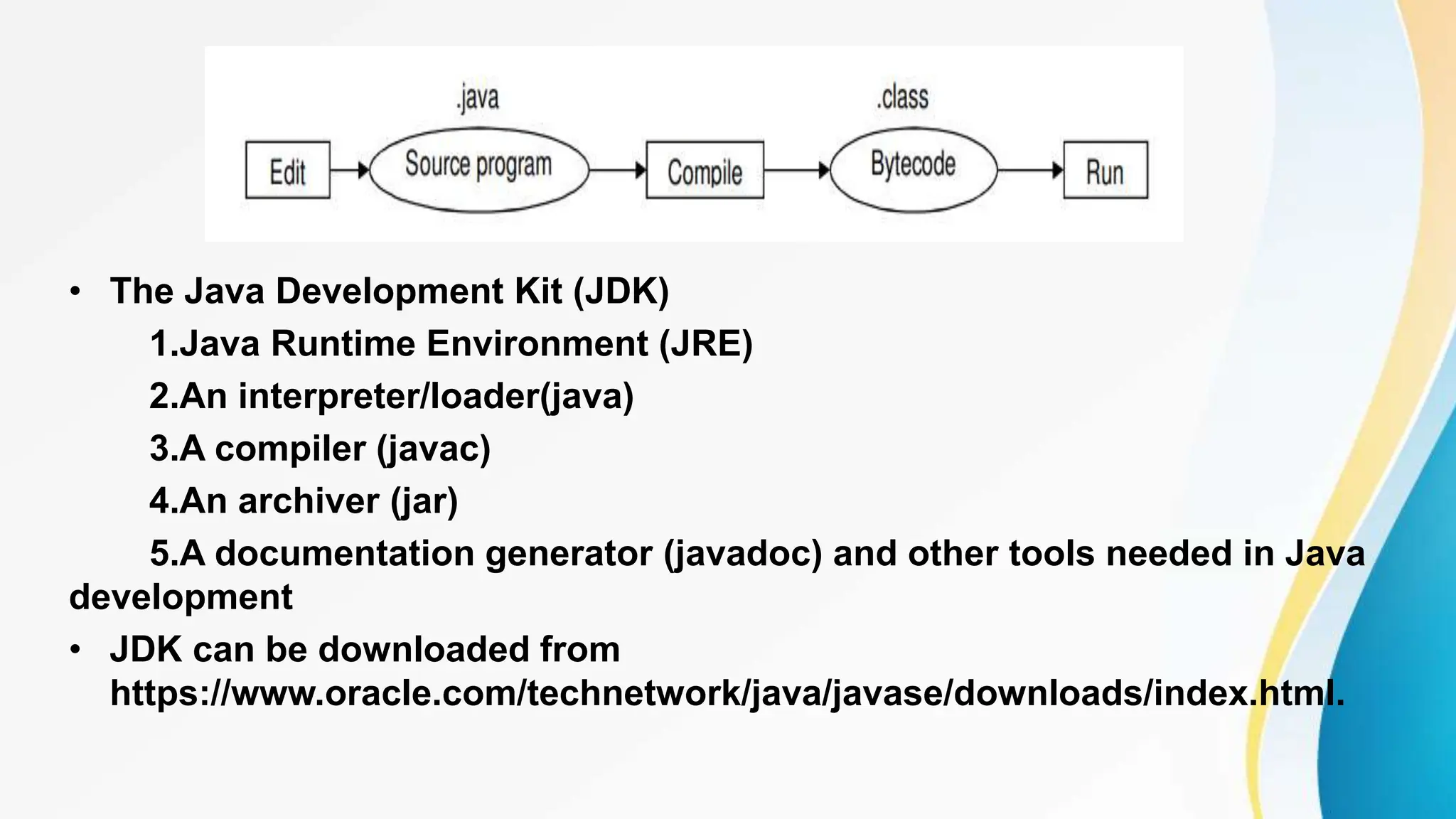
The document provides an overview of Java and programming languages, detailing the evolution from assembly language to Java since its inception in 1995. It describes Java as an object-oriented language, emphasizing its platform independence and the structure of Java programs that consist of classes and objects. Additionally, it outlines the five phases of Java program development and references the tools included in the Java Development Kit (JDK).