The document provides an introduction and comparison of Python and C programming languages. Some key points:
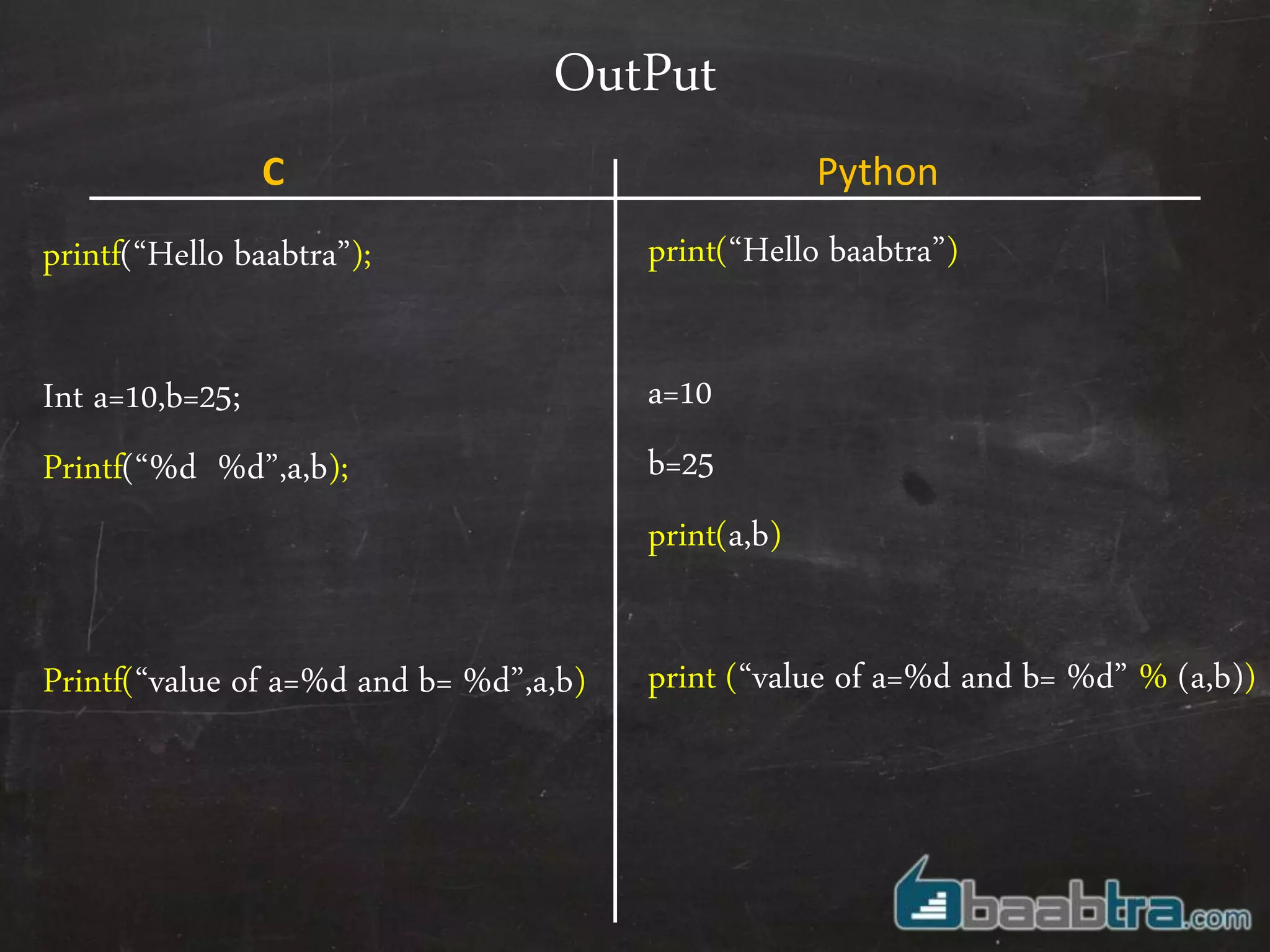
- Python is an interpreted language while C needs compilation. Python makes program development faster.
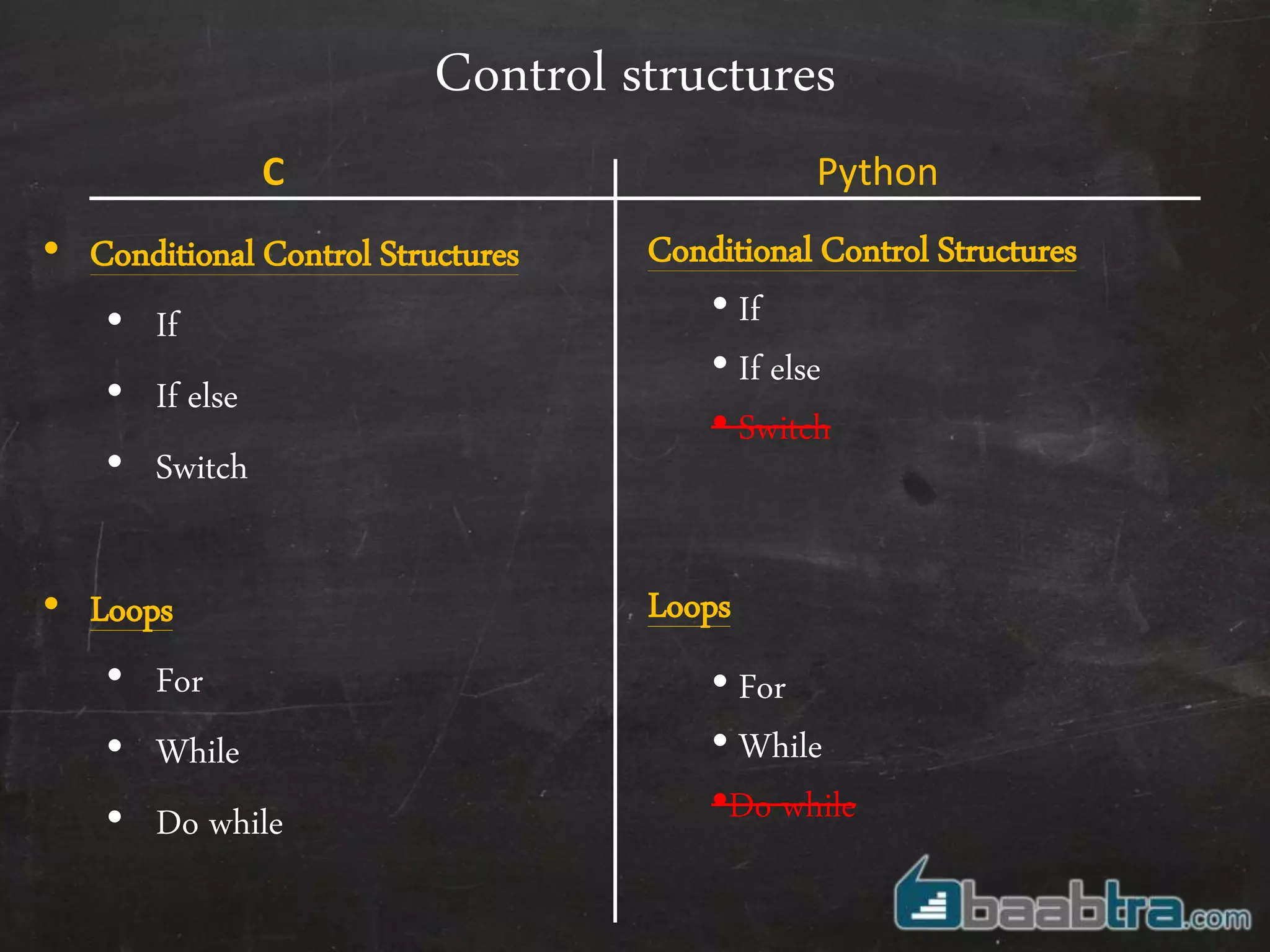
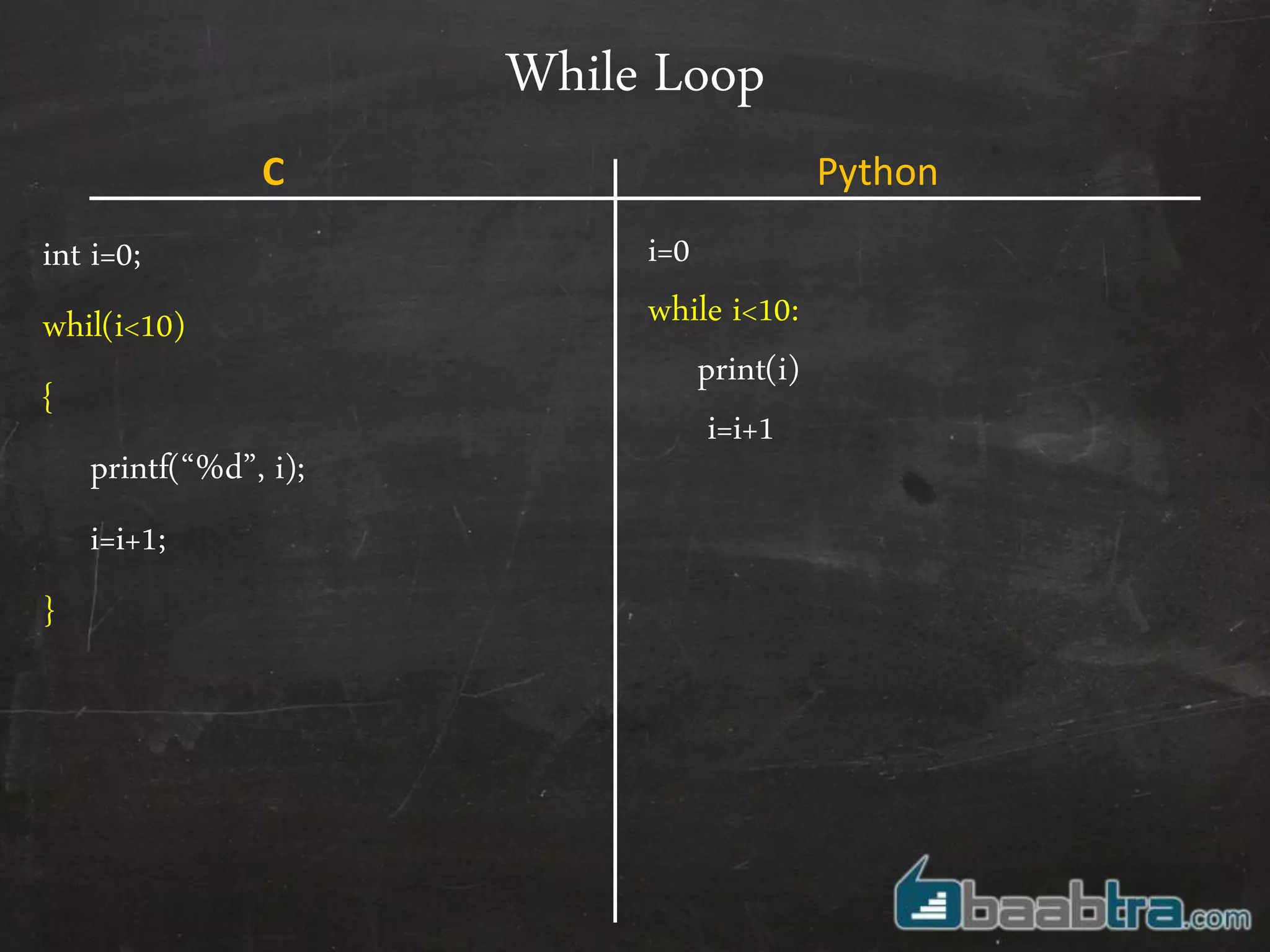
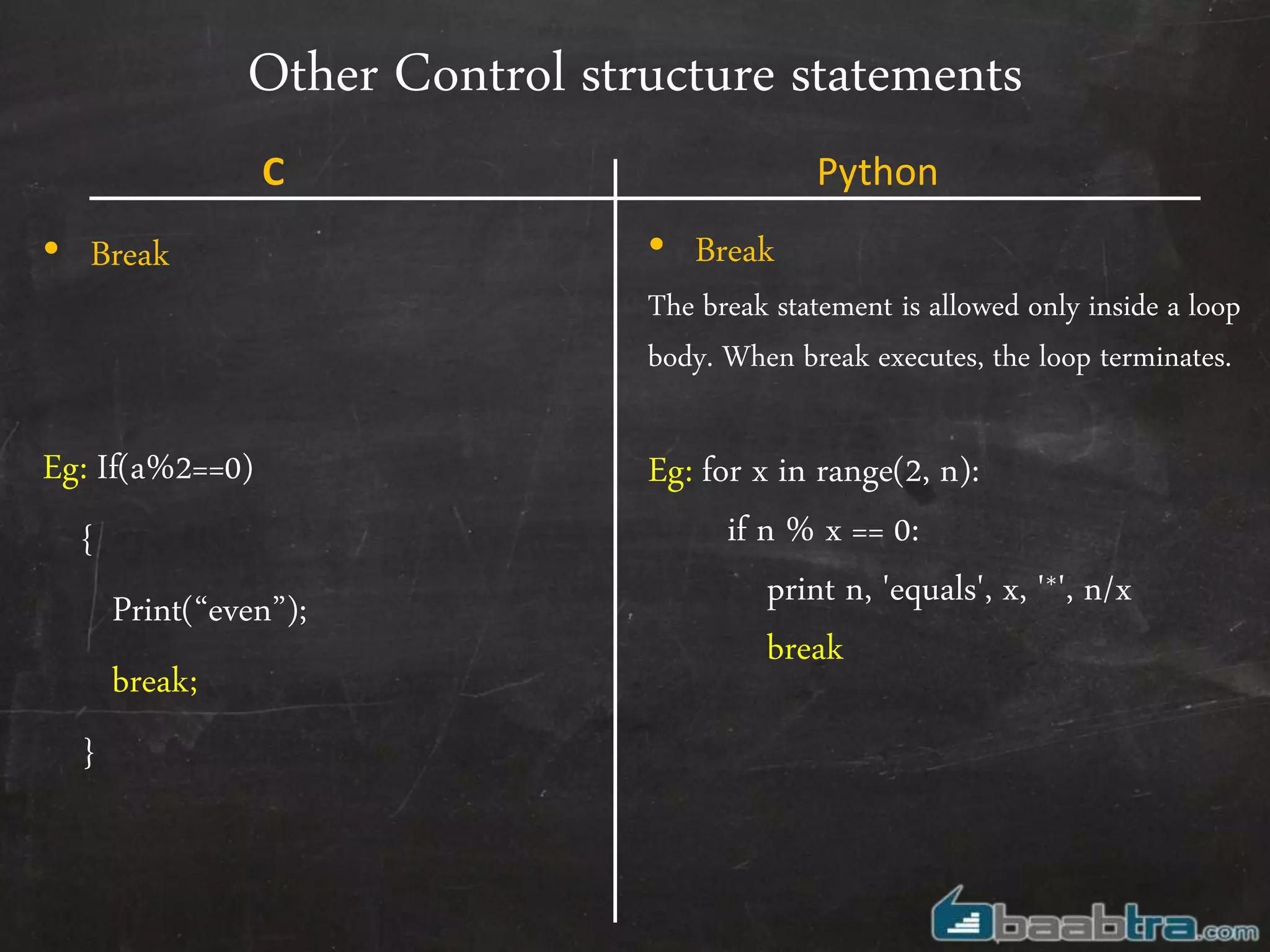
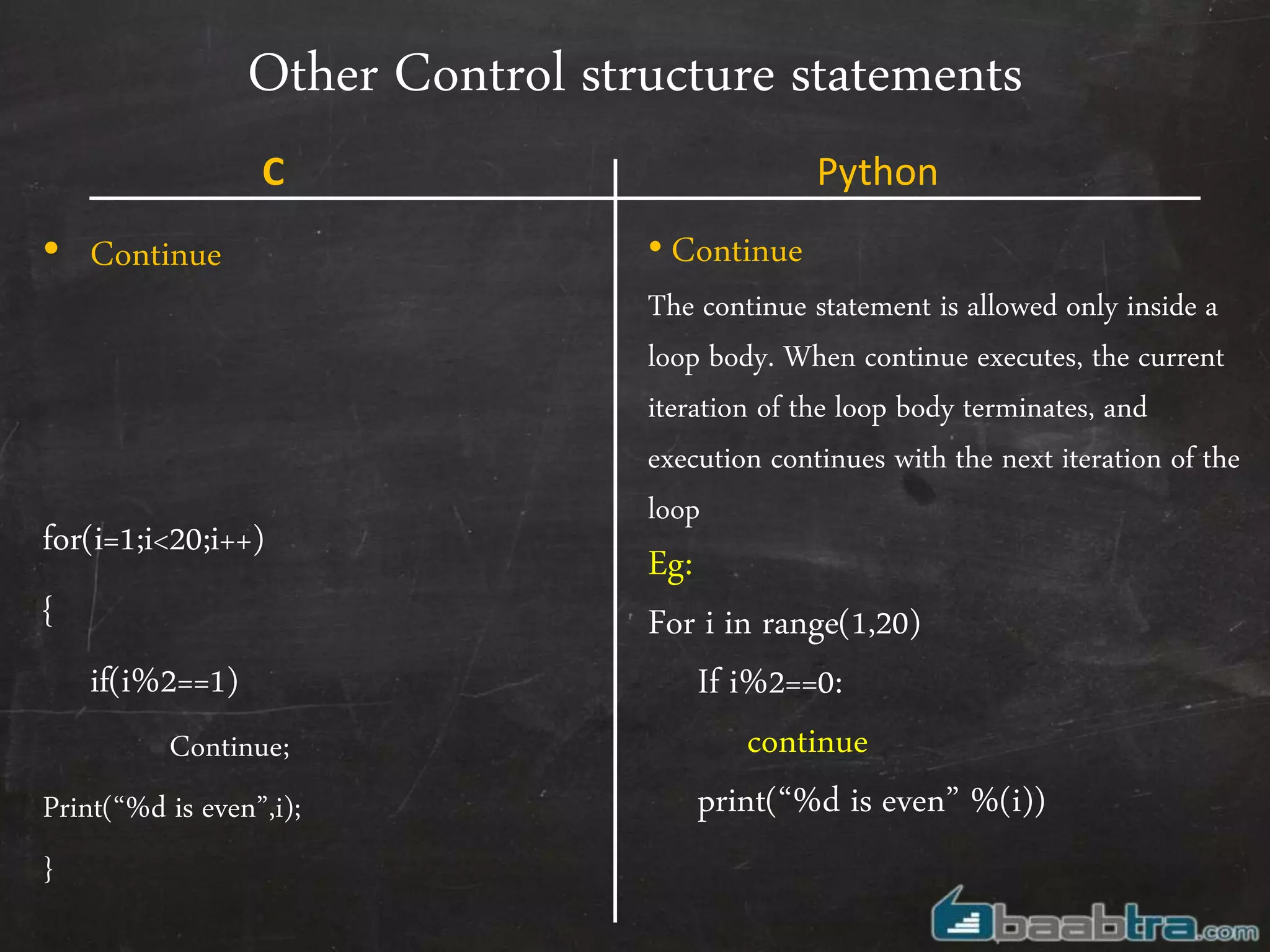
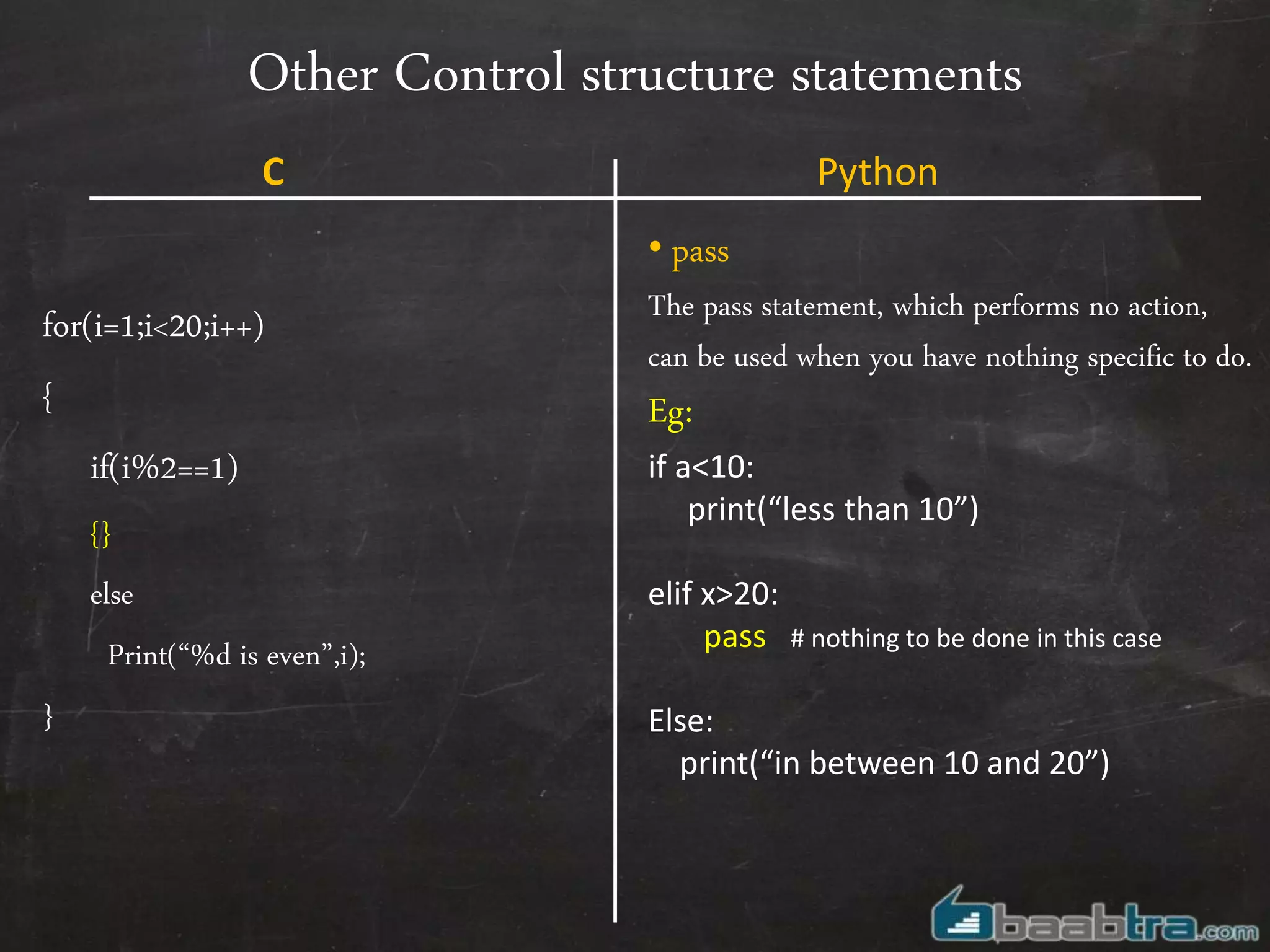
- Variables, input/output, arrays, control structures like if/else, for loops work differently in Python compared to C.
- Python uses lists instead of arrays. Lists are mutable and support slicing.
- Strings are treated as character lists in Python.
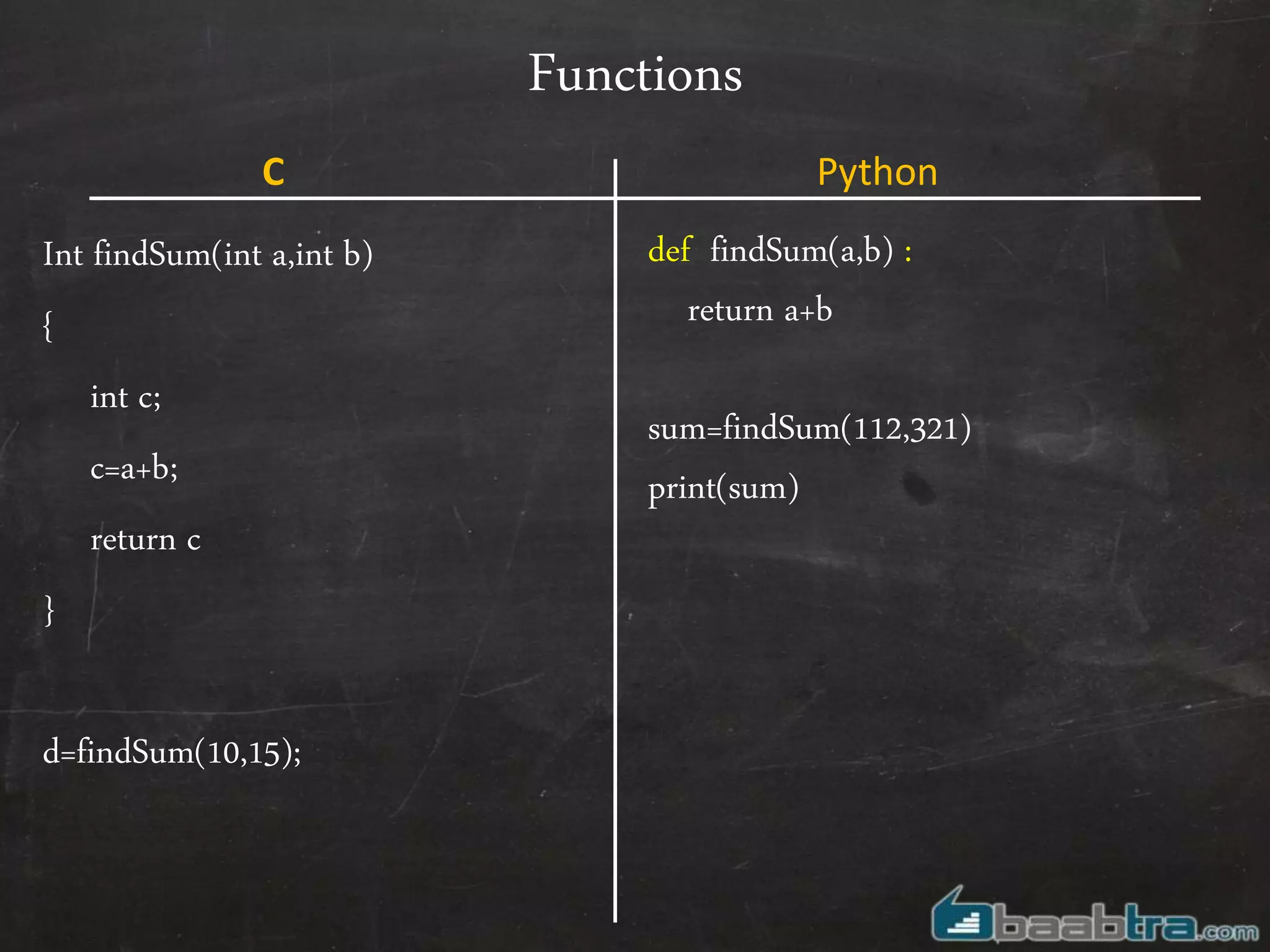
- Functions are defined using def keyword in Python.
- The document also introduces sequences (strings, tuples, lists), dictionaries, and sets in Python - their usage and operations.






![Arrays
int a[]={12,14,15,65,34};
printf(“%d”, a[3]);
No Arrays ! Instead Lists
a = [12,14,15,16,65,34,’baabtra’]
C Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-140811081203-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-python-9-2048.jpg)
![Arrays
int a[]={12,14,15,65,34};
printf(“%d”, a[3]);
No Arrays ! Instead Lists
a = [12,14,15,16,65,34,’baabtra’]
C Python
[ 12 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 65 , 34 , ’baabtra’ ]
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
-7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-140811081203-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-python-10-2048.jpg)
![Lists in detail
• Print(a[2:5]) # prints 15,16,65
• Print(a[-6:-2]) # prints 14,15,16,65
• Print(a[4:]) # prints 65,34,baabtra
• Print(a[:2]) # prints 12,14,15
• a[2] = a[2] + 23; # Lists are mutable,we can change individual items
• a[0:2] = [1, 12] # We can replace a group of items together
• a[0:2] = [] # We can remove items together
• a[:] = [] # Clear the list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-140811081203-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-python-11-2048.jpg)
![Lists in detail
• a.append(25) # adds an element at the end of list
• b =[55,66,77]
a.extend(b)
a=a+b;
• a.insert(1,99) # Inserts 99 at position 1
• a.pop(0) # pop elements at position 0
# Combines two lists](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-140811081203-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-python-12-2048.jpg)
![Strings
char a[]=“baabtra”; a= ‘baabtra’
b=“doesn’t”
C=“baabtra ”mentoring partner””
Strings are character lists, So can be used like any
other lists as we discussed earlier
print (a[0])
a.append(“m”);
C Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-140811081203-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-python-13-2048.jpg)
![Strings in detail
• String slicing
word=‘hello baabtra’
print(word[6:] # prints baabtra
word[: 6] # prints ‘hello ‘
word2= ‘good morning’ + word[6:]
Print(word2) # prints ‘good morning baabtra‘](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-140811081203-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-python-14-2048.jpg)

![For Loop
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
printf(“%d”, i);
}
It’s quite a bit untraditional . We need to
define a range on which loop has to iterate.
This can be done using
Range(10,20) // creating a list with
elements from 10 to 20
For i in range(10) :
print(i) //print numbers up to 10
a=[12,14,16,’baabtra’]
For i in a :
print(i) //prints 12,14,16,baabtra
C Python](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-140811081203-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-python-18-2048.jpg)
![Task
• Write a simple python program which will have an array variable as below
• a= [50,15,12,4,2]
• Create 3 functions which will take the above array as argument and returns
the arithmetic output
–Add() //Outputs 83
–Substract() //Outputs 17
–Multiply() //Outputs 72000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-140811081203-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-python-23-2048.jpg)








![Dictionaries
• A dictionary is an arbitrary collection of objects indexed by nearly
arbitrary values called keys. They are mutable and, unlike
sequences, are unordered.
–Eg :{ 'x':42, 'y':3.14, 'z':7 }
–dict([[1,2],[3,4]]) # similar to {1:2,3:4}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-140811081203-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-python-32-2048.jpg)
![Operation on Dictionaries
• dic={'a':1,'b':2,'c':3}
– len(dic) # returns 3
– del dic['a'] # removes element with key ‘a’
– a in dic # returns ‘True’ .Bur
– dic.items() #Displays elements
– for i in dic.iterkeys():
... print i # Returns key
– for i in dic. itervalues():
... print i # Return values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontopython-140811081203-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-python-33-2048.jpg)




