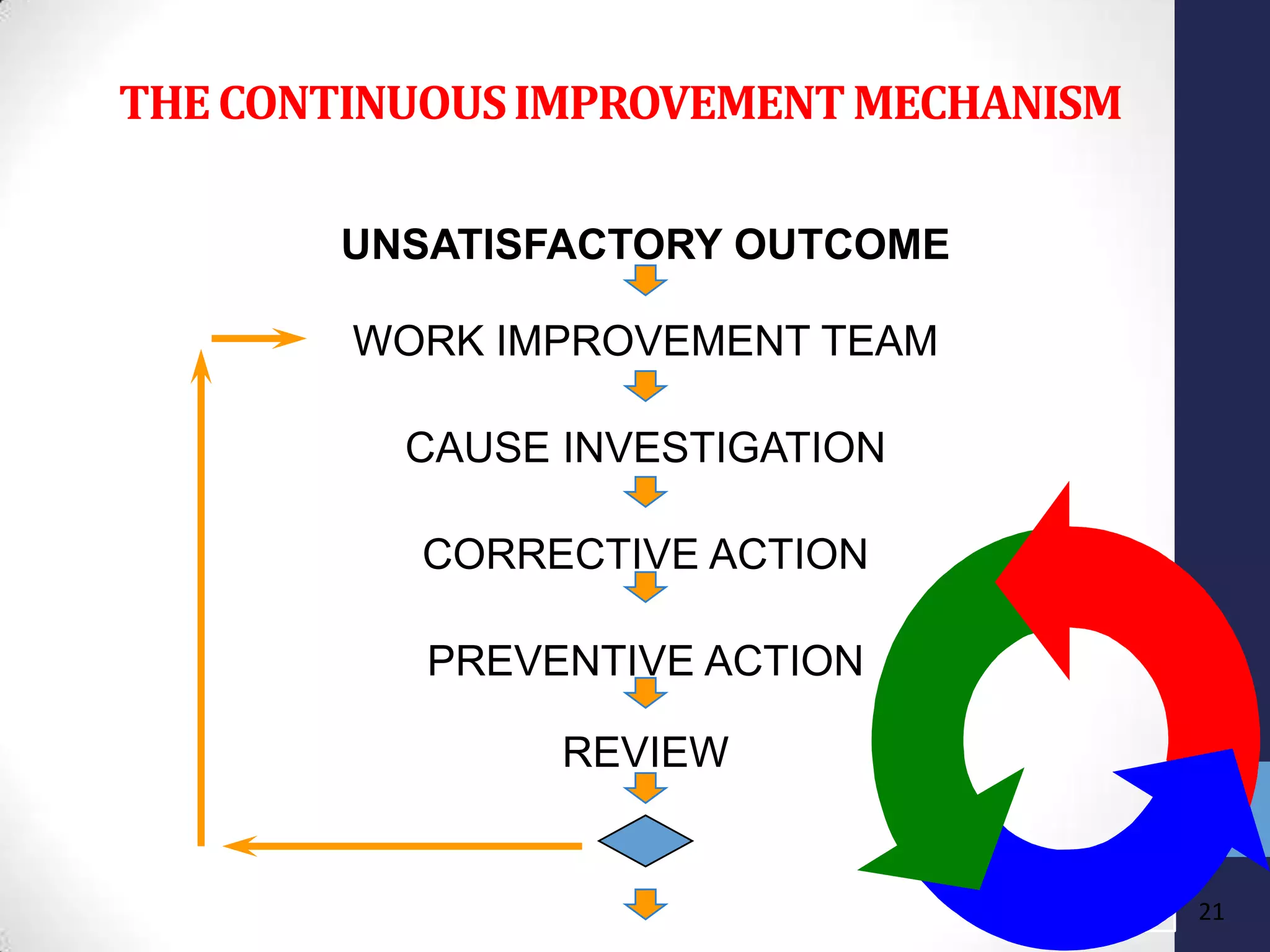
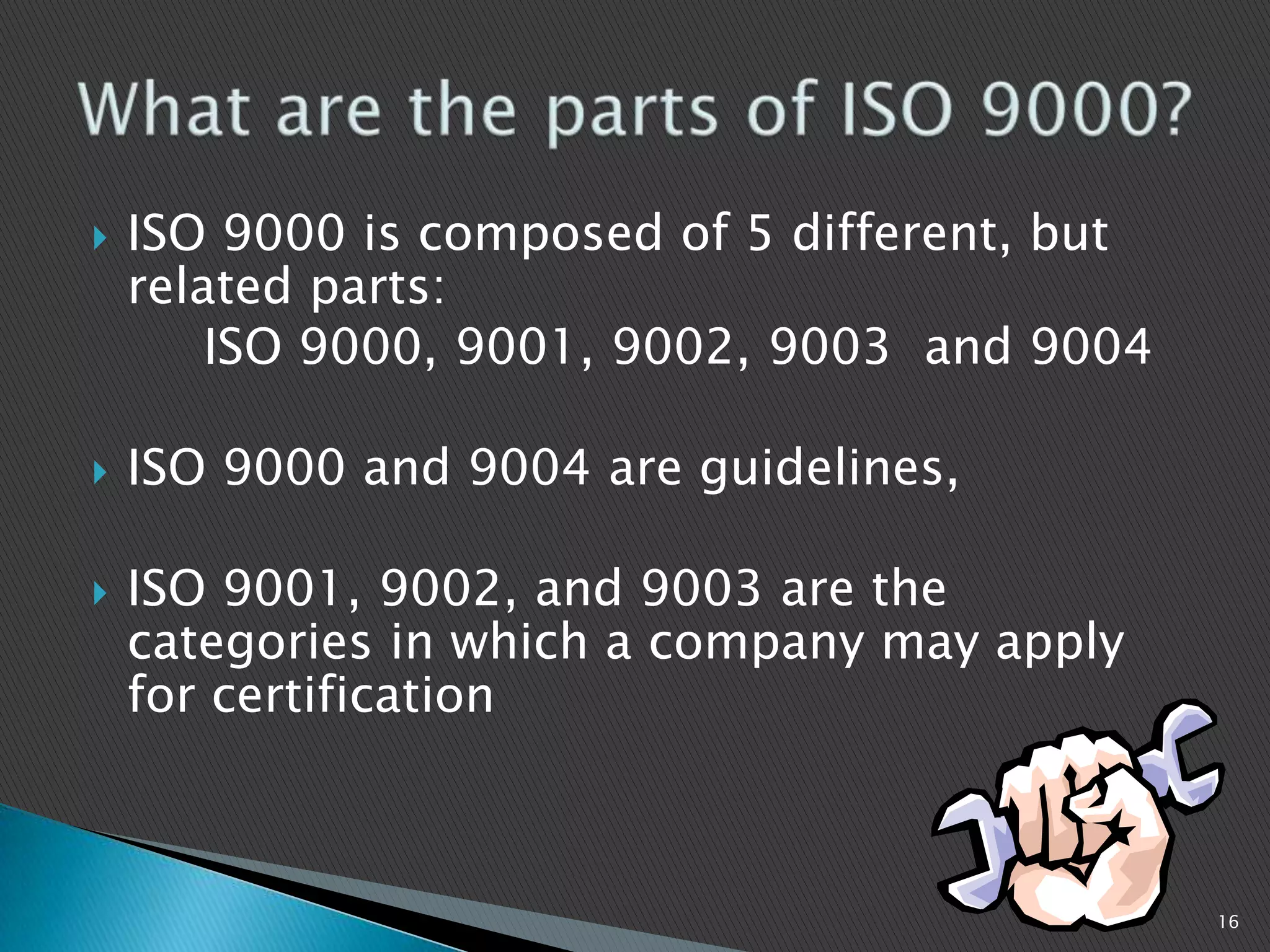
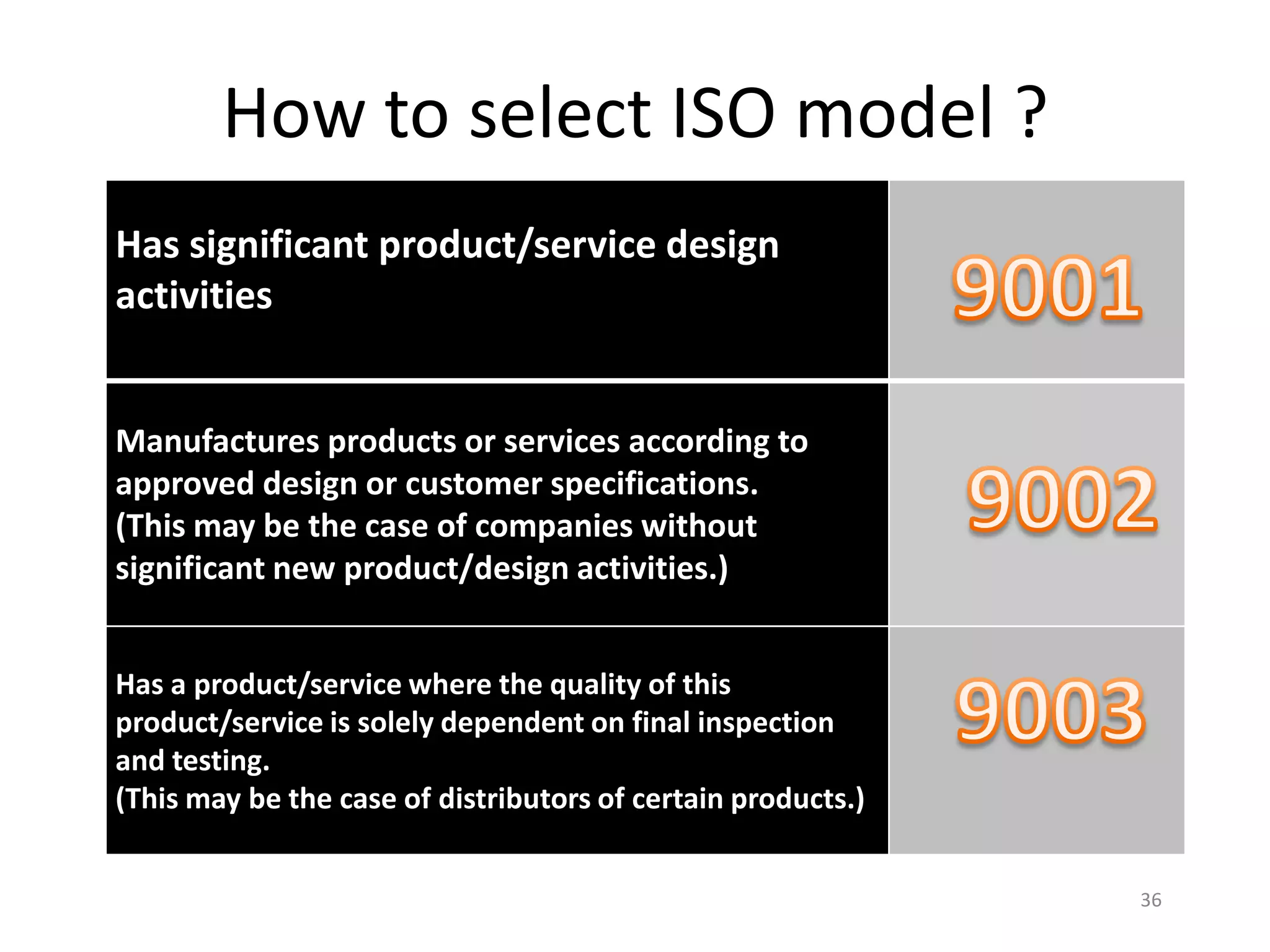
The document discusses ISO 9000 standards. It notes that ISO is the International Organization for Standardization, which has over 11,000 standards across 97 categories. ISO 9000 provides a framework for quality management and can benefit many industries. The key aspects of ISO 9000 include establishing quality management systems, documenting procedures, conducting internal and external audits, and continually improving processes to increase customer satisfaction.