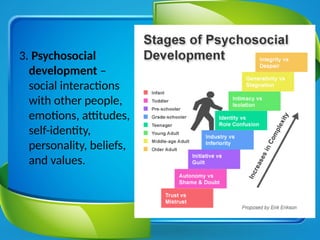
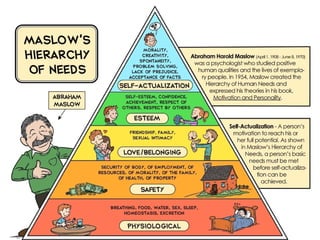
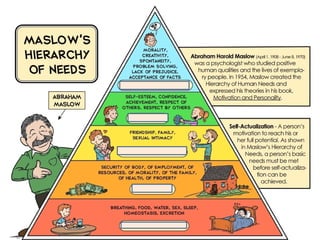
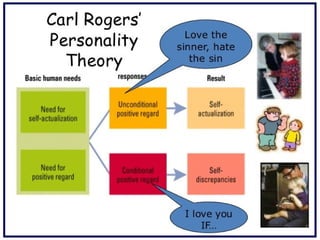
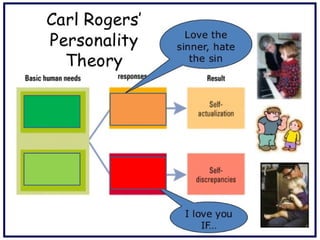
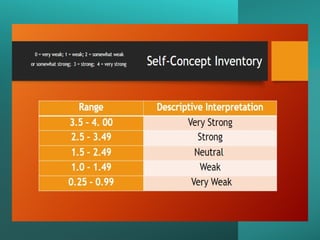
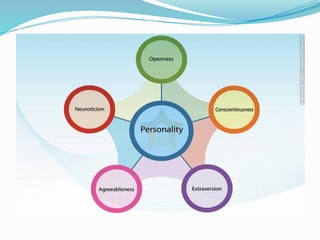
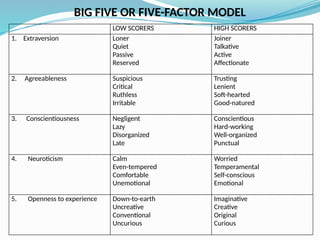
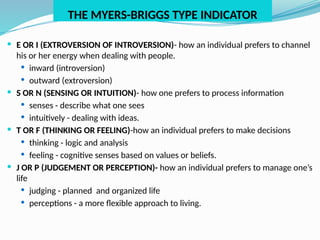
The document outlines personal development goals and the various domains influencing human development, including physical, cognitive, and psychosocial aspects. It discusses theories of personal identity, highlighting the stages of adolescence and the significance of self-awareness and personality traits in shaping an individual's character. It also explores the role of psychology in personal growth, emphasizing the necessity of understanding oneself to foster self-acceptance and maximize potential.