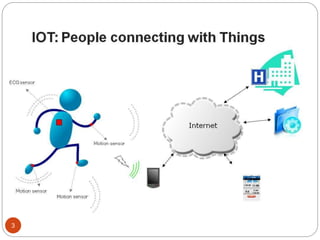
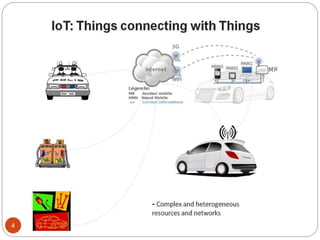
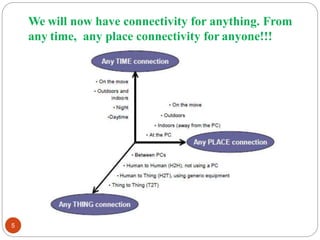
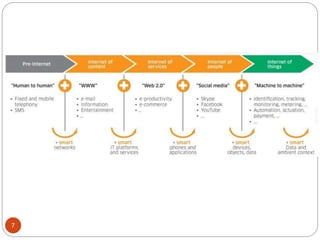
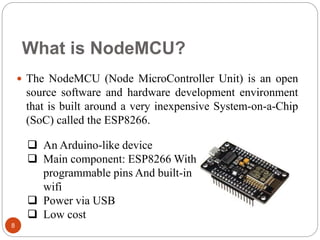
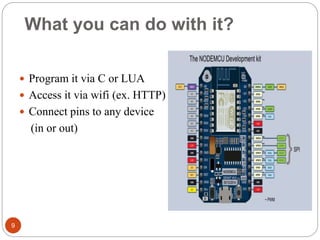
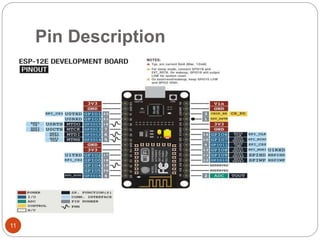
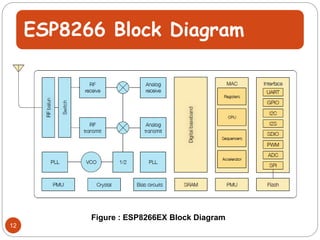
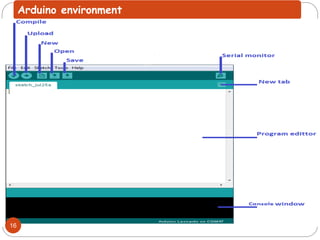
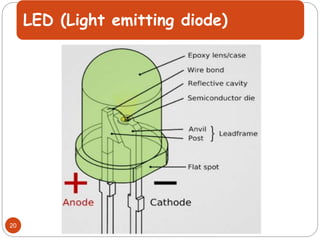
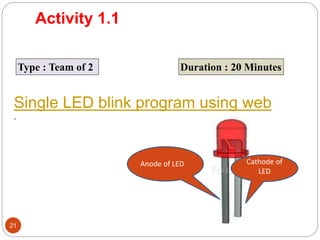
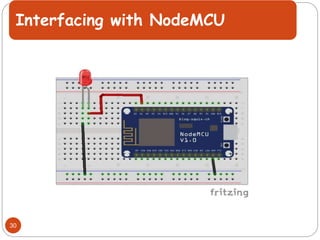
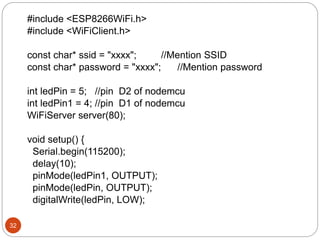
The document provides an overview of NodeMCU, an open-source development environment based on the ESP8266 microcontroller, enabling low-cost, Wi-Fi capable projects. It includes programming instructions using C or Lua, along with practical activities for interfacing with LEDs and serial communication. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of platform-based development and outlines learning outcomes for participants.