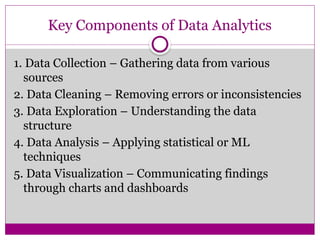
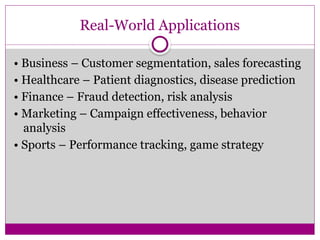
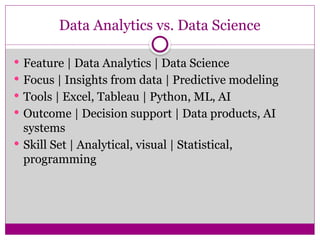
Data Analytics is the science of examining raw data to uncover patterns, trends, relationships, and insights that support decision-making. It involves applying techniques from statistics, computer science, and domain knowledge to extract meaningful conclusions from data.