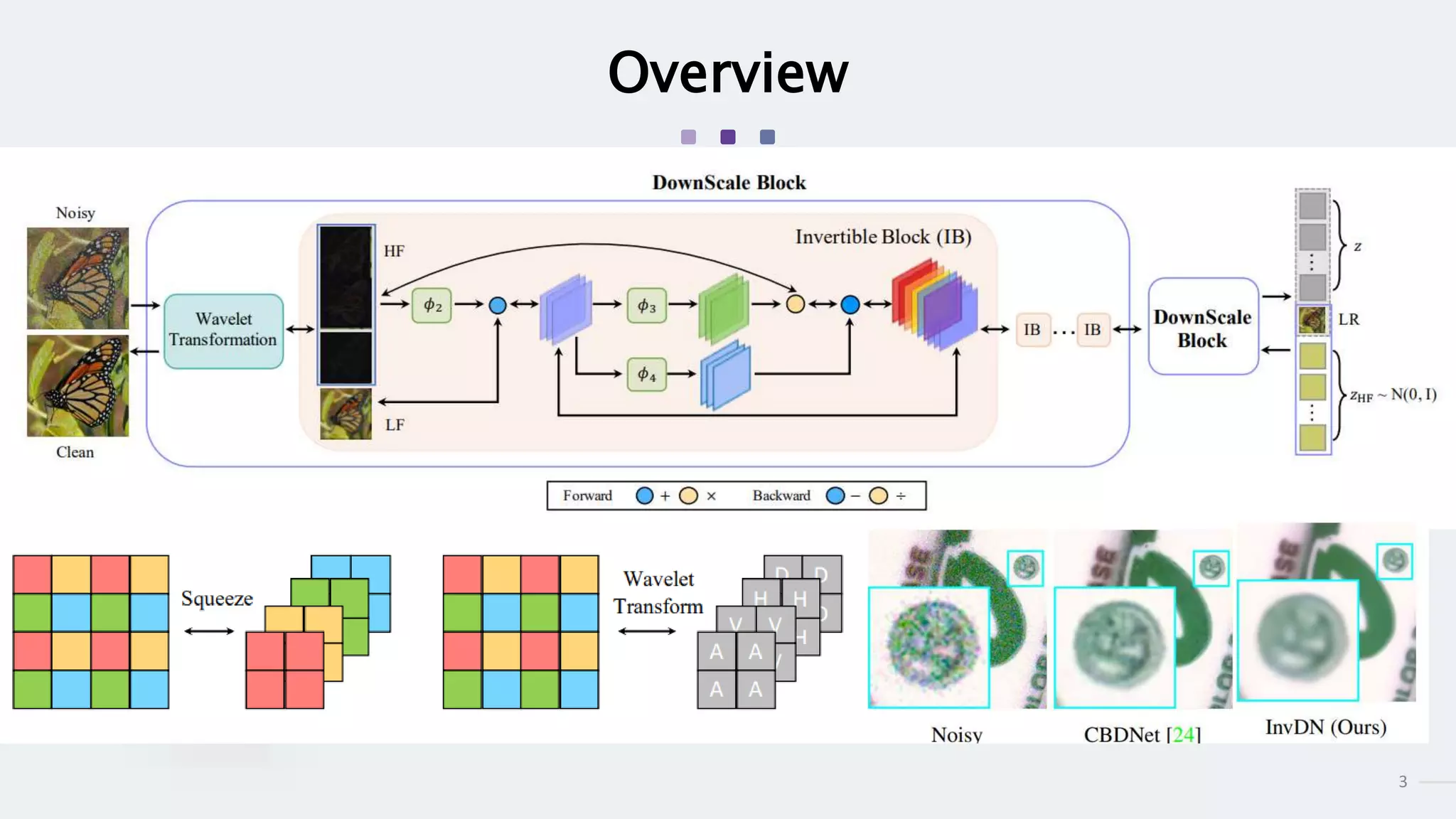
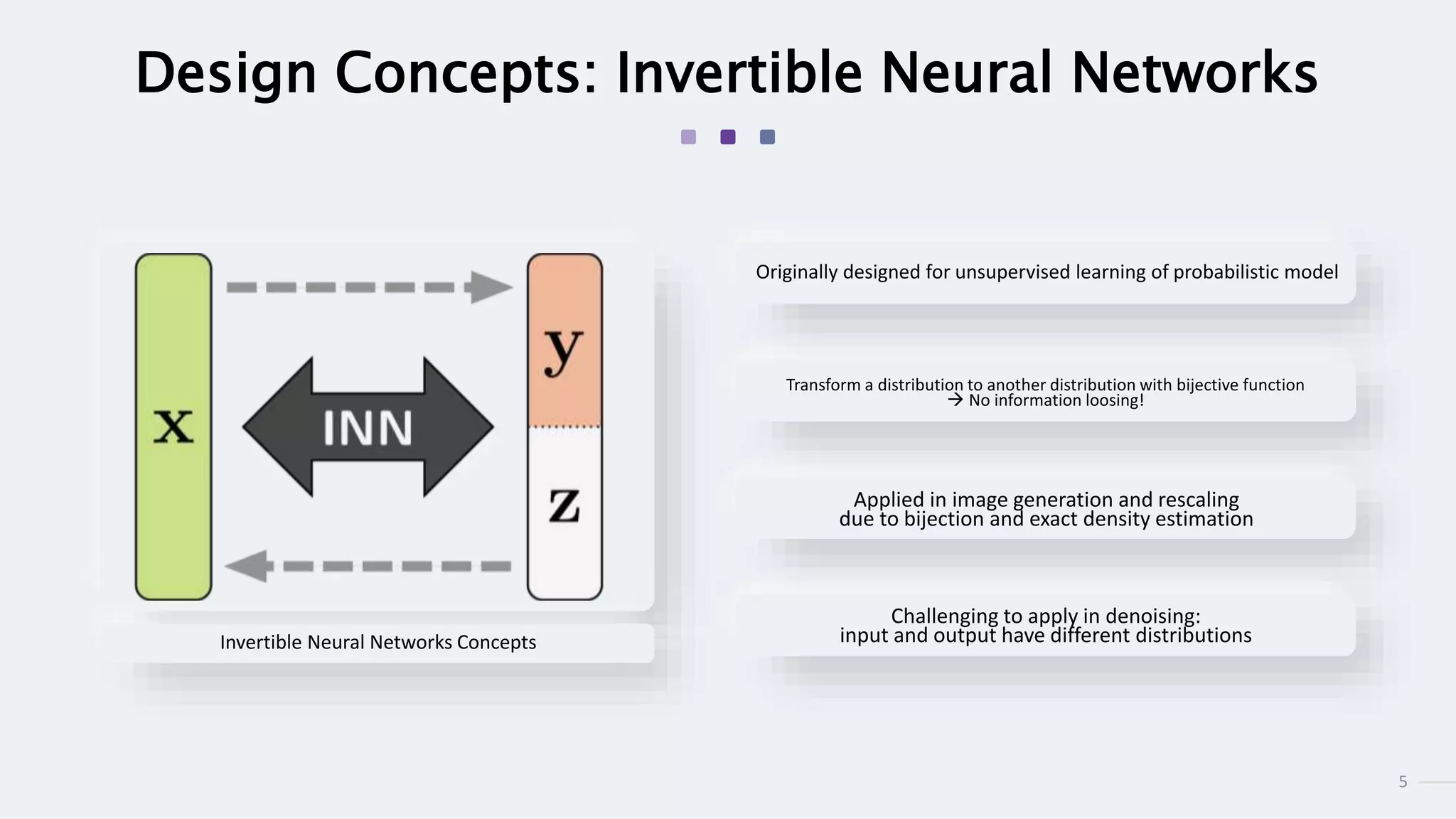
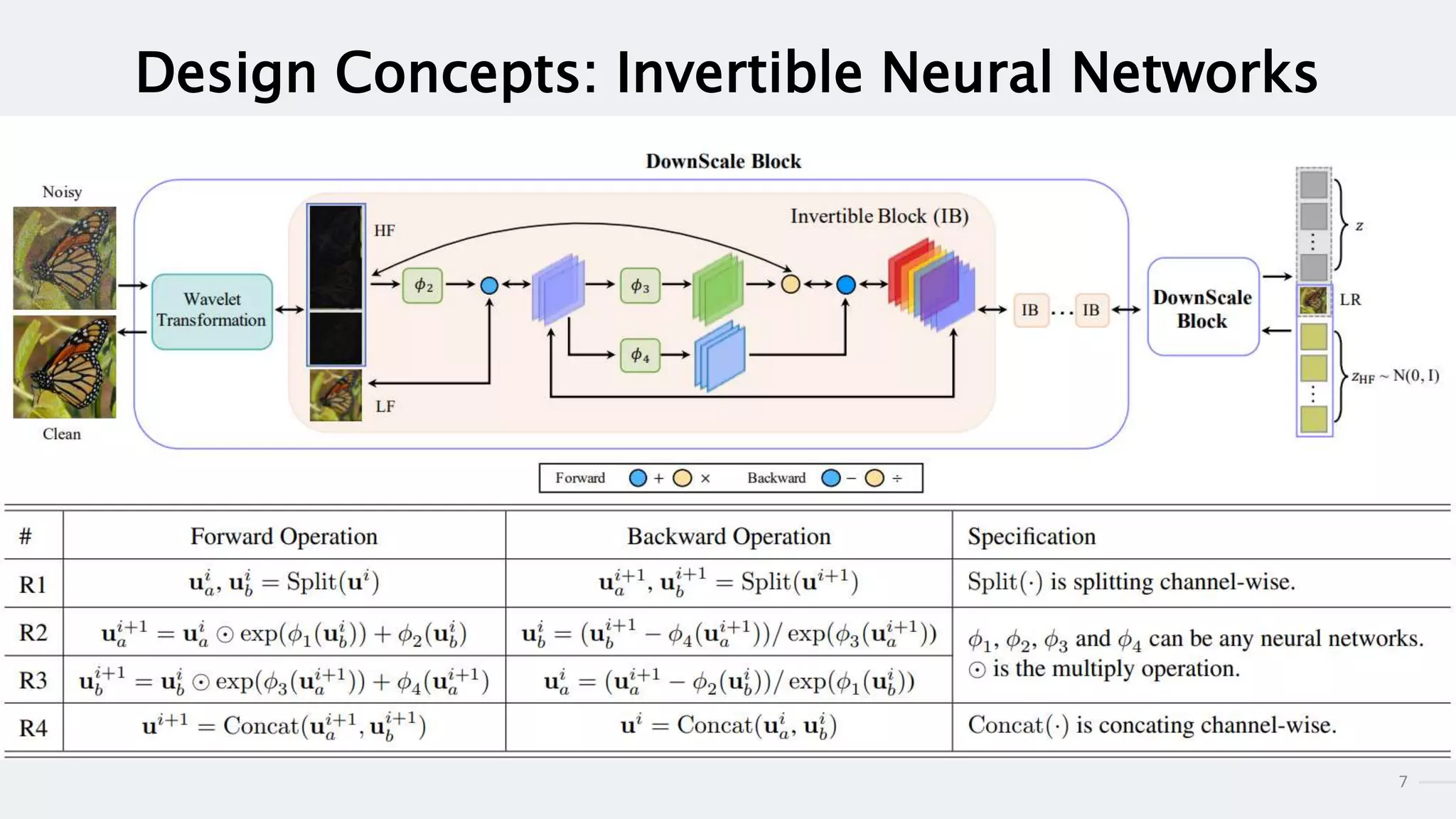
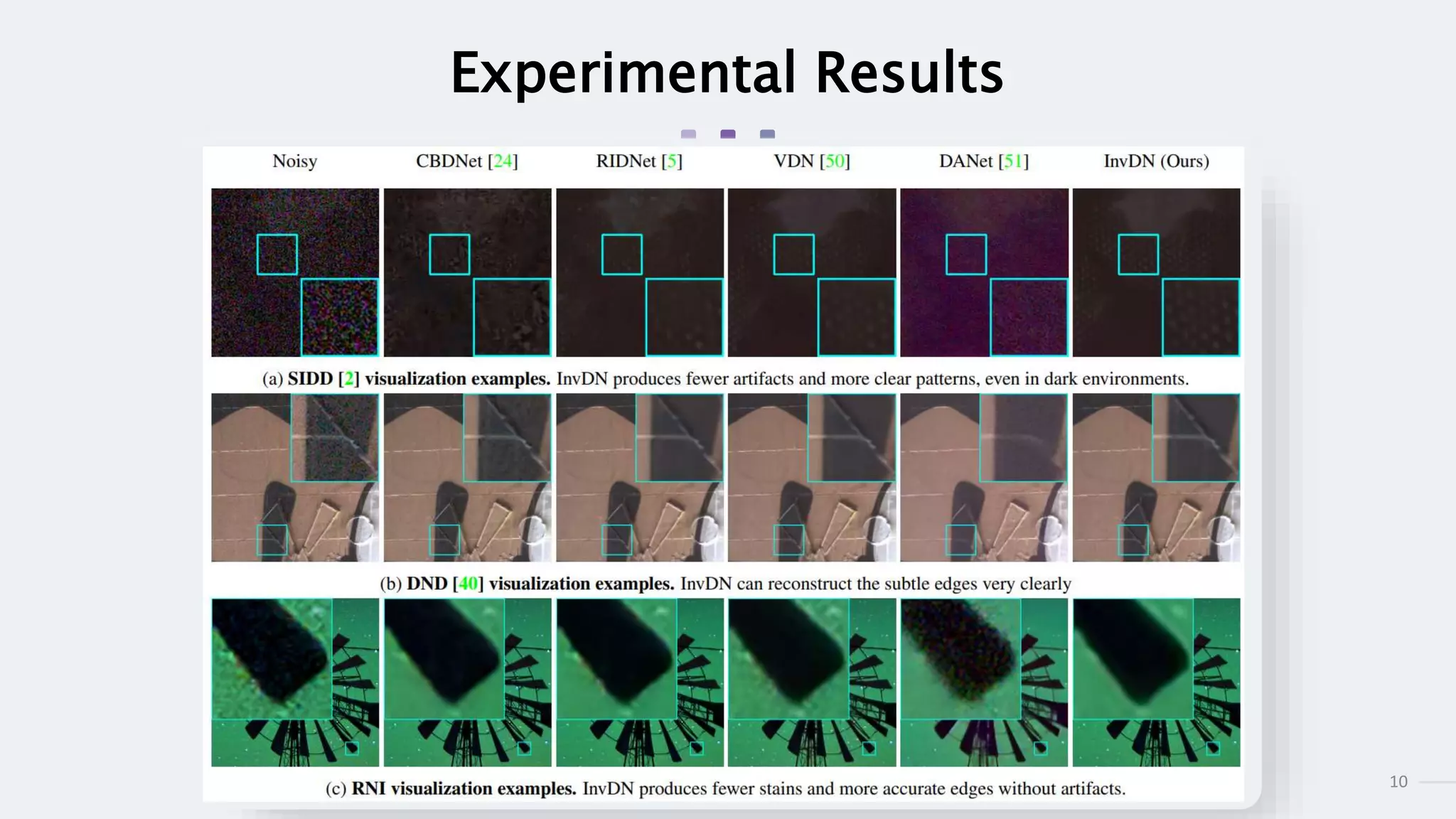
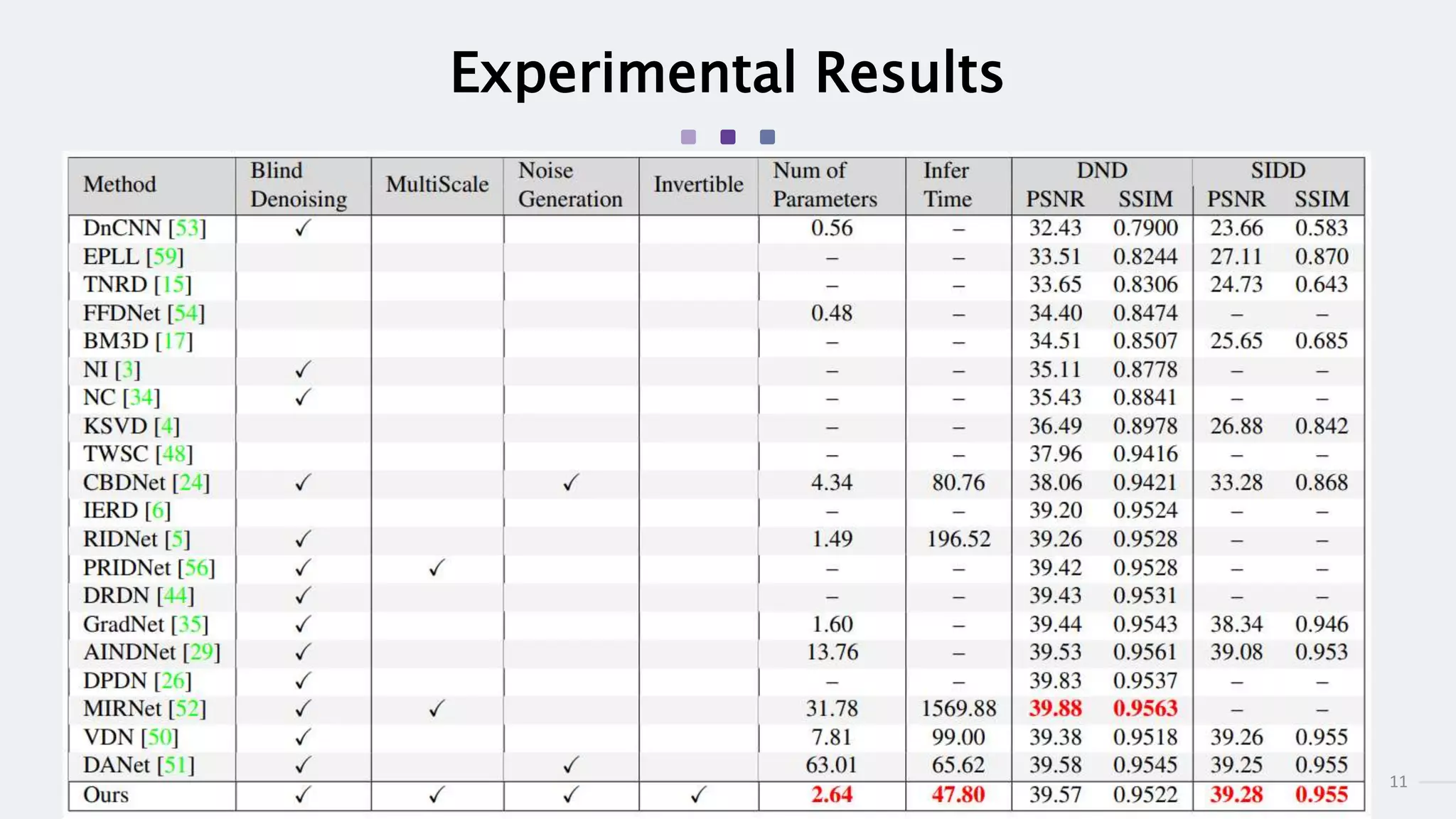
This document summarizes an academic paper on invertible denoising networks (InvDN), a new type of neural network designed for real image denoising. The key points are:
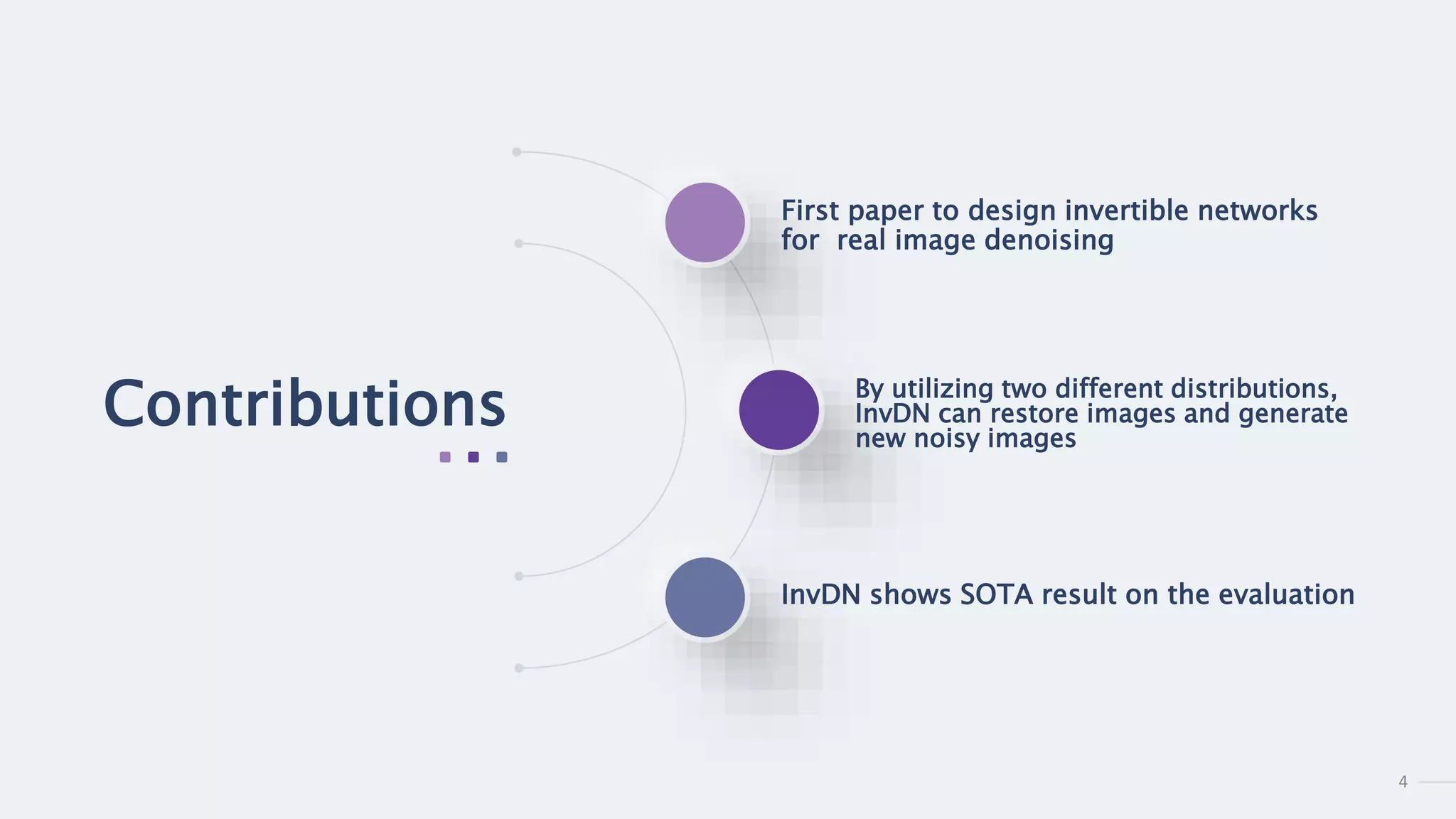
1) InvDN is the first paper to design invertible networks for real image denoising by utilizing two different distributions - one for the noisy image and one for the clean image.
2) InvDN shows state-of-the-art results on benchmark datasets by restoring images and generating new noisy images from the restored clean images.
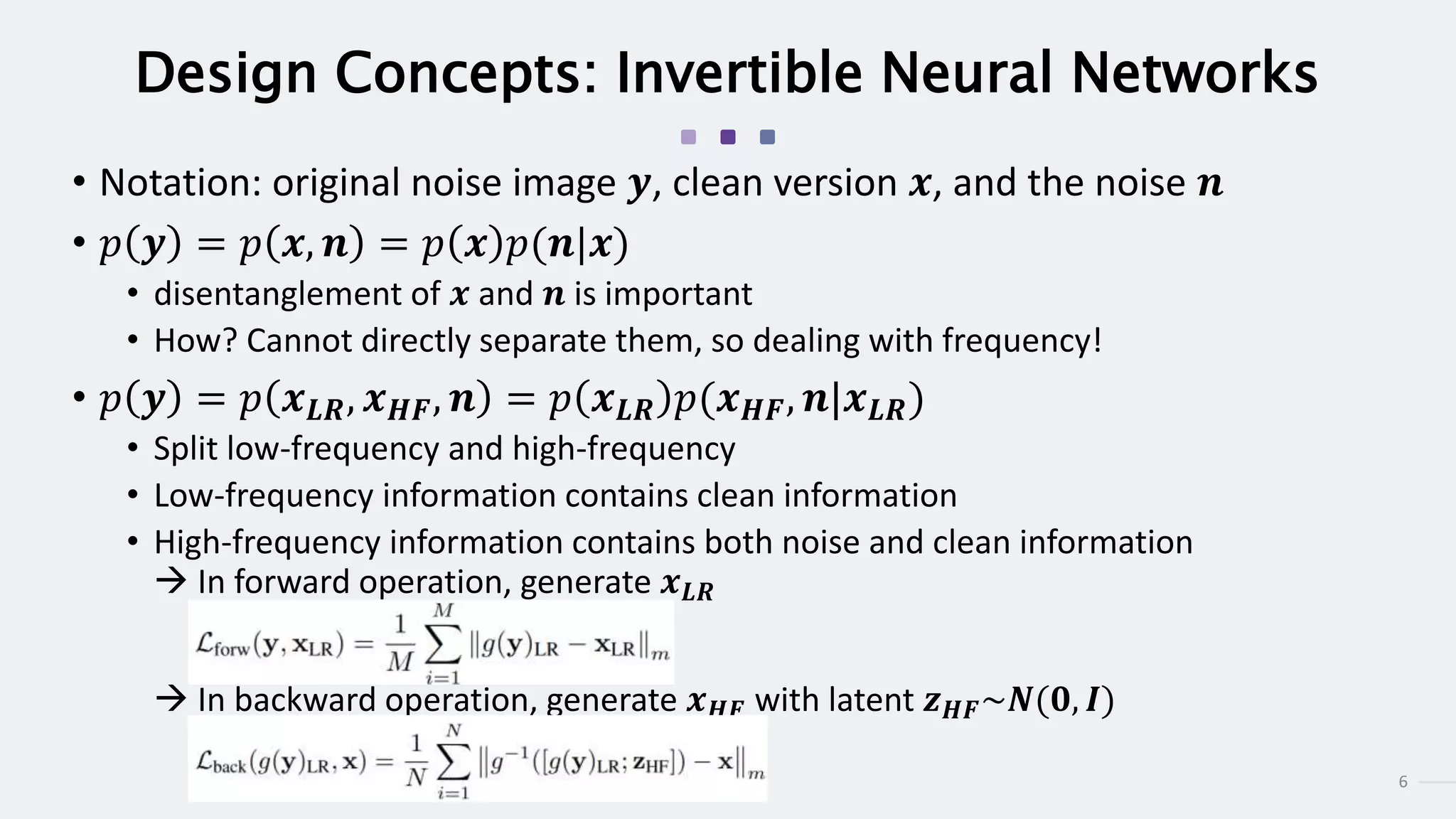
3) InvDN works by splitting images into low and high frequency components in the frequency domain and handling each separately, allowing the disentanglement of clean image and noise information needed for