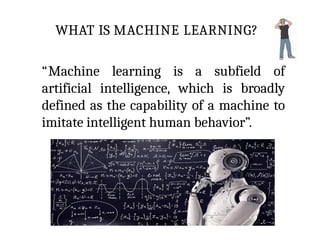
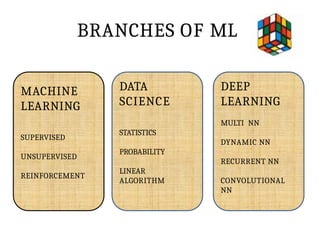
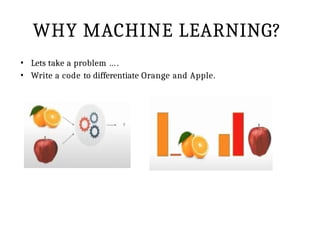
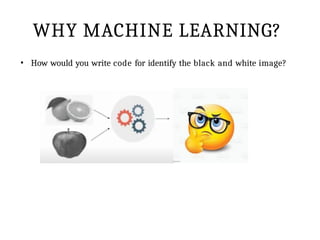
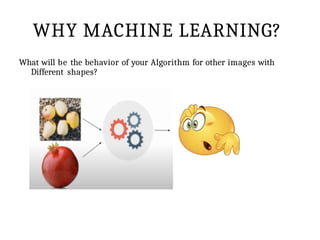
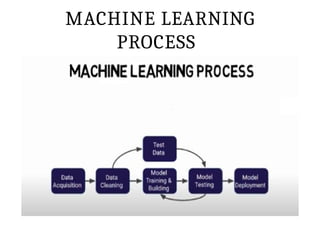
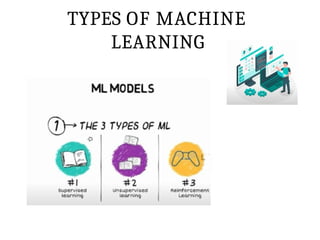
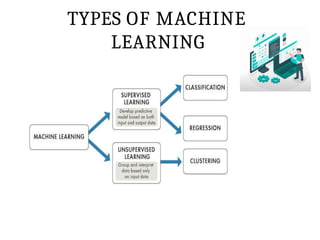
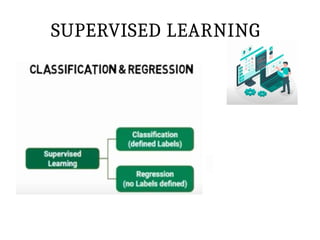
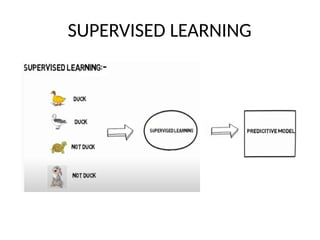
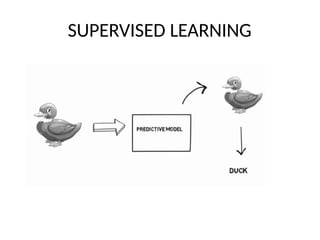
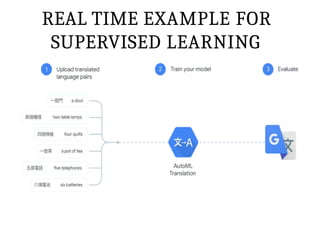
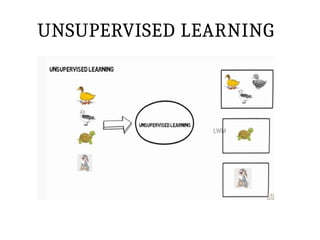
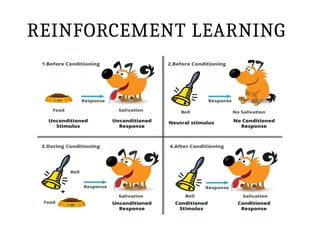
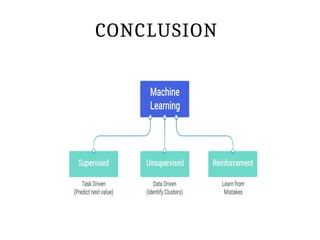
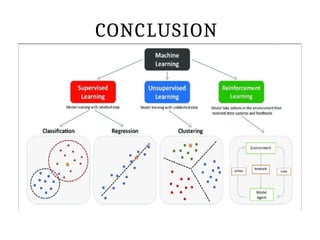
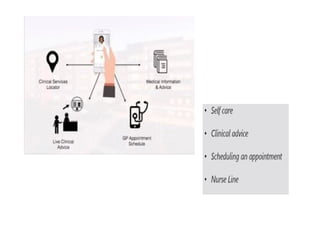
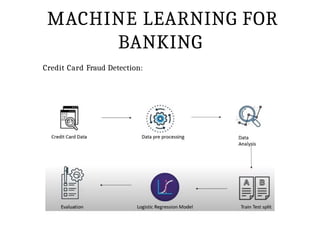
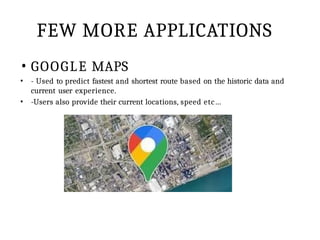
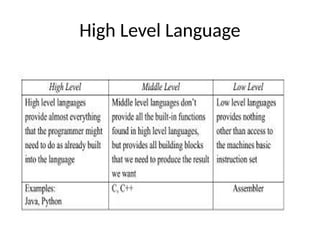
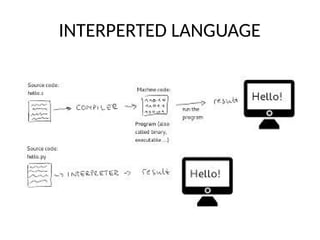
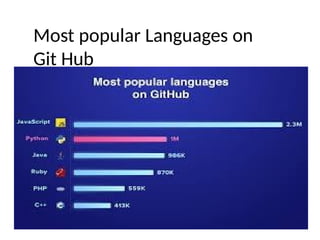
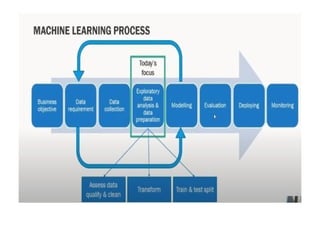
This PPT explain briefly about Machine learning and its categories with real time examples,This presentation provides a beginner-friendly introduction to Machine Learning (ML), covering key concepts, types of learning (supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement), common algorithms, and real-world applications. Ideal for students, professionals, and enthusiasts looking to understand the basics and scope of ML in today's data-driven world.