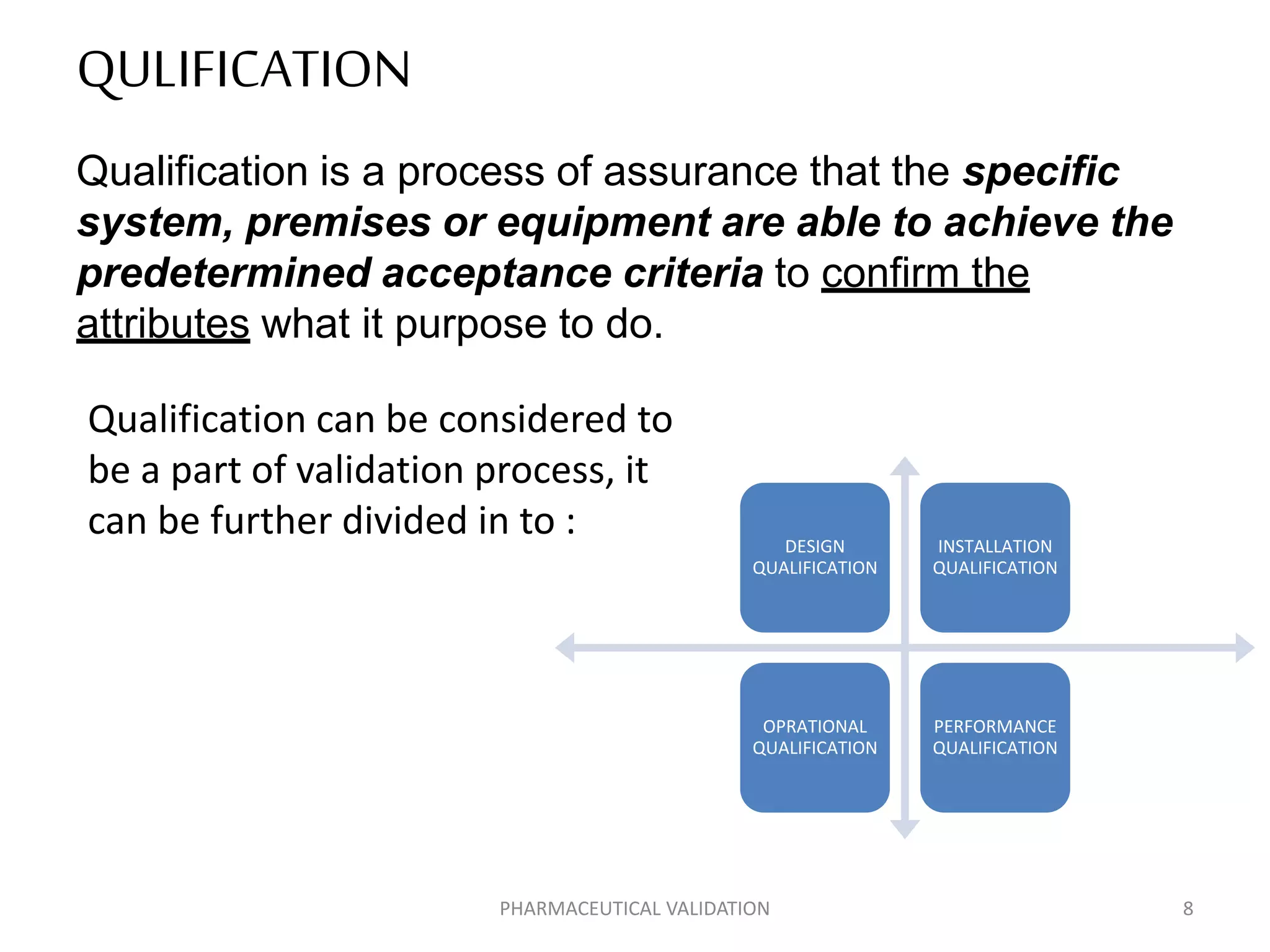
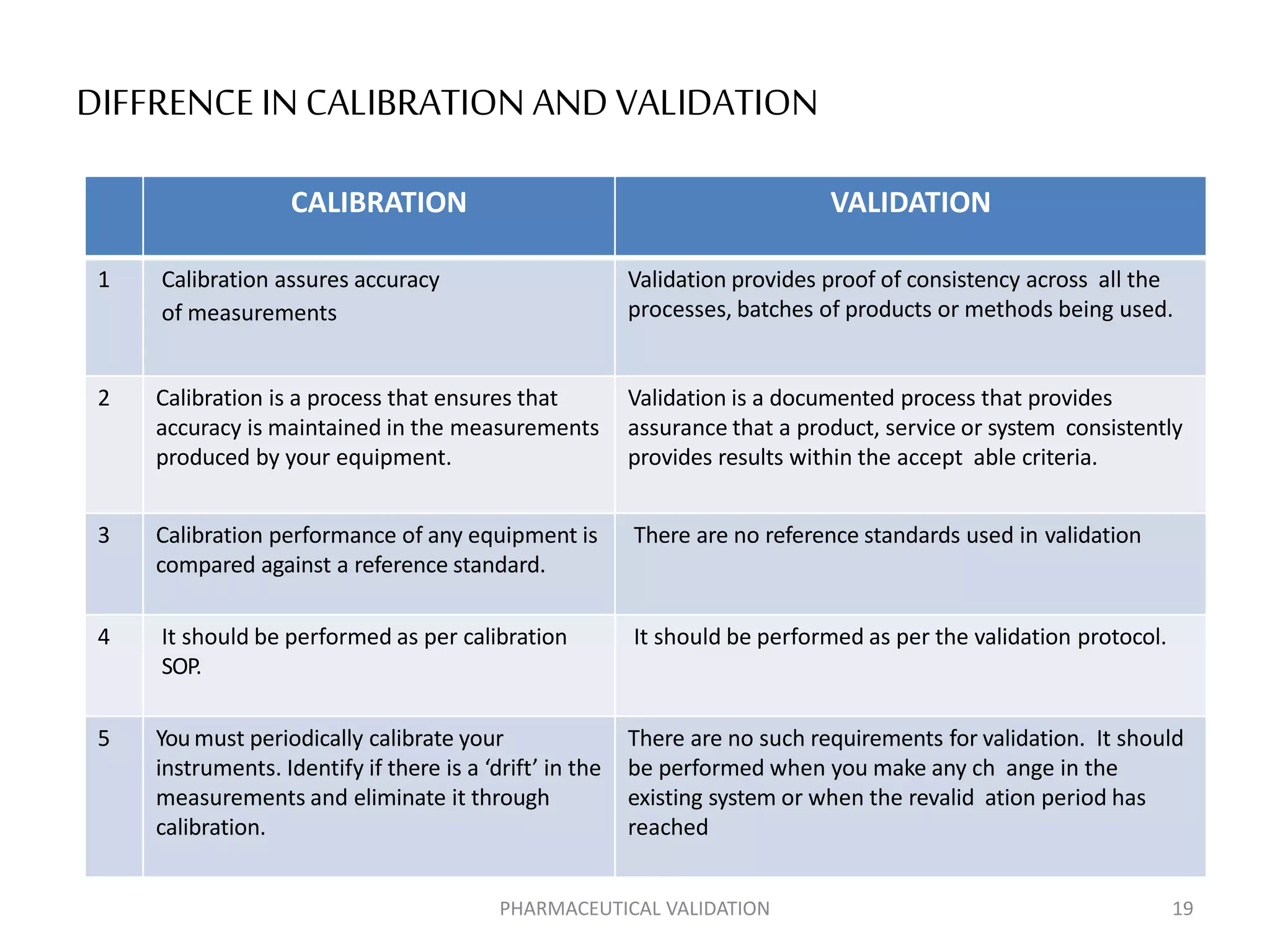
The document outlines the concepts of calibration and validation in pharmaceuticals, detailing their definitions, types, and importance. Calibration ensures measurement accuracy, while validation ensures consistent product quality across processes. It highlights the significance of both for regulatory compliance and quality assurance in the pharmaceutical industry.