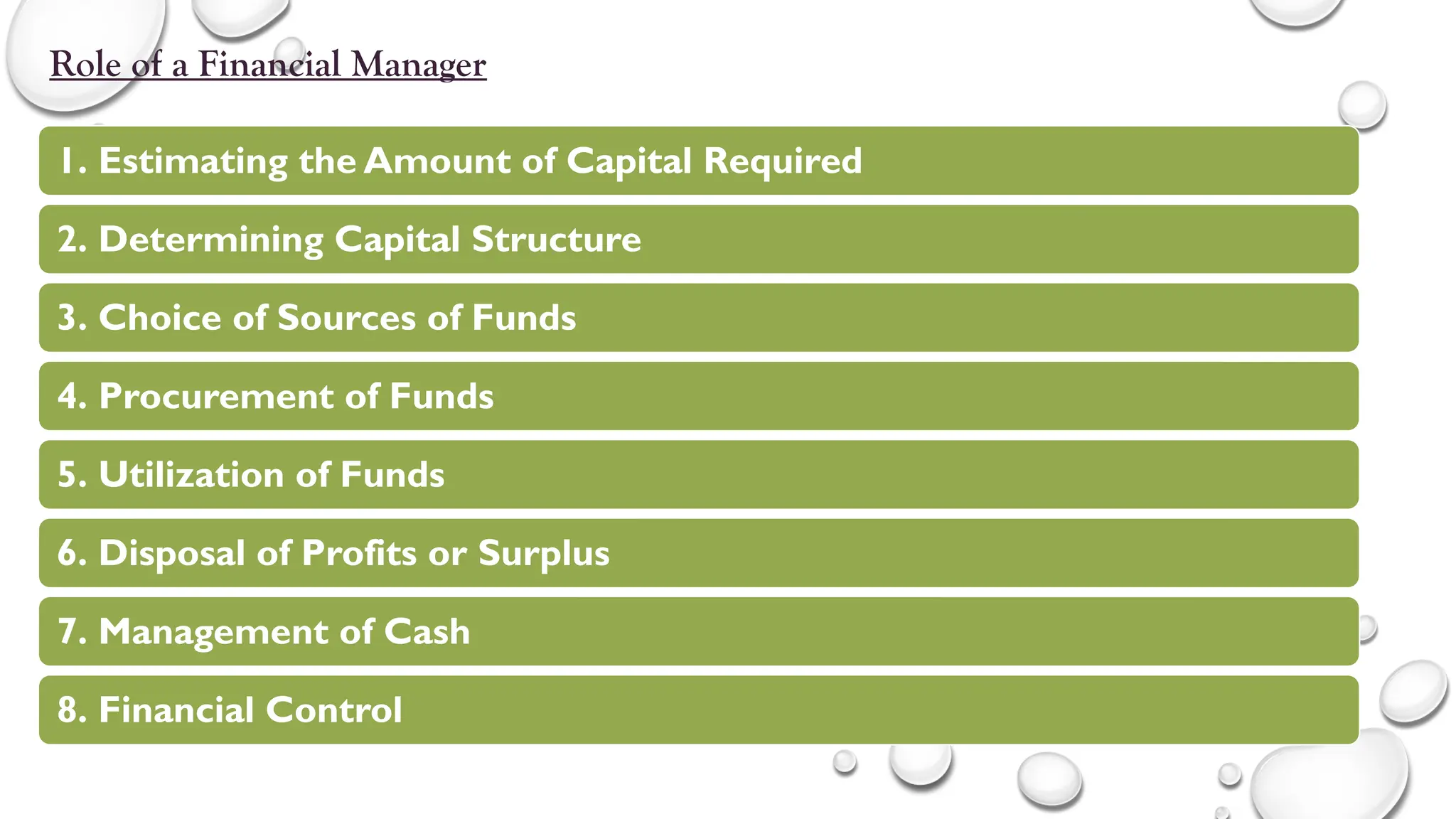
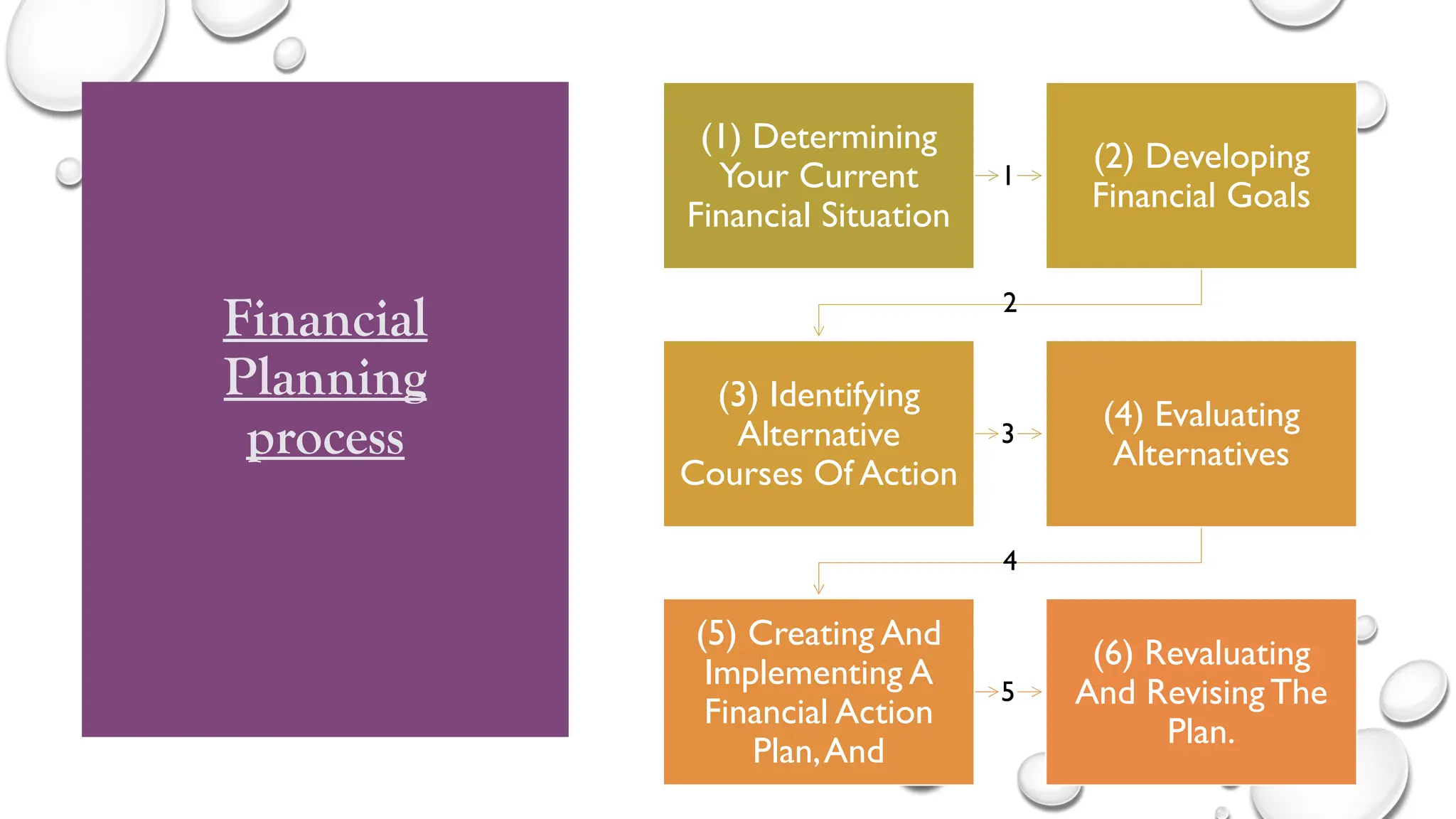
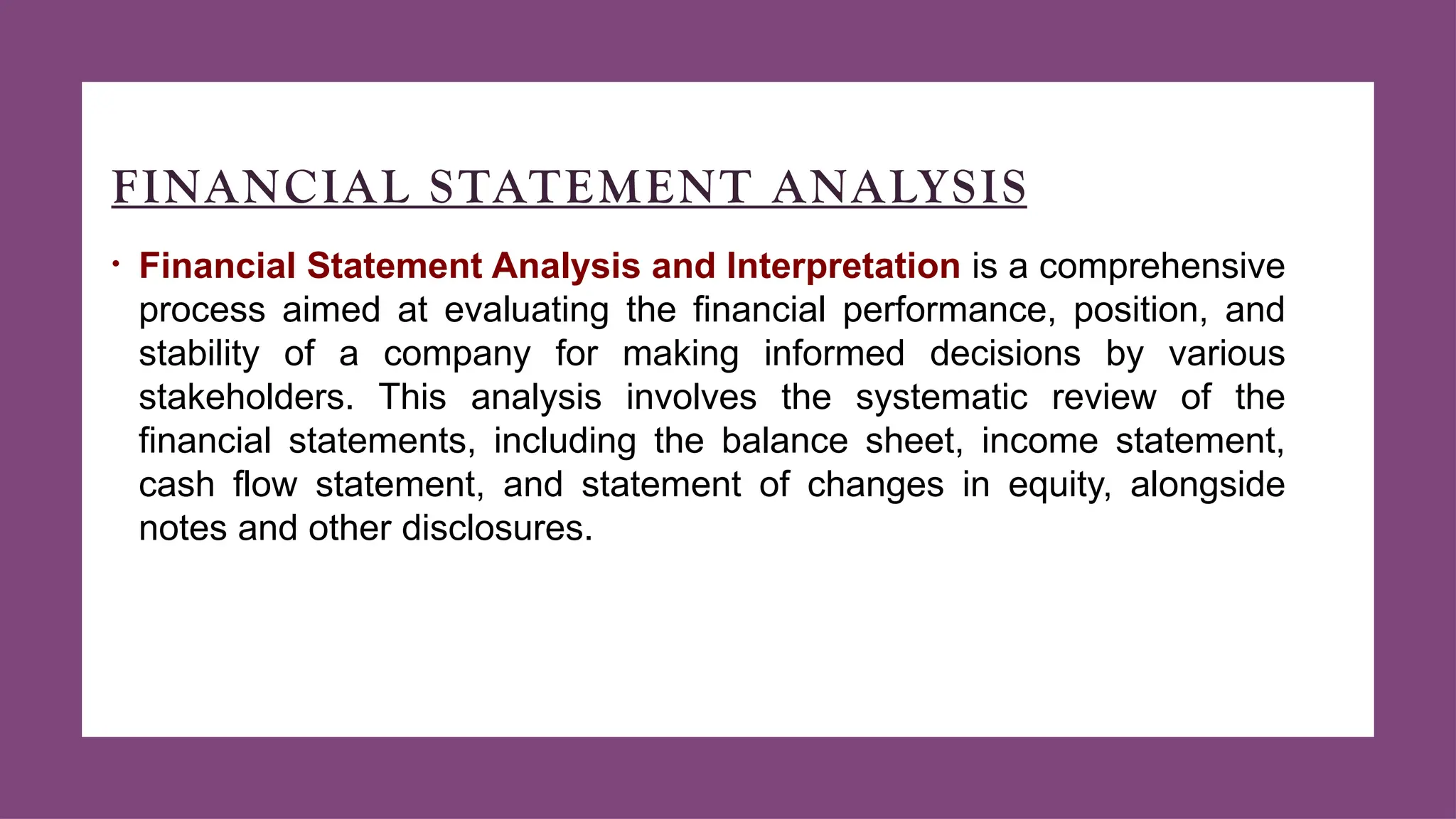
The document provides a comprehensive overview of financial management, covering fundamental concepts such as financial decision-making, capital budgeting, sources of finance, working capital management, and cost of capital. It emphasizes the role and responsibilities of financial managers, the importance of financial planning, and the components of the financial system. Additionally, it outlines financial statement analysis as a critical tool for evaluating company performance and making informed decisions.