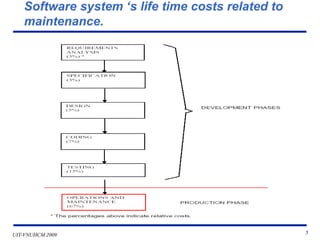
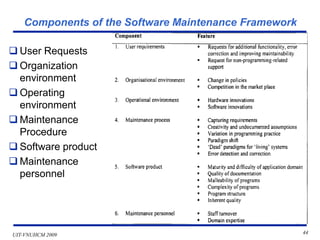
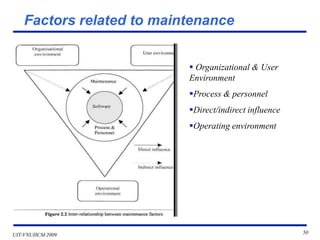
This document discusses software system operation, maintenance, and management. It covers topics like resource management, problem management, facilities management, security management, and cost management as they relate to system operation. Maintenance is described as modifying a system after development to fix bugs, update specifications, or improve functionality. Effective maintenance requires communication between users and developers, tracking issues, analyzing problems, and documenting changes. The document provides details on maintenance tasks, types of maintenance work, and factors that influence maintenance costs.