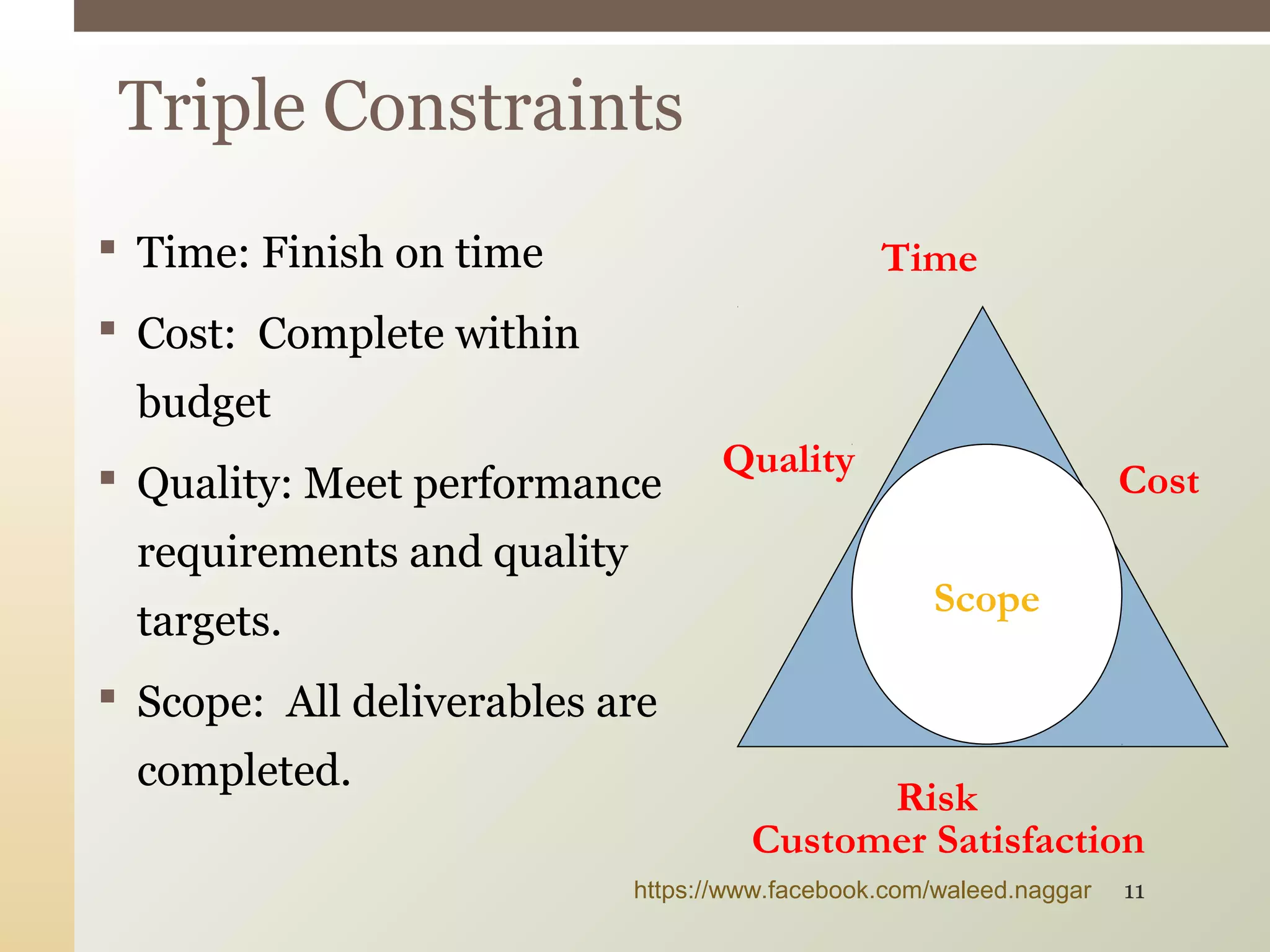
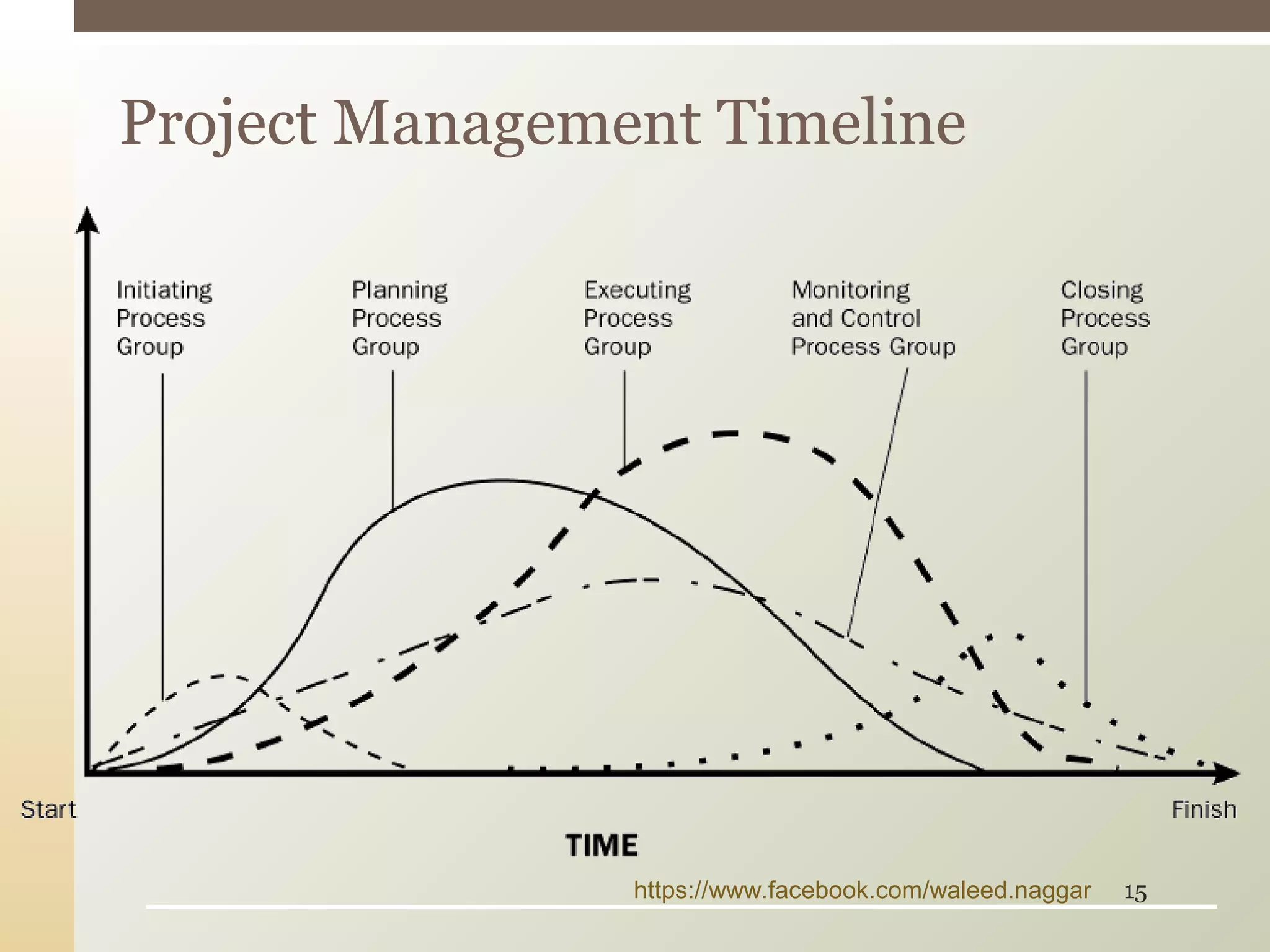
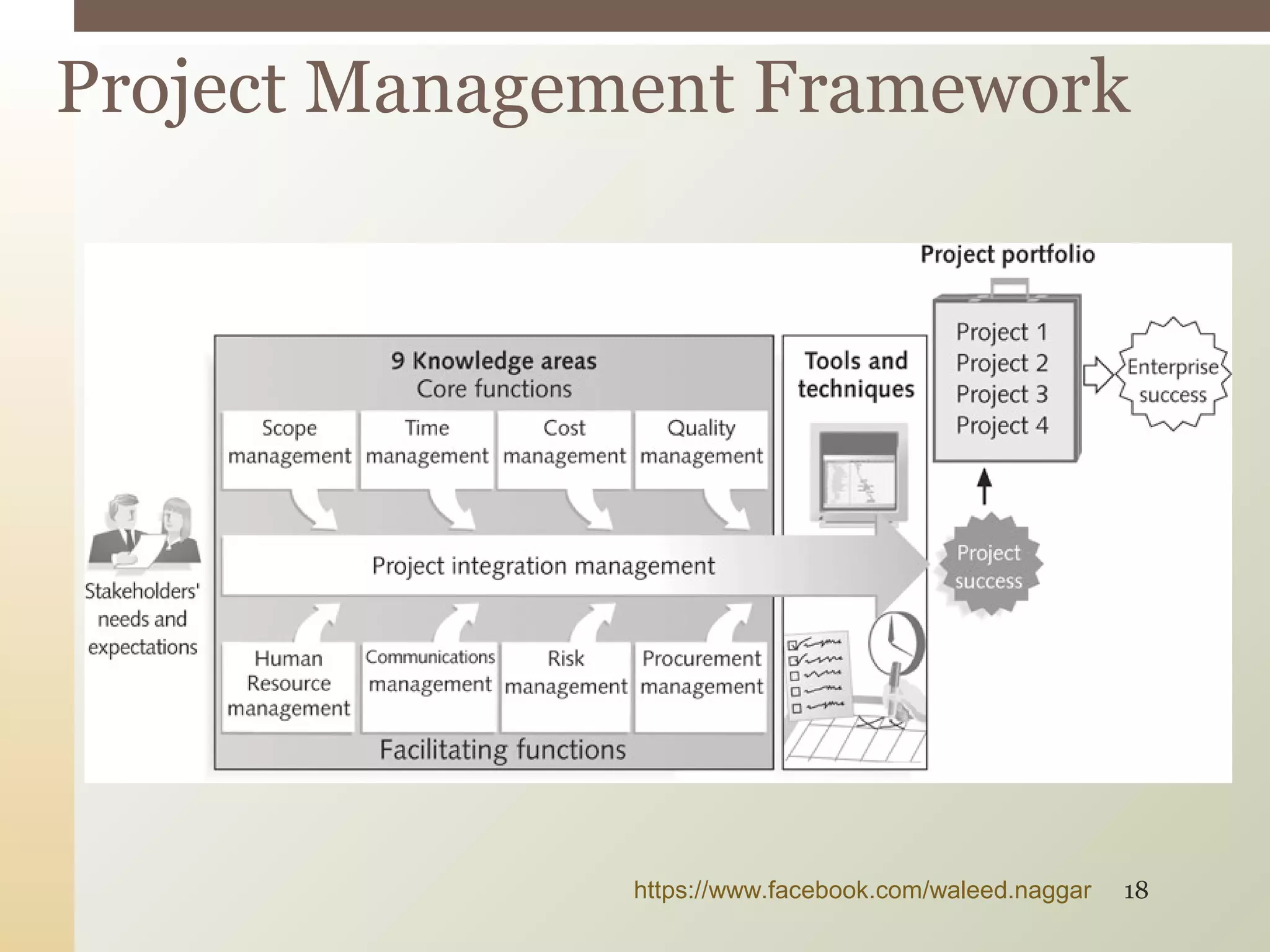
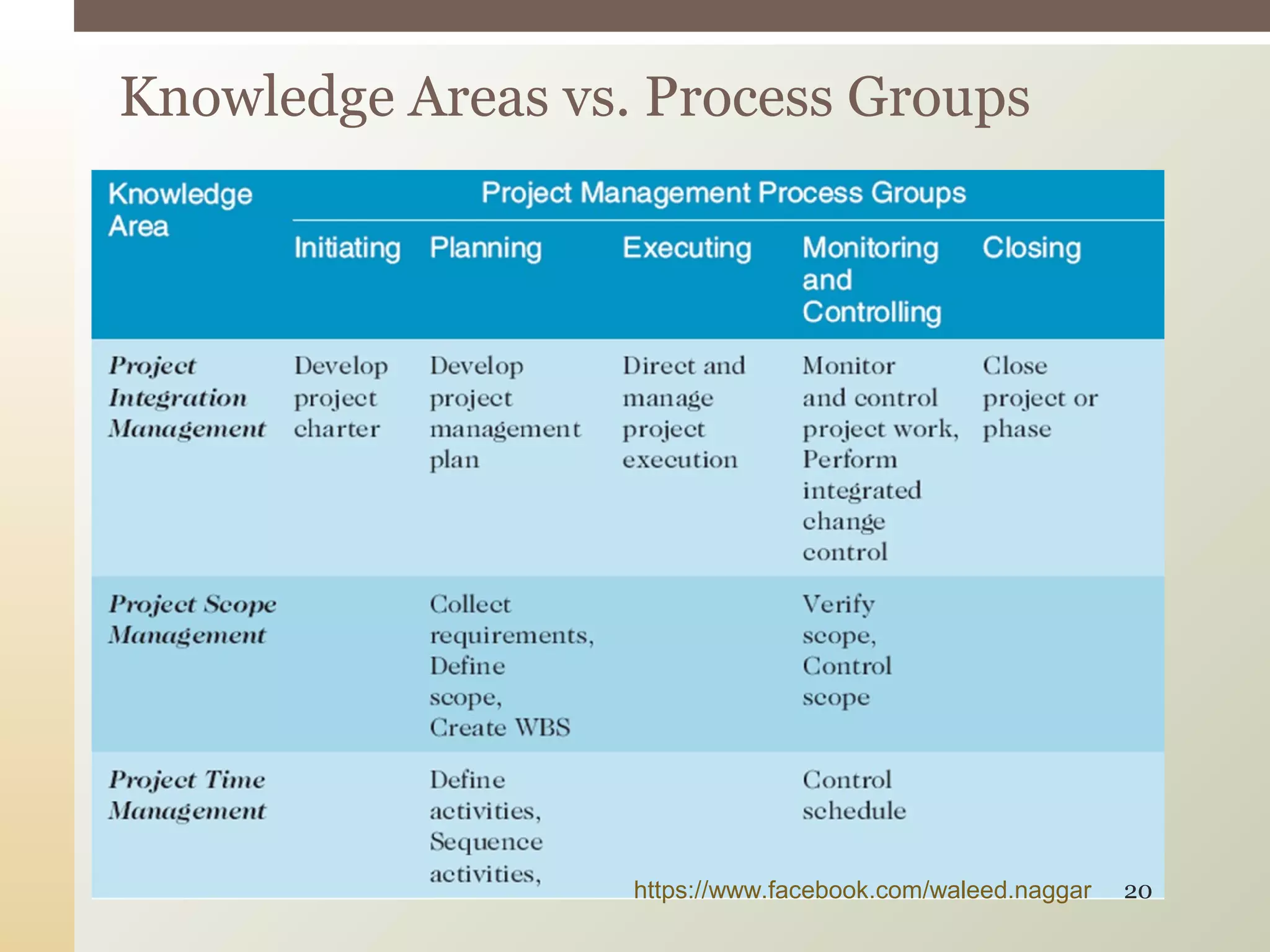
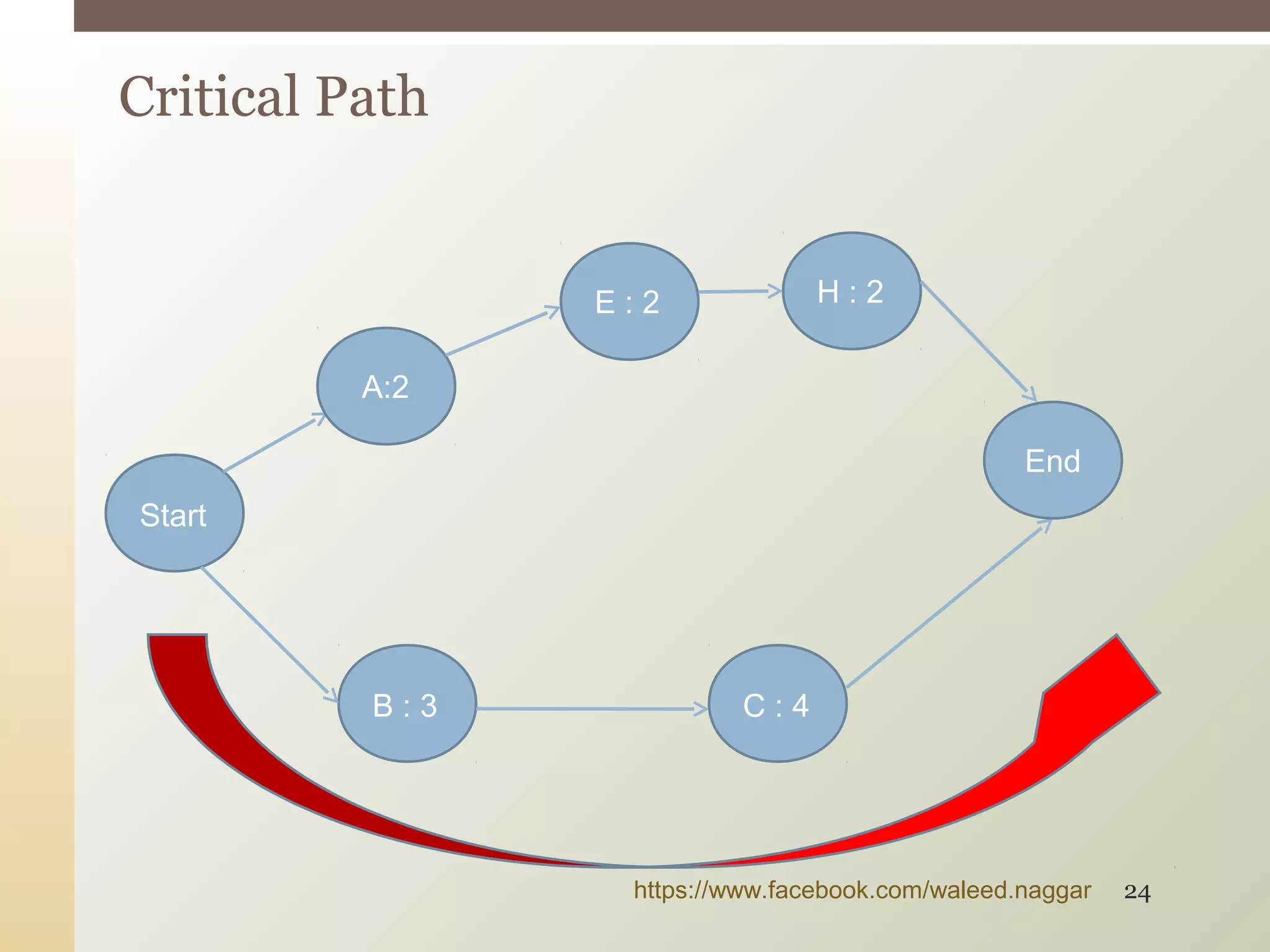
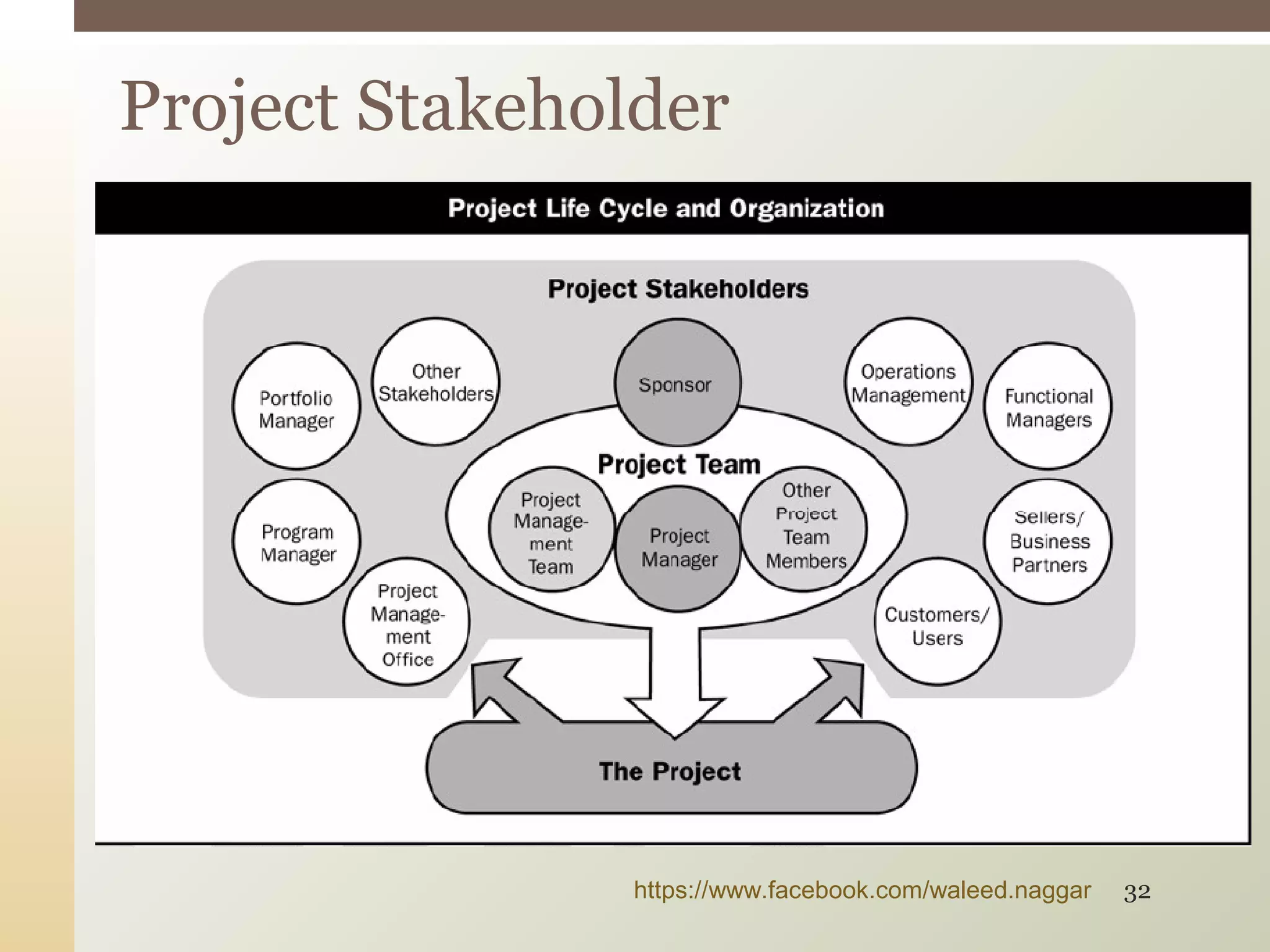
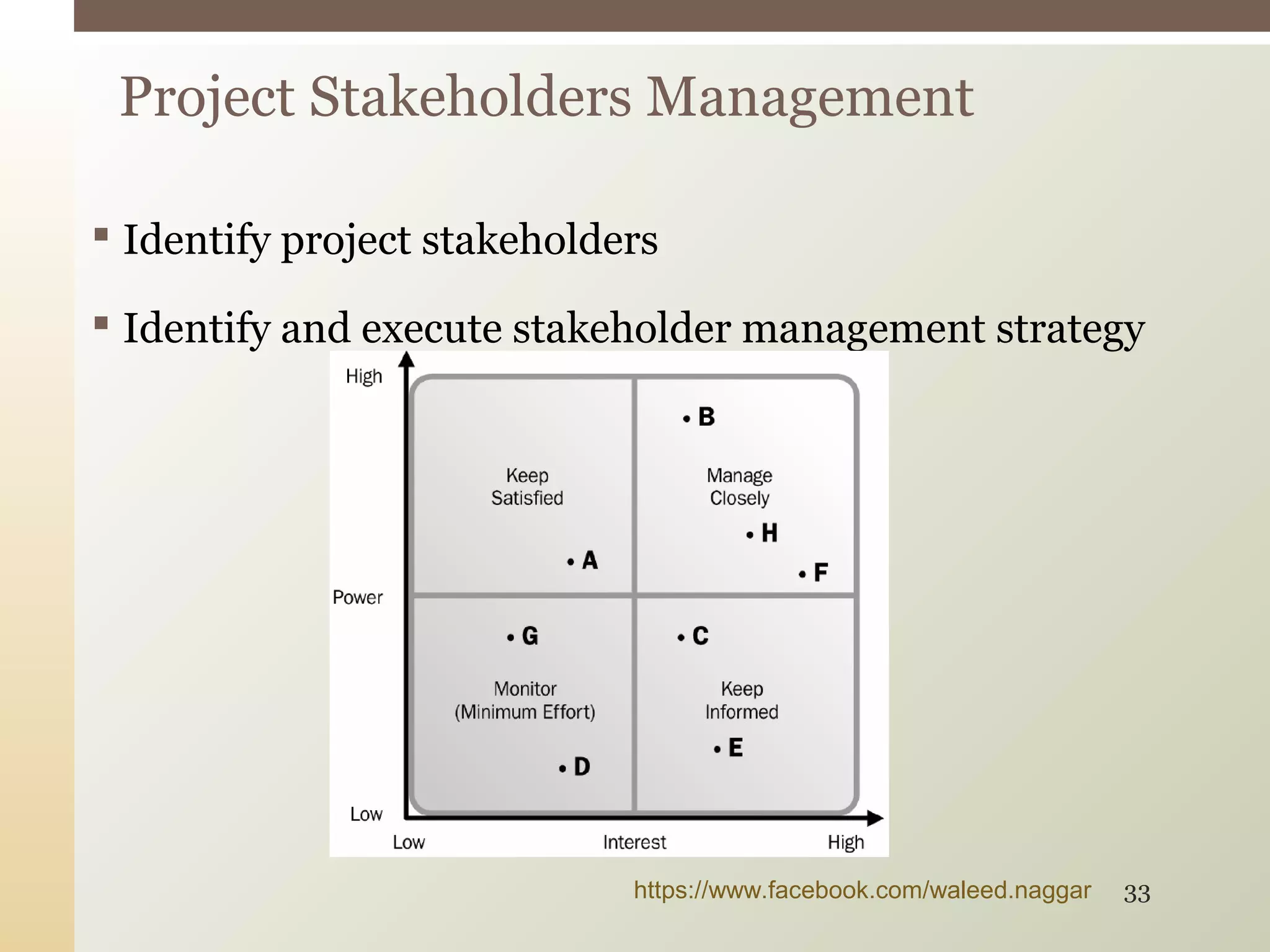
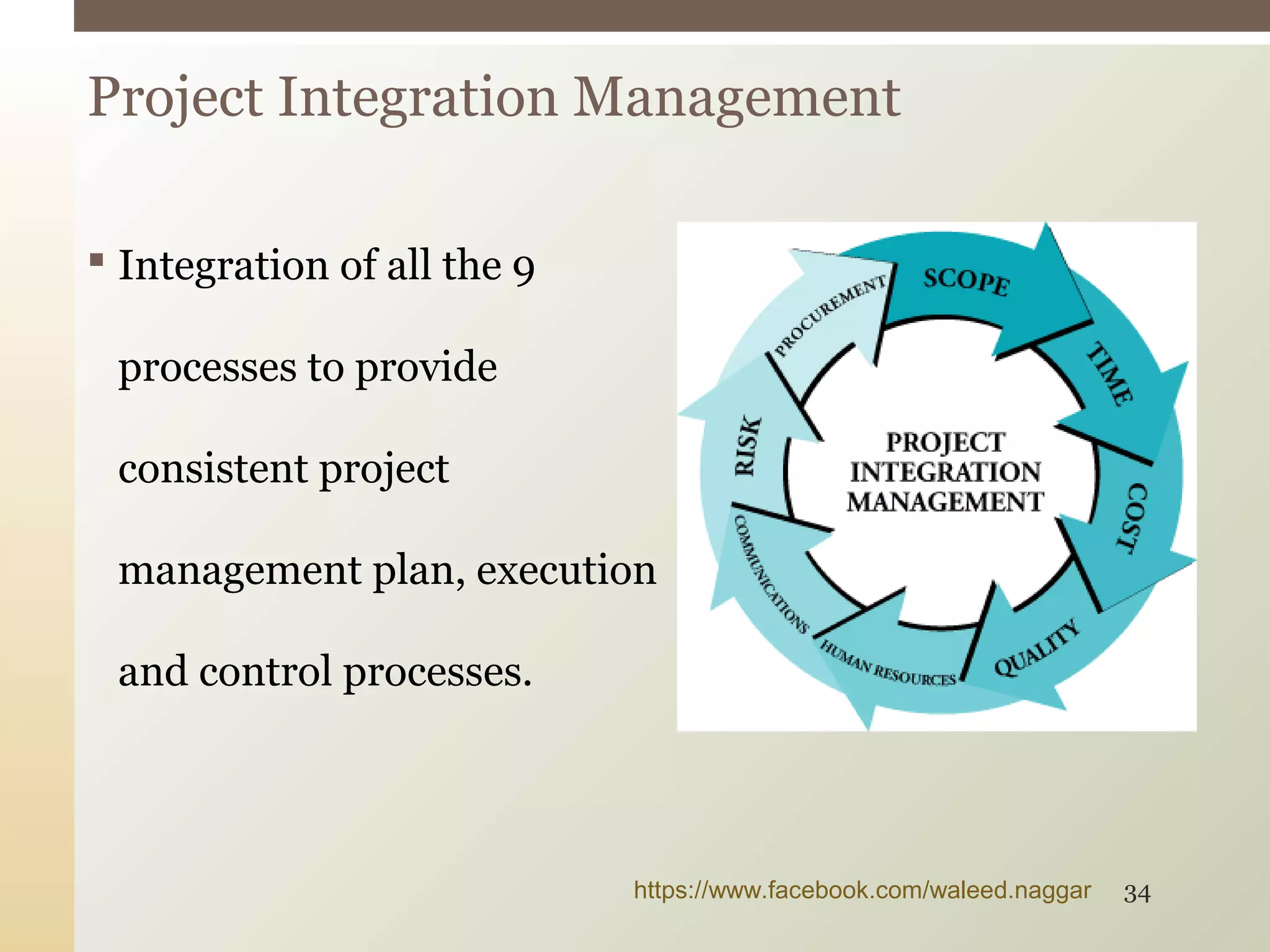
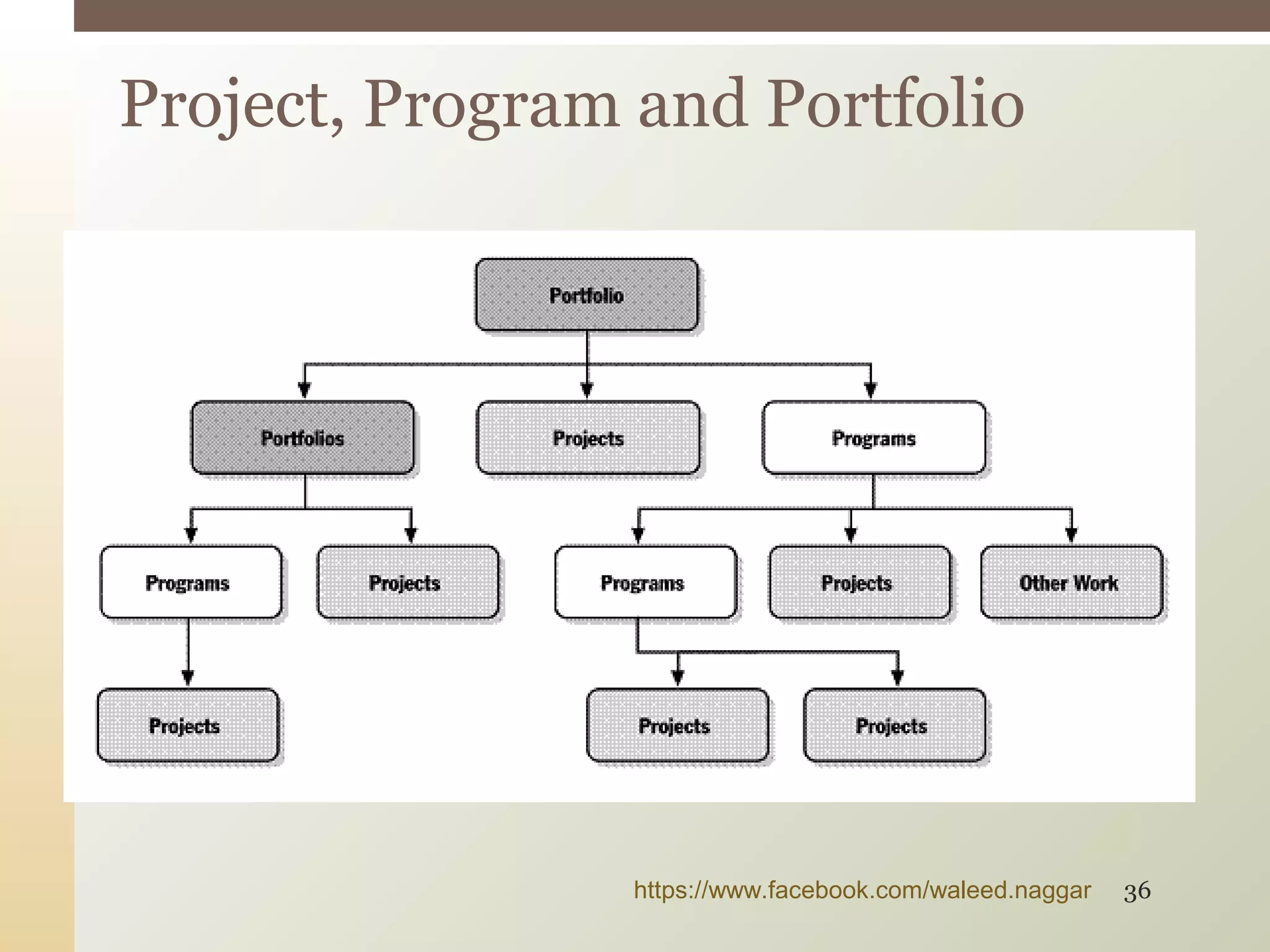
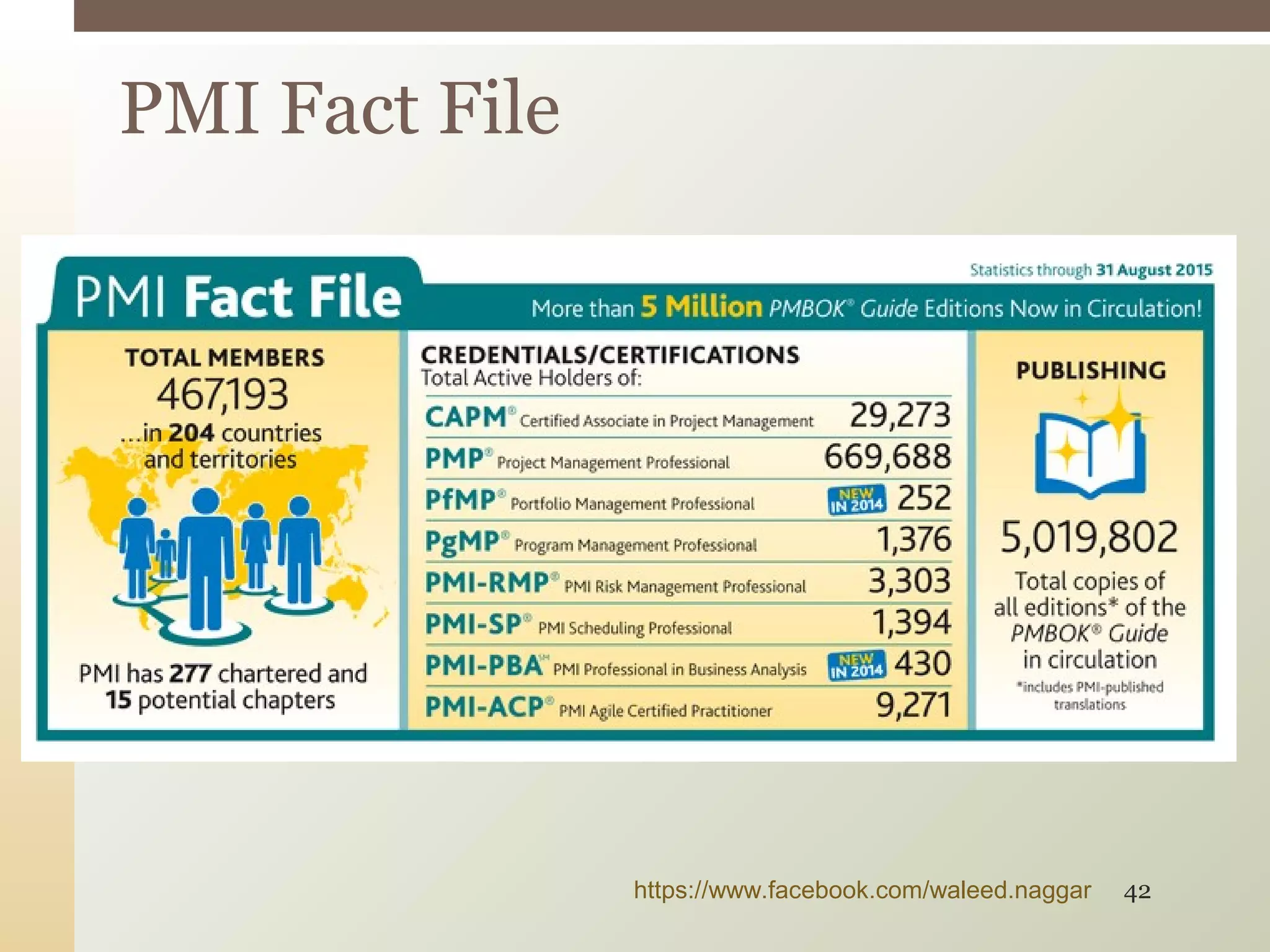
This document provides an introduction to project management. It defines what a project is and explains that project management involves planning, organizing, and controlling project activities to meet stakeholder needs. The key aspects of project management are the triple constraint of scope, time and cost. There are nine knowledge areas that project managers must understand, including scope, time, cost, quality, and risk management. The document also discusses the differences between projects, programs and portfolios and provides an overview of the project management life cycle and processes.