Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
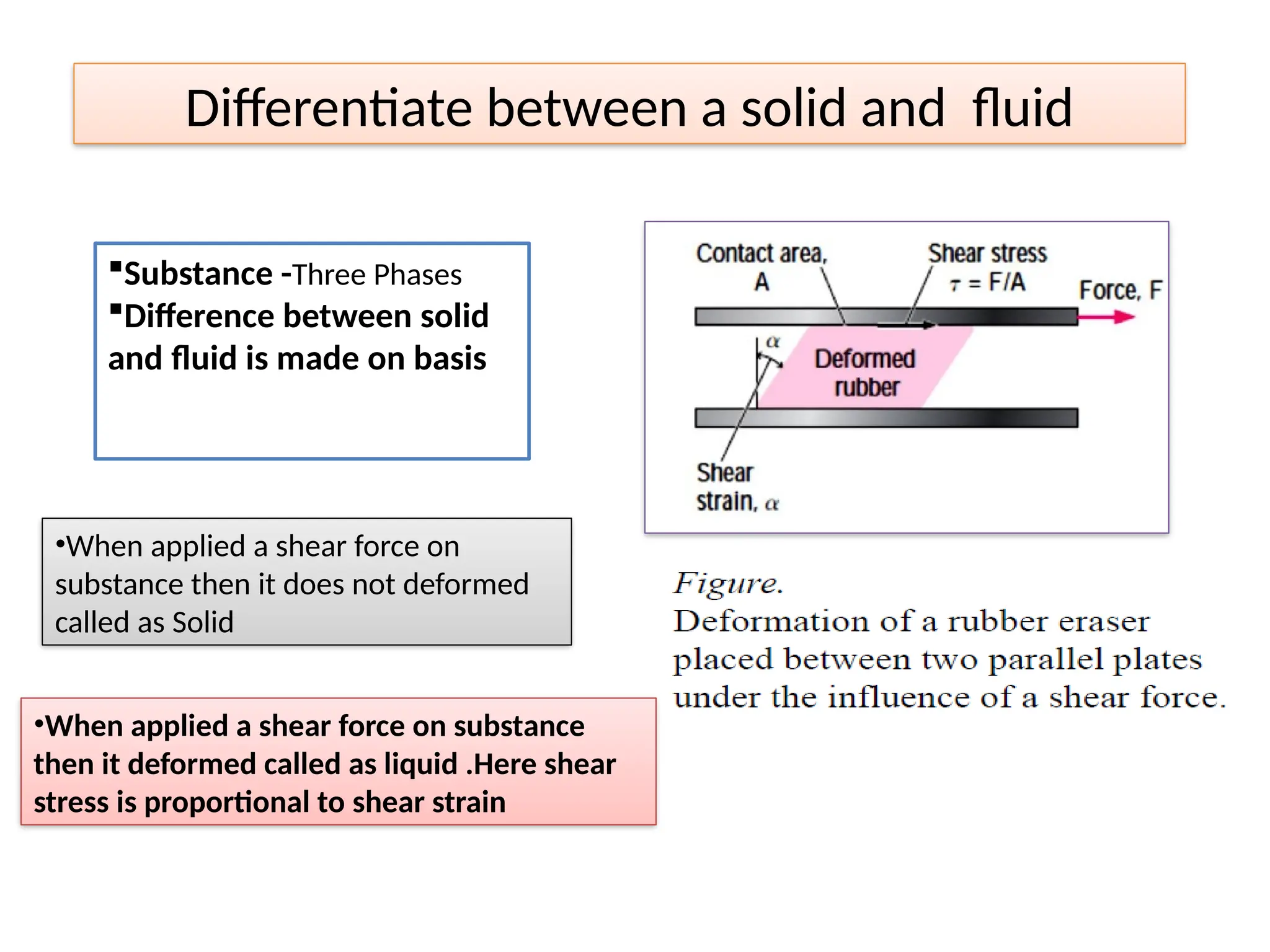
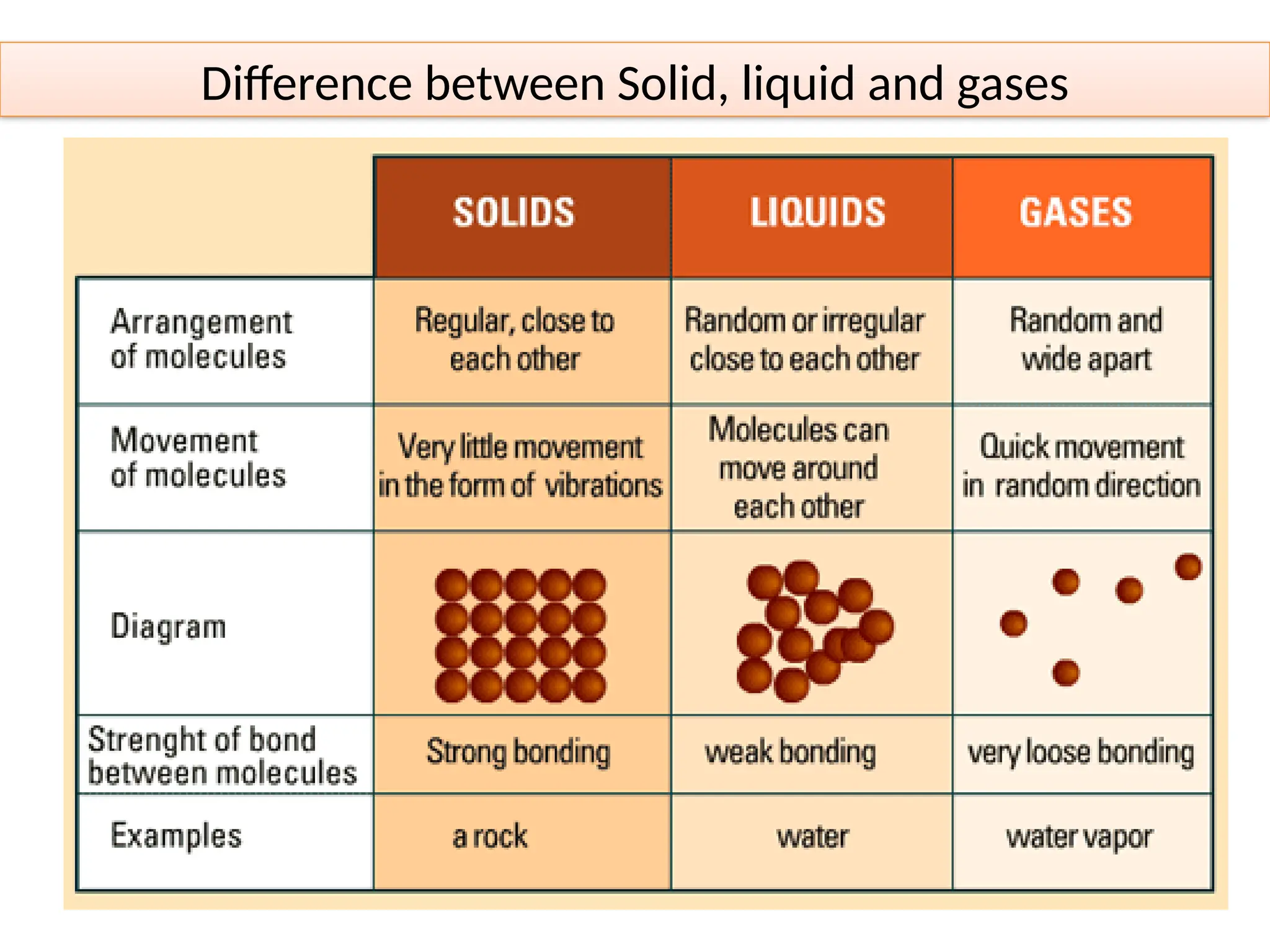
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior of fluids (liquids and gases) and their interactions with solid boundaries. It is an essential field in engineering, physics, and applied sciences, covering various applications such as aerodynamics, hydraulics, and industrial processes.
Fluid mechanics is divided into:
Fluid Statics (Hydrostatics): The study of fluids at rest.
Fluid Dynamics: The study of fluids in motion.
Hydraulics: Application of fluid mechanics in engineering systems like pipes, pumps, and turbines.
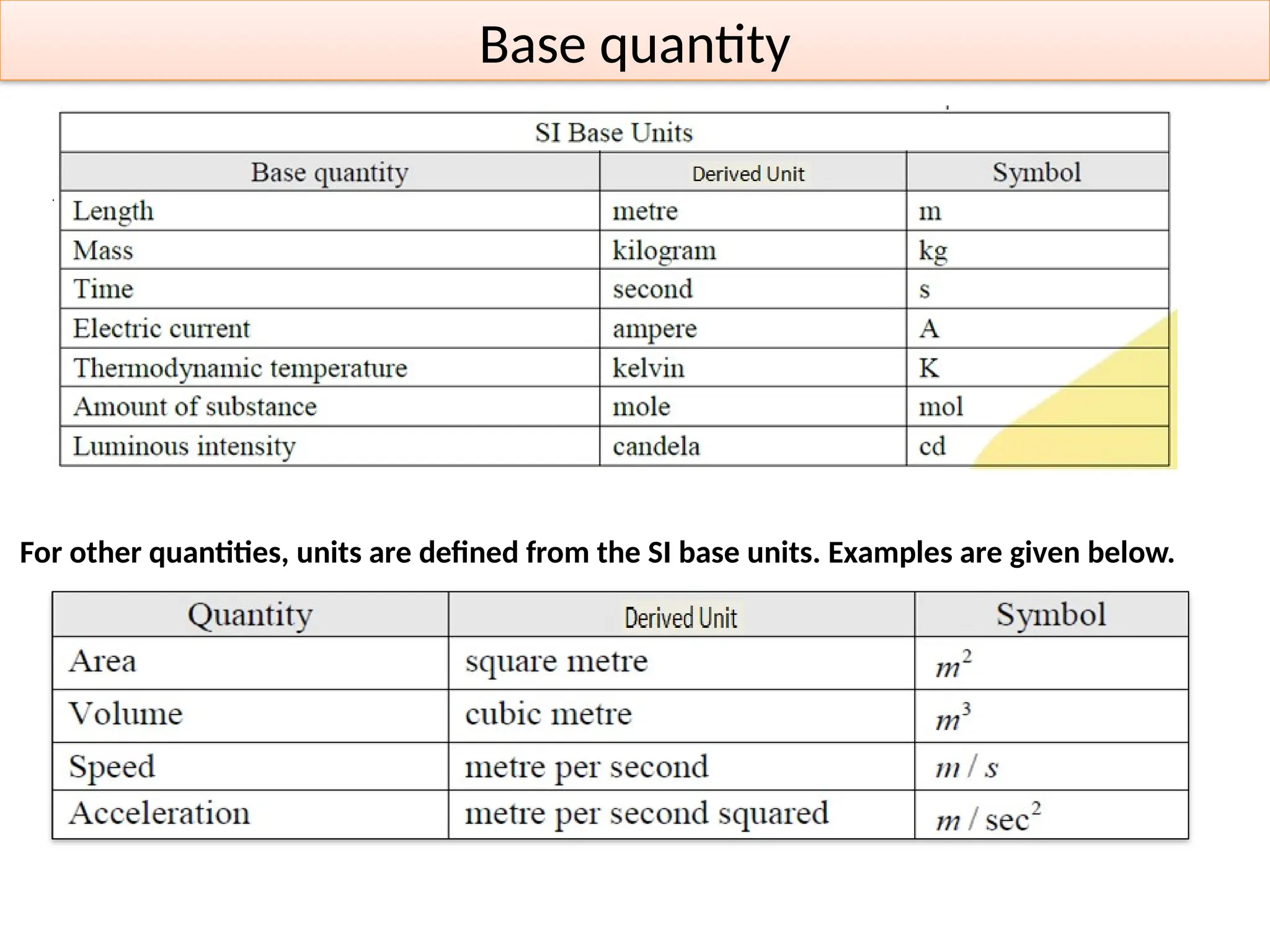
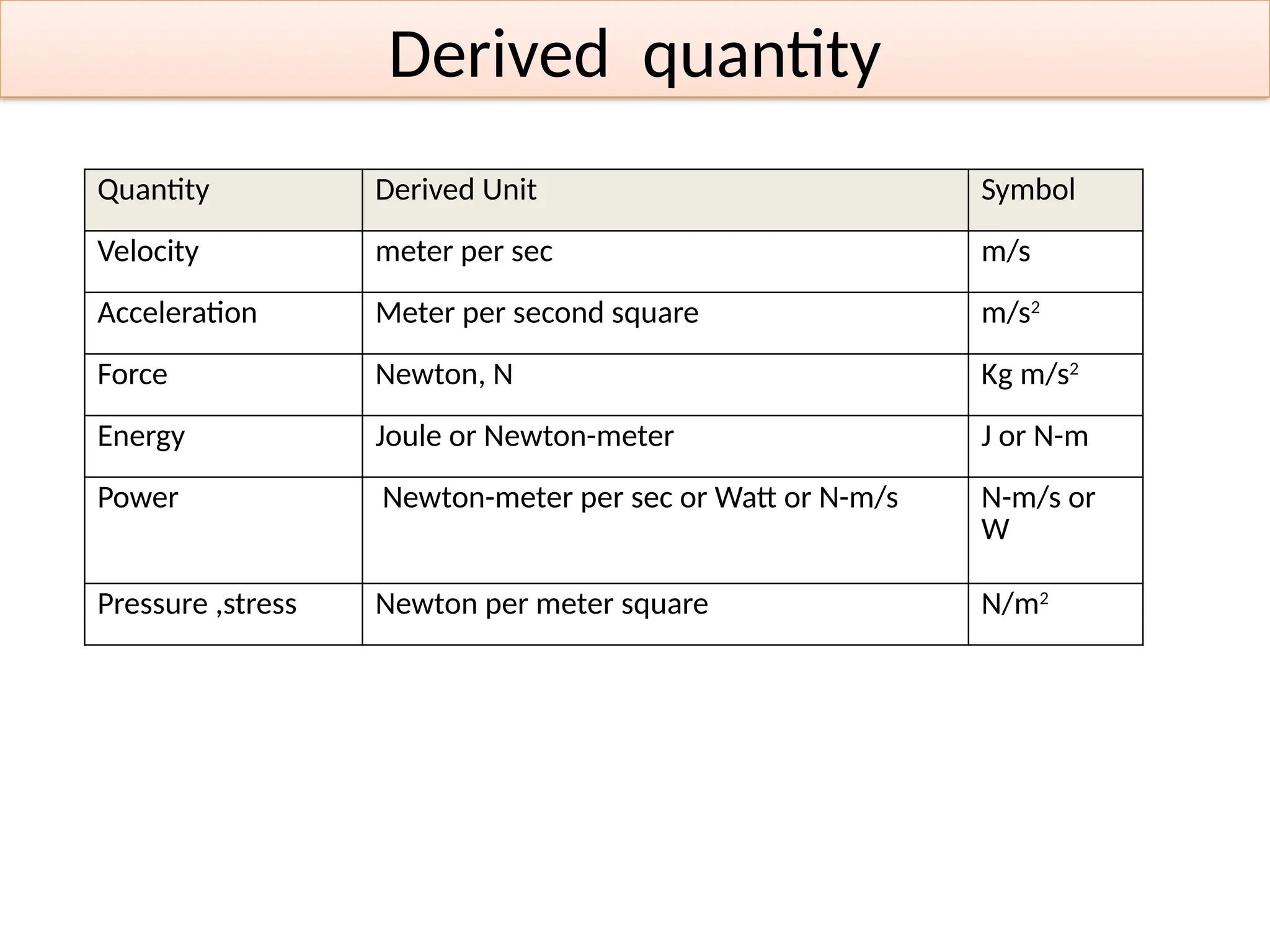
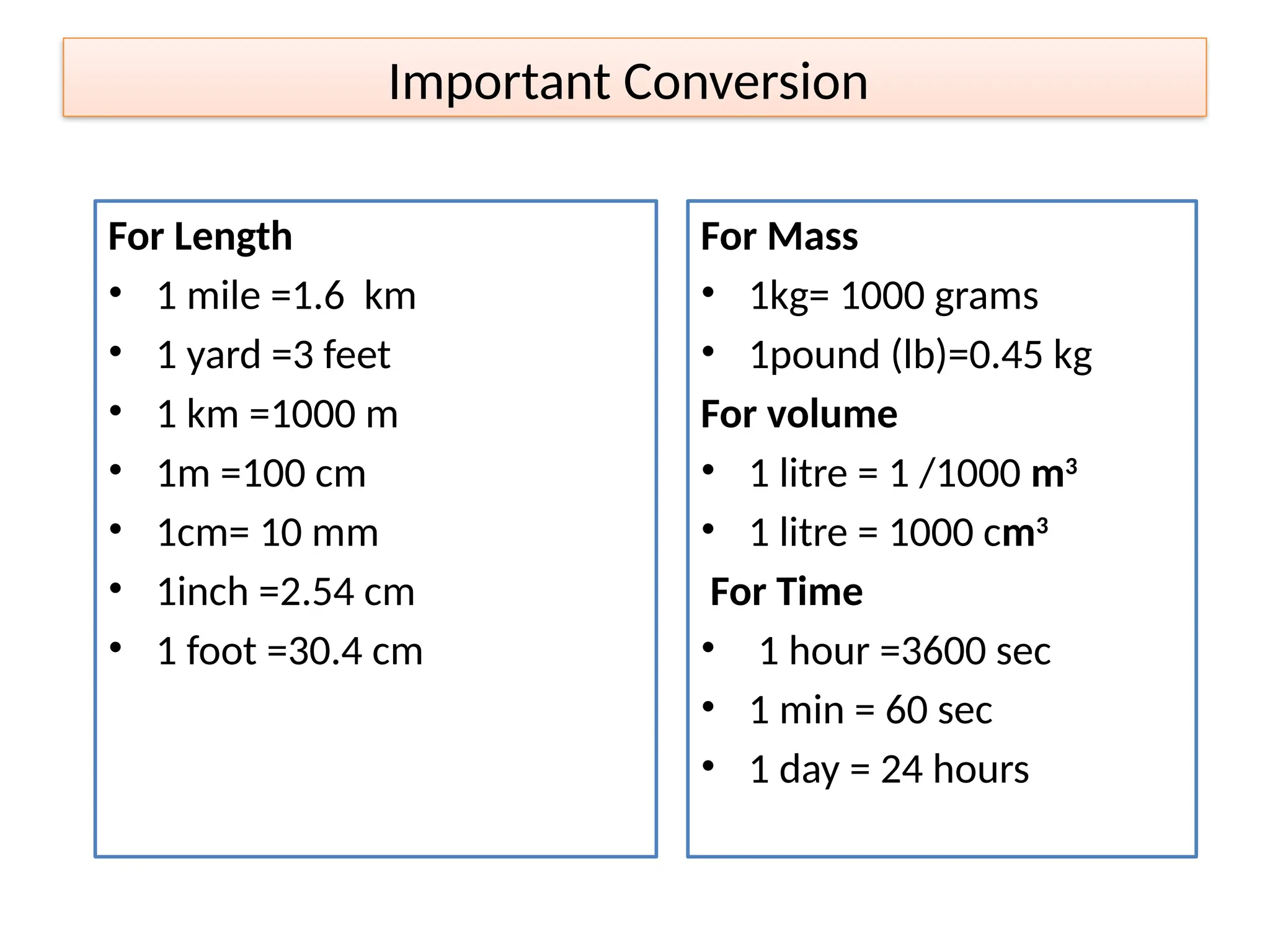
Units of Measurement in Fluid Mechanics
Units are essential for expressing physical quantities in a standardized way. The two main unit systems used in fluid mechanics are:
International System of Units (SI)
British/Imperial System (FPS - Foot-Pound-Second)