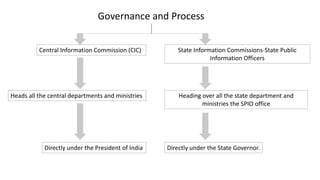
The Right to Information (RTI) Act, enacted in India in 2005, empowers citizens to request information from public authorities, promoting transparency and accountability in governance. It covers various governmental institutions and mandates the proactive disclosure of information, although private entities are not directly included. However, challenges such as bureaucratic delays, information overload, and accessibility issues persist, which may hinder the effectiveness of the RTI framework.