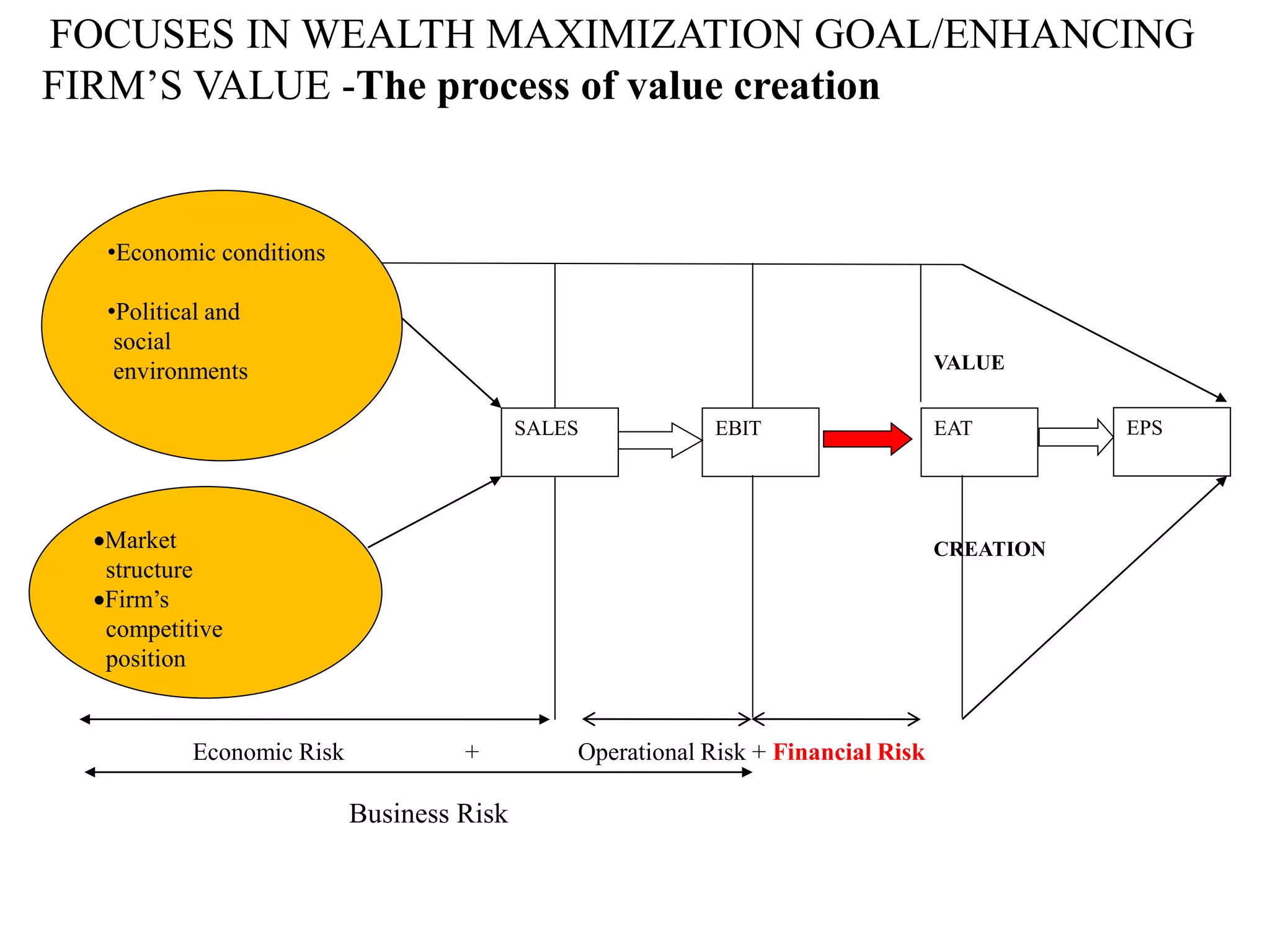
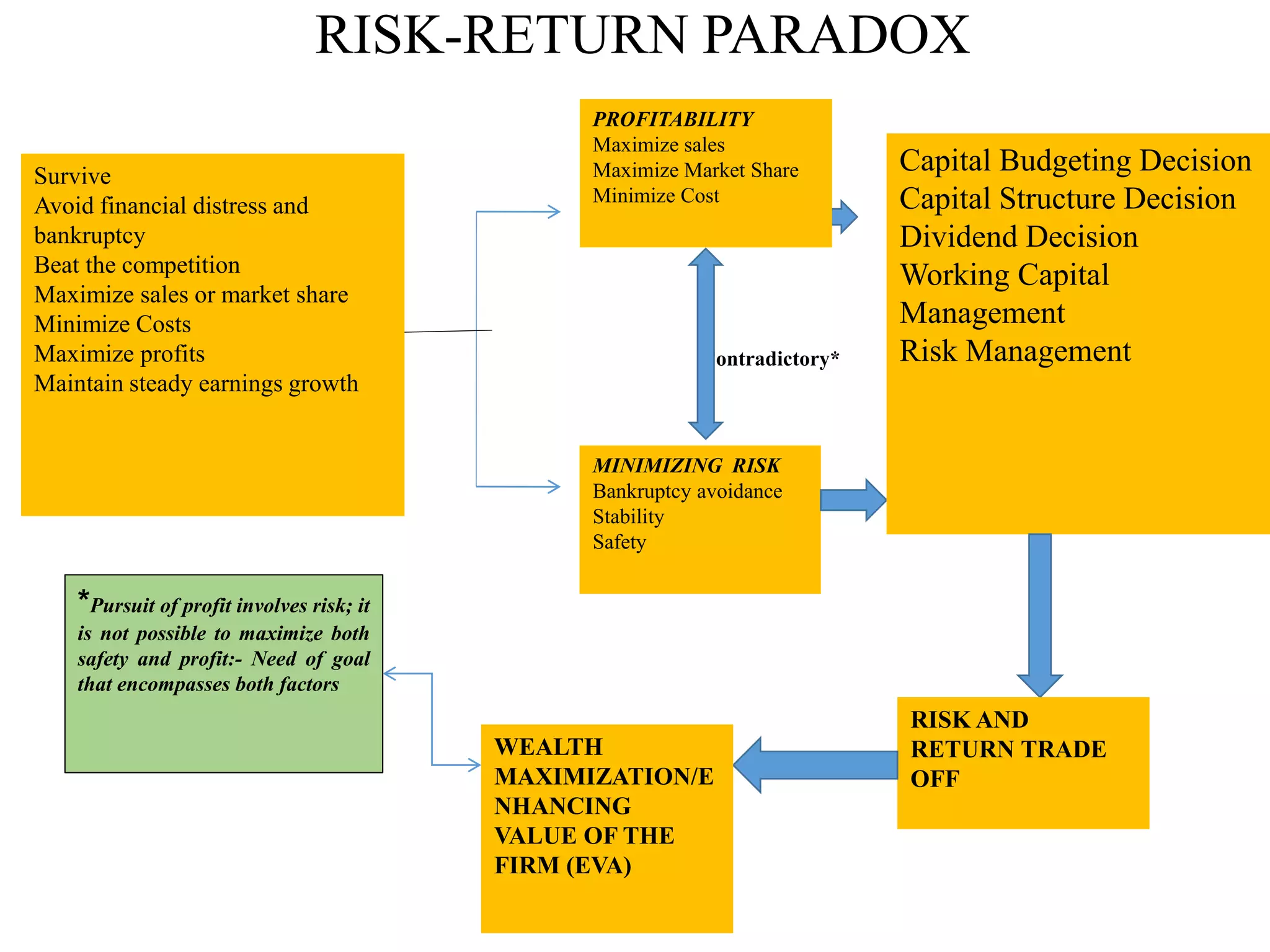
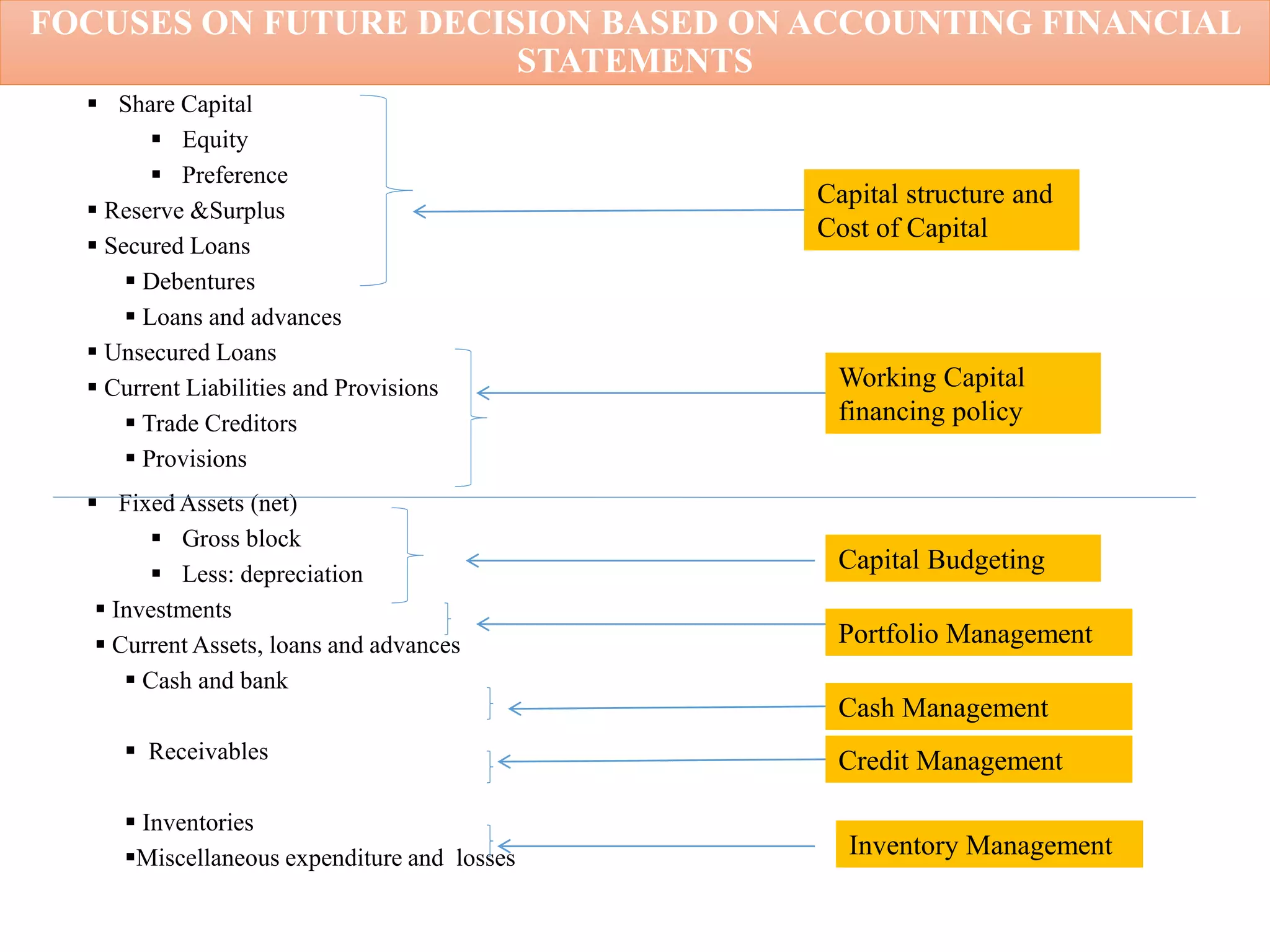
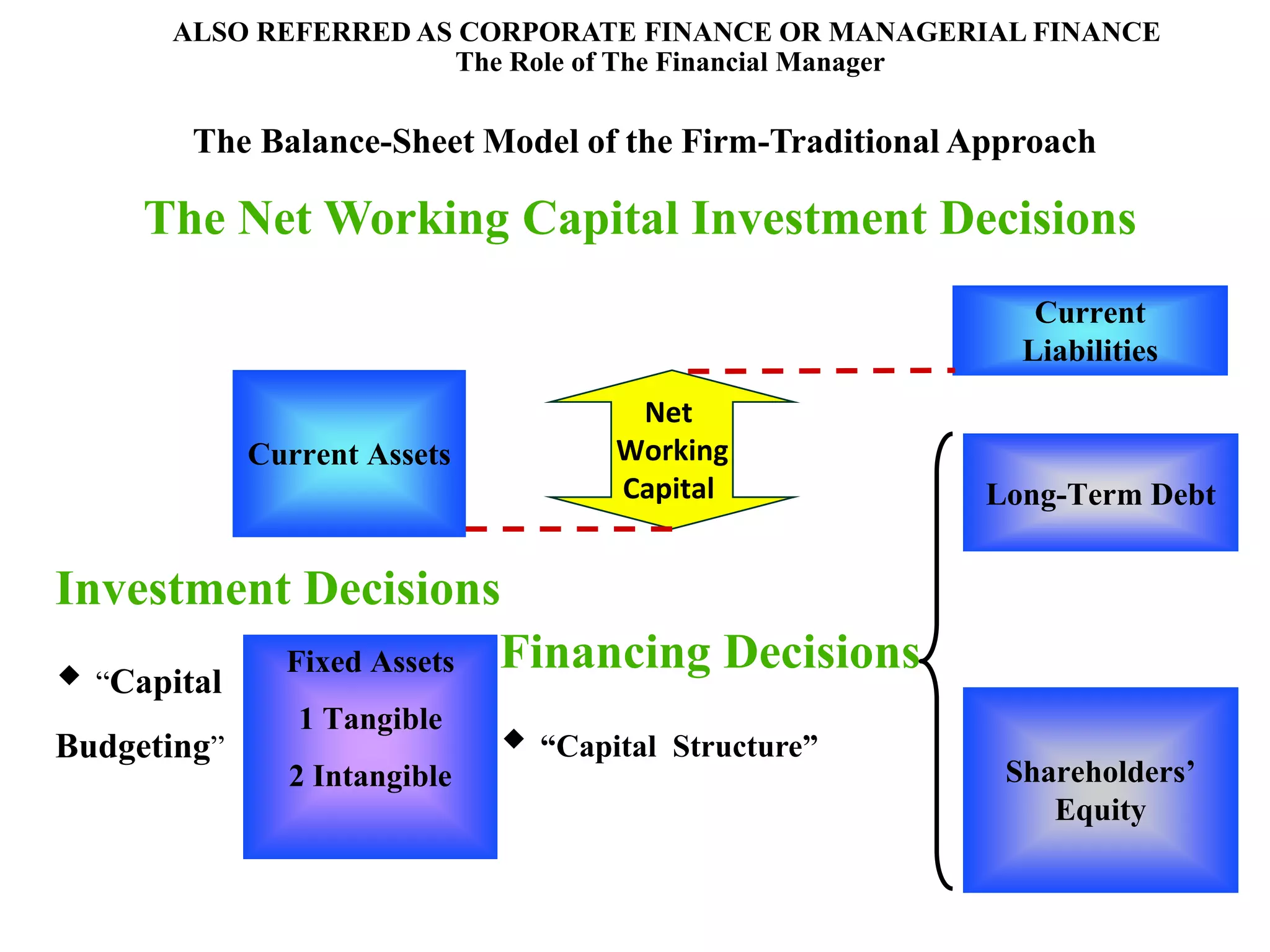
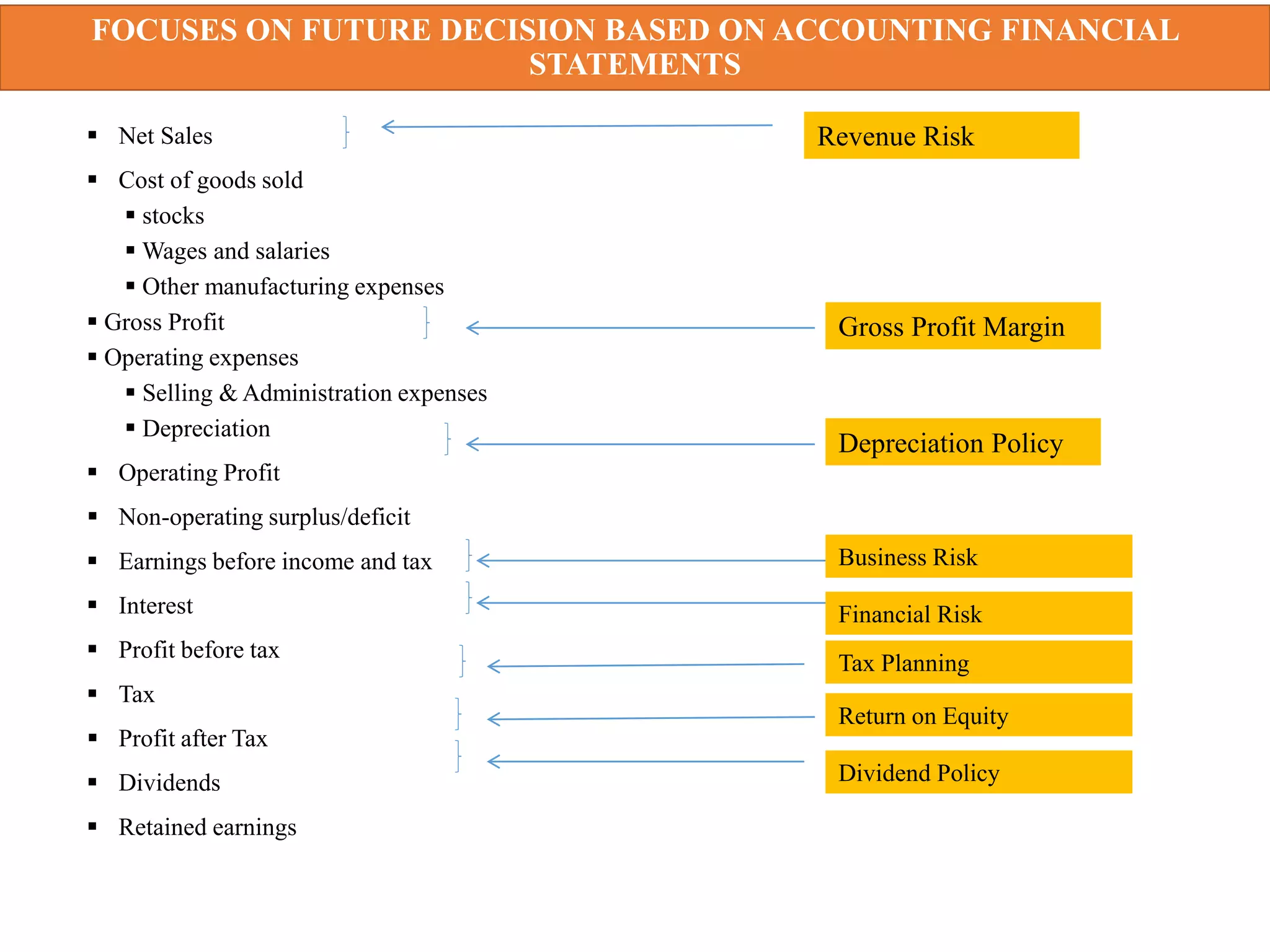
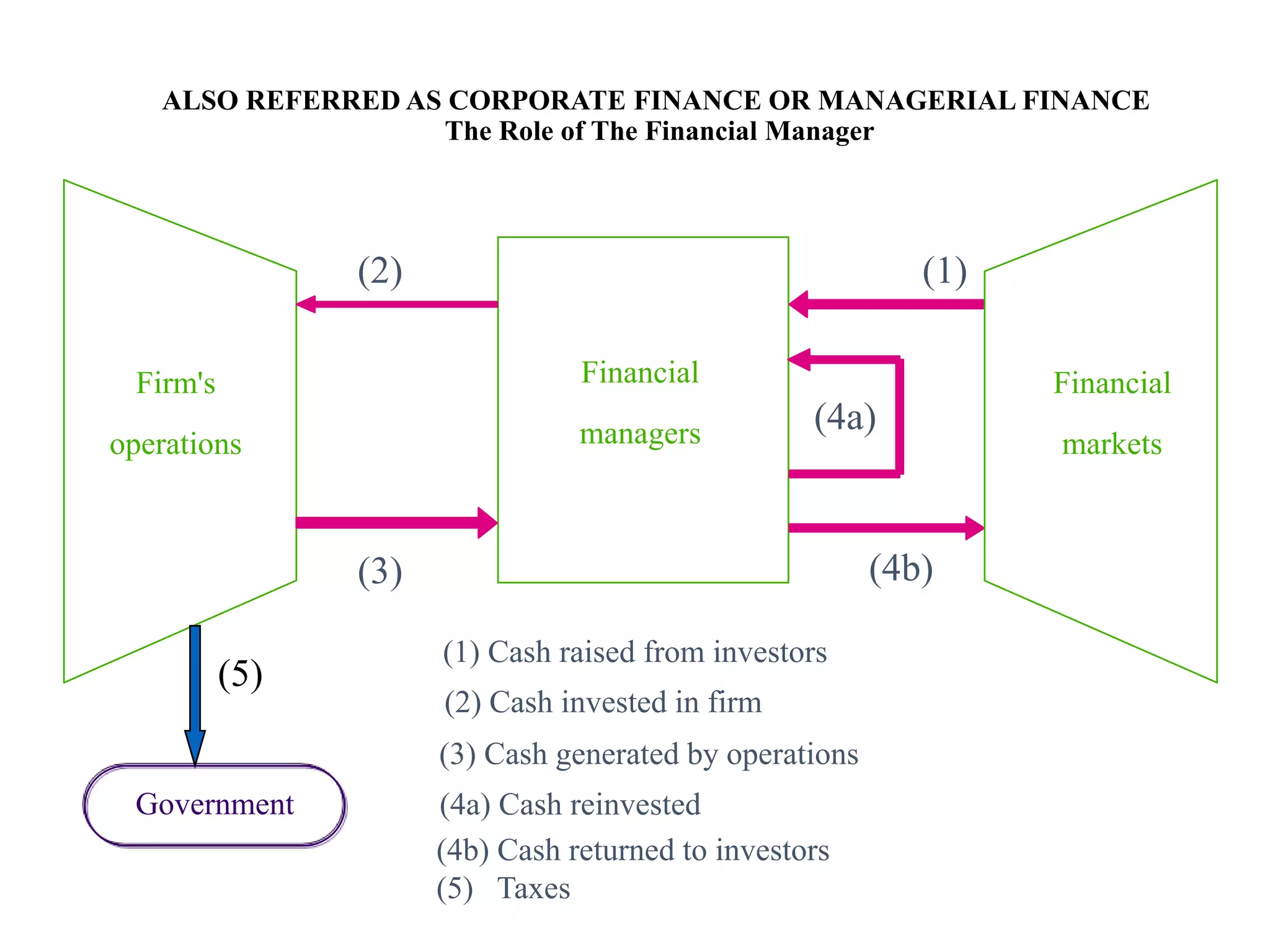
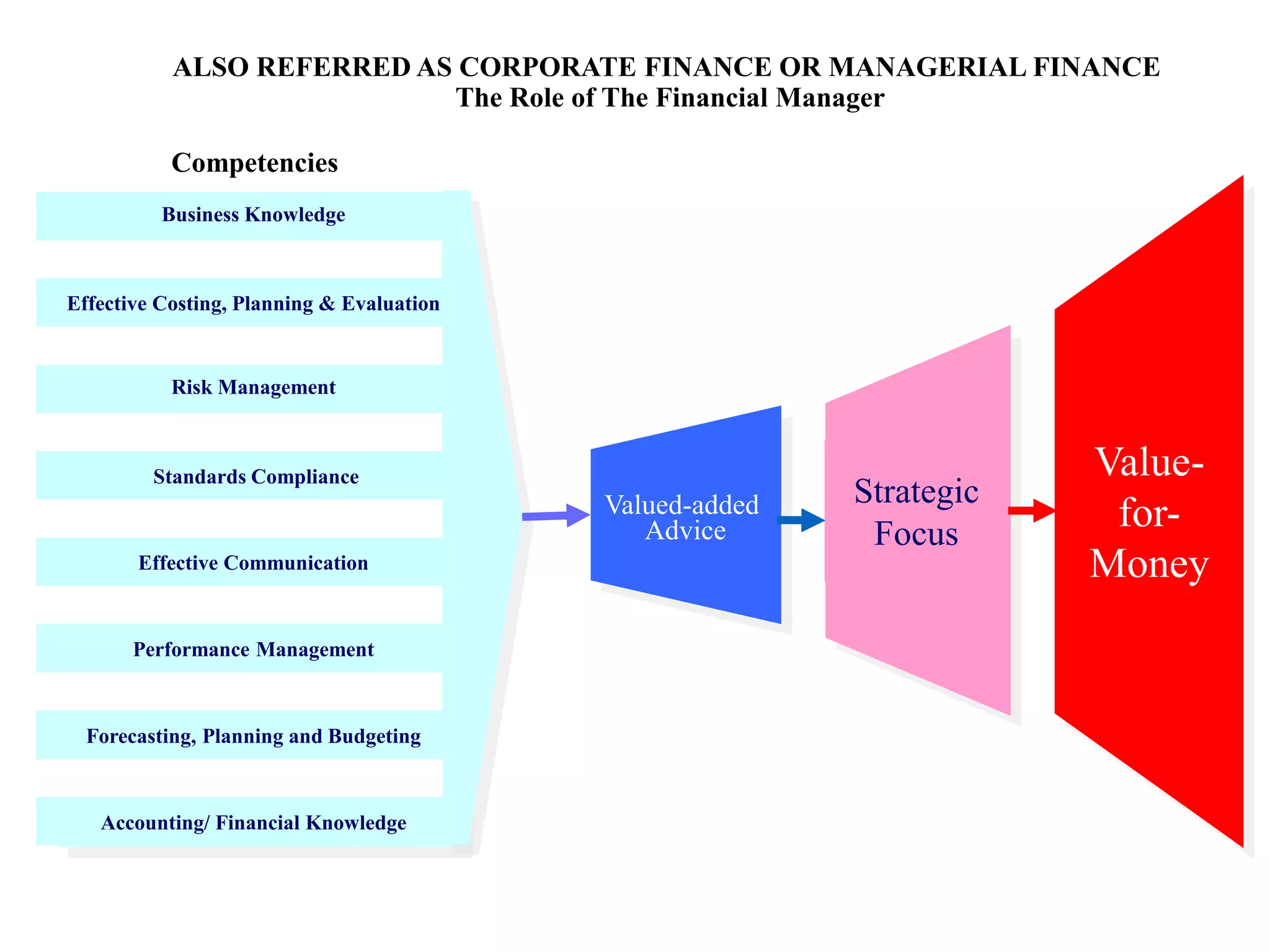
This document provides an overview of financial management. It defines key terms like finance, financial management, and discusses the nature and objectives of financial management. It also discusses the relationship between financial management and other business functions like economics, accounting, production etc. Additionally, it covers topics like agency theory, business policies and their impact on financial decisions, and contemporary issues in financial management.