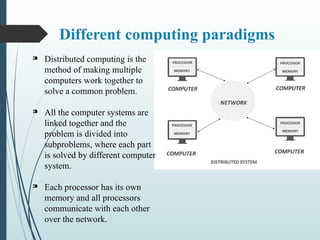
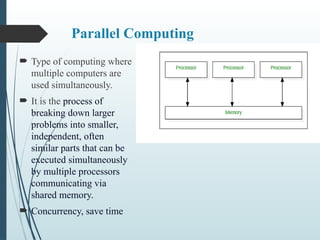
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing, allowing access to technology services without maintaining physical servers. It includes various computing paradigms like distributed, parallel, cluster, grid, utility, and edge computing, which optimize resource use and efficiency. Cloud computing enables faster innovation and scaling for businesses by providing various services over the internet.