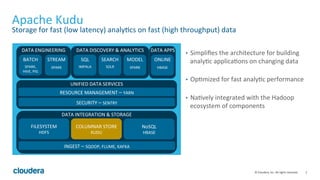
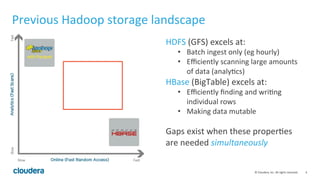
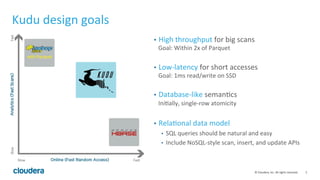
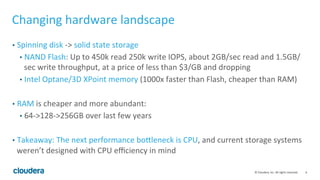
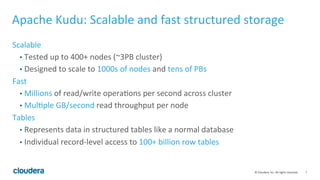
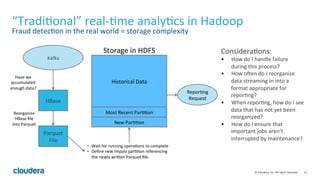
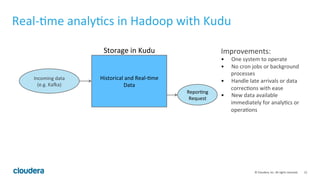
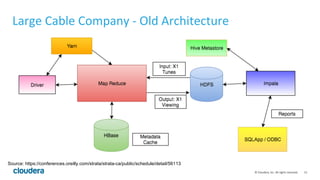
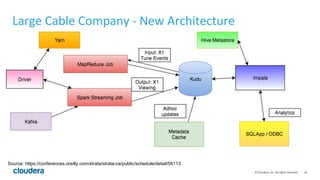
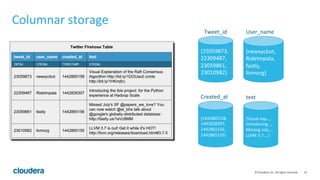
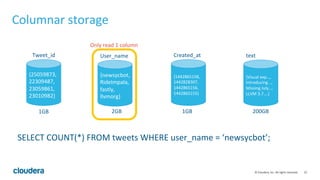
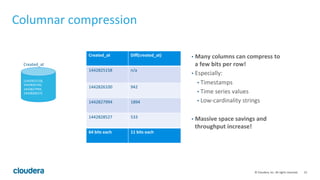
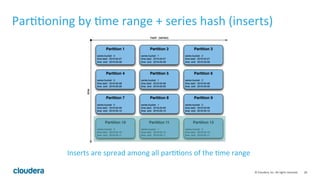
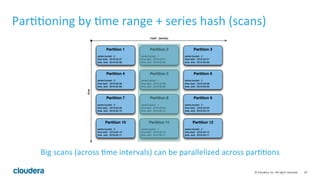
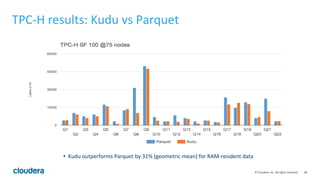
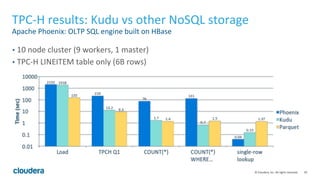
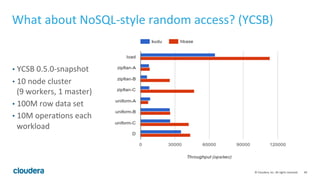
Apache Kudu is a storage layer for Apache Hadoop that provides low-latency queries and high throughput for fast data access use cases like real-time analytics. It was designed to address gaps in HDFS and HBase by providing both efficient scanning of large amounts of data as well as efficient lookups of individual rows. Kudu tables store data in a columnar format and use a distributed architecture with tablets and masters to enable high performance and scalability for workloads involving both sequential and random access of data.